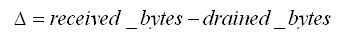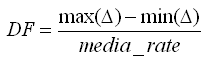
Media Delivery Index
Encyclopedia
The Media Delivery Index (MDI) is a set of measures that can be used to monitor both the quality of a delivered video
stream as well as to show system margin for IPTV
systems by providing an accurate measurement of jitter
and delay at network level (Internet Protocol, IP
), which are the main causes for quality loss. Identifying and quantizing such problems in this kind of networks is key to maintaining high quality video delivery and providing indications that warn system operators with enough advance notice to allow corrective action.
The Media Delivery Index is typically displayed as two numbers separated by a colon: the Delay Factor (DF) and the Media Loss Rate (MLR).
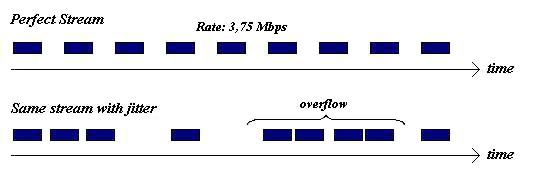
, some packets arrive in bursts
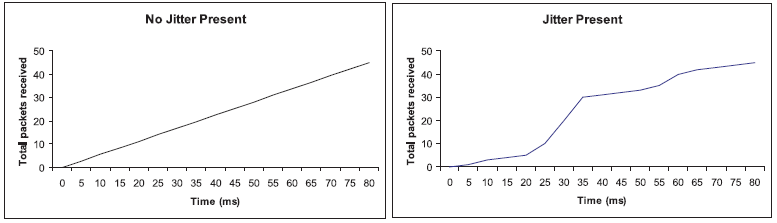
with interpacket delays shorter than when they were transmitted, while others are delayed such that they arrive with greater delay between packets than when they were transmitted from the source (see figure below). This time difference between when a packet actually arrives and the expected arrival time is defined as packet jitter
or time distortion.
 A receiver
A receiver
displaying the video at its nominal rate must accommodate the varying input stream arrival times by buffering the data arriving early and assuring that there is enough already stored data to face the possible delays in the received data (because of this the buffer is filled before displaying
).
Similarly, the network infrastructure (switches, routers,…) uses buffers at each node to avoid packet loss. These buffers must be sized appropriately to handle network congestion
.
Packet delays can be caused by multiple facts, among which there are the way traffic
is routed through the infrastructure and possible differences between link
speeds in the infrastructure.
Moreover, some methods for delivering Quality of Service (QOS)
using packet metering algorithms may intentionally hold back packets to meet the quality specifications in the transmission
. This is achieved by using buffer memories.
The effects of all these facts on the amount of packets received by a specific point in the network can be seen in the next graphics:
or environmental electrical noise
that creates corrupted packets. Even small packet loss rates result in a poor video display.
variation and packet loss have been shown to be the key characteristics in determining whether a network
can transport good quality video. These features are represented as the Delay Factor (DF) and the Media Loss Rate (MLR), and they are combined to produce the Media Delivery Index (MDI), which is displayed as:
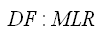
and at a specific time. In other words, it is a time value indicating how many milliseconds’ worth of data the buffers must be able to contain in order to eliminate time distortions (jitter
).
It is computed
as packets arrive at the node and is displayed/recorded at regular intervals (typically one second).
It is calculated as follows:
Maximum acceptable DF: 9-50 ms
It is computed
by subtracting the number of media packets received during an interval from the number of media packets expected during that interval and scaling the value to the chosen time period (typically one second):
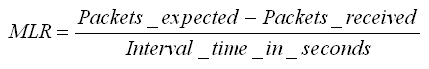
Maximum acceptable channel zapping MLR: 0
Maximum acceptable average MLR:
It must be said that the maximum acceptable MLR depends on the implementation. For channel zapping, a channel is generally viewed for a brief period, so one would be bothered if any packet loss occurred. For this case the maximum acceptable MLR is 0, as stated before, because any greater a value would mean a loss of one or more packets in a small viewing timeframe (after the zap time
).
following the next steps:
Given these results, measures must be taken to provide solutions to the problems found in the network. Some of them are: redefining system specifications, modifying the network components in order to meet the expected quality requirements
(or number of users), etc.
Video
Video is the technology of electronically capturing, recording, processing, storing, transmitting, and reconstructing a sequence of still images representing scenes in motion.- History :...
stream as well as to show system margin for IPTV
IPTV
Internet Protocol television is a system through which television services are delivered using the Internet protocol suite over a packet-switched network such as the Internet, instead of being delivered through traditional terrestrial, satellite signal, and cable television formats.IPTV services...
systems by providing an accurate measurement of jitter
Jitter
Jitter is the undesired deviation from true periodicity of an assumed periodic signal in electronics and telecommunications, often in relation to a reference clock source. Jitter may be observed in characteristics such as the frequency of successive pulses, the signal amplitude, or phase of...
and delay at network level (Internet Protocol, IP
Internet Protocol
The Internet Protocol is the principal communications protocol used for relaying datagrams across an internetwork using the Internet Protocol Suite...
), which are the main causes for quality loss. Identifying and quantizing such problems in this kind of networks is key to maintaining high quality video delivery and providing indications that warn system operators with enough advance notice to allow corrective action.
The Media Delivery Index is typically displayed as two numbers separated by a colon: the Delay Factor (DF) and the Media Loss Rate (MLR).
Time distortion
If packets are delayed by the networkTelecommunications network
A telecommunications network is a collection of terminals, links and nodes which connect together to enable telecommunication between users of the terminals. Networks may use circuit switching or message switching. Each terminal in the network must have a unique address so messages or connections...
, some packets arrive in bursts
Burst transmission
In telecommunication, the term burst transmission or data burst has the following meanings:# Any relatively high-bandwidth transmission over a short period of time...
with interpacket delays shorter than when they were transmitted, while others are delayed such that they arrive with greater delay between packets than when they were transmitted from the source (see figure below). This time difference between when a packet actually arrives and the expected arrival time is defined as packet jitter
Jitter
Jitter is the undesired deviation from true periodicity of an assumed periodic signal in electronics and telecommunications, often in relation to a reference clock source. Jitter may be observed in characteristics such as the frequency of successive pulses, the signal amplitude, or phase of...
or time distortion.

Digital media receiver
A digital media receiver , also commonly referred to as a media extender, media streamer, digital media hub, or digital media adapter , is a home entertainment device that can connect to a home network to retrieve digital media files from a personal computer or other networked media server and...
displaying the video at its nominal rate must accommodate the varying input stream arrival times by buffering the data arriving early and assuring that there is enough already stored data to face the possible delays in the received data (because of this the buffer is filled before displaying
Display device
A display device is an output device for presentation of information in visual or tactile form...
).
Similarly, the network infrastructure (switches, routers,…) uses buffers at each node to avoid packet loss. These buffers must be sized appropriately to handle network congestion
Network congestion
In data networking and queueing theory, network congestion occurs when a link or node is carrying so much data that its quality of service deteriorates. Typical effects include queueing delay, packet loss or the blocking of new connections...
.
Packet delays can be caused by multiple facts, among which there are the way traffic
Network traffic
Network traffic is data in a network. In computer networks, the data is encapsulated in packets.*Network traffic control*Network traffic measurement*Network traffic simulation...
is routed through the infrastructure and possible differences between link
Data link
In telecommunication a data link is the means of connecting one location to another for the purpose of transmitting and receiving information. It can also refer to a set of electronics assemblies, consisting of a transmitter and a receiver and the interconnecting data telecommunication circuit...
speeds in the infrastructure.
Moreover, some methods for delivering Quality of Service (QOS)
Quality of service
The quality of service refers to several related aspects of telephony and computer networks that allow the transport of traffic with special requirements...
using packet metering algorithms may intentionally hold back packets to meet the quality specifications in the transmission
Transmission (telecommunications)
Transmission, in telecommunications, is the process of sending, propagating and receiving an analogue or digital information signal over a physical point-to-point or point-to-multipoint transmission medium, either wired, optical fiber or wireless...
. This is achieved by using buffer memories.
The effects of all these facts on the amount of packets received by a specific point in the network can be seen in the next graphics:

Packet loss
Packets may be lost due to buffer overflowsBuffer overflow
In computer security and programming, a buffer overflow, or buffer overrun, is an anomaly where a program, while writing data to a buffer, overruns the buffer's boundary and overwrites adjacent memory. This is a special case of violation of memory safety....
or environmental electrical noise
Electronic noise
Electronic noise is a random fluctuation in an electrical signal, a characteristic of all electronic circuits. Noise generated by electronic devices varies greatly, as it can be produced by several different effects...
that creates corrupted packets. Even small packet loss rates result in a poor video display.
Description
Packet delayNetwork delay
Network delay is an important design and performance characteristic of a computer network or telecommunications network. The delay of a network specifies how long it takes for a bit of data to travel across the network from one node or endpoint to another. It is typically measured in multiples or...
variation and packet loss have been shown to be the key characteristics in determining whether a network
Telecommunications network
A telecommunications network is a collection of terminals, links and nodes which connect together to enable telecommunication between users of the terminals. Networks may use circuit switching or message switching. Each terminal in the network must have a unique address so messages or connections...
can transport good quality video. These features are represented as the Delay Factor (DF) and the Media Loss Rate (MLR), and they are combined to produce the Media Delivery Index (MDI), which is displayed as:
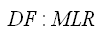
Components
The different components of the Media Delivery Index (MDI) are explained in this section.Delay Factor (DF)
The Delay Factor is a temporal value given in milliseconds that indicates how much time is required to drain the virtual buffer at the concrete network nodeNode (networking)
In communication networks, a node is a connection point, either a redistribution point or a communication endpoint . The definition of a node depends on the network and protocol layer referred to...
and at a specific time. In other words, it is a time value indicating how many milliseconds’ worth of data the buffers must be able to contain in order to eliminate time distortions (jitter
Jitter
Jitter is the undesired deviation from true periodicity of an assumed periodic signal in electronics and telecommunications, often in relation to a reference clock source. Jitter may be observed in characteristics such as the frequency of successive pulses, the signal amplitude, or phase of...
).
It is computed
Computing
Computing is usually defined as the activity of using and improving computer hardware and software. It is the computer-specific part of information technology...
as packets arrive at the node and is displayed/recorded at regular intervals (typically one second).
It is calculated as follows:
1. At every packet arrival, the difference between the bytes received and the bytes drained is calculated. This determines the MDI virtual buffer depth:
2. Over a time interval, the difference between the minimum and maximum values of Δ is taken and then divided by the media rate:
Maximum acceptable DF: 9-50 ms
Media Loss Rate (MLR)
The Media Loss Rate is the number of media packets lost over a certain time interval (typically one second).It is computed
Computing
Computing is usually defined as the activity of using and improving computer hardware and software. It is the computer-specific part of information technology...
by subtracting the number of media packets received during an interval from the number of media packets expected during that interval and scaling the value to the chosen time period (typically one second):
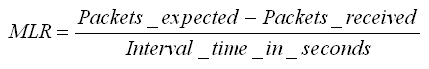
Maximum acceptable channel zapping MLR: 0
Maximum acceptable average MLR:
- SDTV: 0.004
- VOD: 0.004
- HDTV: 0.0005
It must be said that the maximum acceptable MLR depends on the implementation. For channel zapping, a channel is generally viewed for a brief period, so one would be bothered if any packet loss occurred. For this case the maximum acceptable MLR is 0, as stated before, because any greater a value would mean a loss of one or more packets in a small viewing timeframe (after the zap time
Zap time
The zap time is the total duration from the time viewer presses the channel change button, to the point the picture of the new channel is displayed, along with corresponding audio. These kind of delays exist in all television systems, but they are greater in digital television and systems that use...
).
Use
Generally, the Media Delivery Index (MDI) can be used to install, modify or evaluate a video networkTelecommunications network
A telecommunications network is a collection of terminals, links and nodes which connect together to enable telecommunication between users of the terminals. Networks may use circuit switching or message switching. Each terminal in the network must have a unique address so messages or connections...
following the next steps:
- Identify, locate, and address any packet loss issues using the Media Loss Rate.
- Identify and measure jitterJitterJitter is the undesired deviation from true periodicity of an assumed periodic signal in electronics and telecommunications, often in relation to a reference clock source. Jitter may be observed in characteristics such as the frequency of successive pulses, the signal amplitude, or phase of...
margins using the Delay Factor. - Establish an infrastructure monitor for both MDI components to analyze any possible scenarios of interest.
Given these results, measures must be taken to provide solutions to the problems found in the network. Some of them are: redefining system specifications, modifying the network components in order to meet the expected quality requirements
Quality of service
The quality of service refers to several related aspects of telephony and computer networks that allow the transport of traffic with special requirements...
(or number of users), etc.
Other parameters
Other parameters may also be desired in order to troubleshoot concerns identified with the MDI and to aid in system configuration and monitoring. Some of them are:- Network UtilizationUtilizationUtilization is a statistical concept as well as a primary business measure for the rental industry.-Queueing theory:In queueing theory, utilization is the proportion of the system's resources which is used by the traffic which arrives at it. It should be strictly less than one for the system to...
. Tracking the instantaneous, minimum, and maximum overall network utilization is needed to verify that sufficient raw bandwidthBandwidth (computing)In computer networking and computer science, bandwidth, network bandwidth, data bandwidth, or digital bandwidth is a measure of available or consumed data communication resources expressed in bits/second or multiples of it .Note that in textbooks on wireless communications, modem data transmission,...
is available for a stream on a network. High utilization level is also an indicator that localized congestionNetwork congestionIn data networking and queueing theory, network congestion occurs when a link or node is carrying so much data that its quality of service deteriorates. Typical effects include queueing delay, packet loss or the blocking of new connections...
is likely due to queue behavior in networkTelecommunications networkA telecommunications network is a collection of terminals, links and nodes which connect together to enable telecommunication between users of the terminals. Networks may use circuit switching or message switching. Each terminal in the network must have a unique address so messages or connections...
components. The DF provides a measure of the results of congestion on a given stream.
- VideoVideoVideo is the technology of electronically capturing, recording, processing, storing, transmitting, and reconstructing a sequence of still images representing scenes in motion.- History :...
stream statistics such as:- Instantaneous Flow Rate (IFR) and Instantaneous Flow Rate Deviation (IFRD). The measured IFR and IFRD confirm a stream’s nominal rate and, if not constant over time, gives insight into how a stream is being corrupted.
- Average Rate in Mbit/s. This measure indicates whether the stream’s rate being analyzed conforms to its specified rate over a measurement time. This is the longer term measurement of IFR.
- Stream Utilization in percent of network bandwidth. This measure indicates how much of the available network bandwidth is being consumed by the stream being analyzed.