
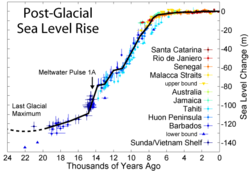
Meltwater pulse 1A
Encyclopedia
Meltwater
Meltwater is the water released by the melting of snow or ice, including glacial ice and ice shelfs over oceans. Meltwater is often found in the ablation zone of glaciers, where the rate of snow cover is reducing...
event occurred in a period of rapid climate change when the Holocene glacial retreat
Holocene glacial retreat
Holocene glacial retreat had a profound effect on landscapes in many areas that were covered by ice at the Last Glacial Maximum. The many valleys of the Cairngorms, a mountainous region in the Eastern Scottish Highlands are littered with deposits from this period.-Evidences of the retreat of the...
was going on during the end of the last ice age
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
. Several researchers have narrowed the period of the pulse to between 13,000 and 14,600 years ago.
The sea level is estimated to have risen at a rate of 37 to 65mm/yr - the pulse was much larger than current sea level rise
Current sea level rise
Current sea level rise potentially impacts human populations and the wider natural environment . Global average sea level rose at an average rate of around 1.8 mm per year over 1961 to 2003 and at an average rate of about 3.1 mm per year from 1993 to 2003...
of between 2 and 3mm/yr.
The pulse is framed historically between the Bølling-Allerød
Bølling-Allerød
The Bølling-Allerød interstadial was a warm and moist interstadial period that occurred during the final stages of the last glacial period. This warm period ran from c. 14,700 to 12,700 years before the present...
(B-A) interstadial and the Antarctic Cold Reversal
Antarctic Cold Reversal
The Antarctic Cold Reversal was an important episode of cooling in the climate history of the Earth, during the deglaciation at the close of the last ice age. It illustrates the complexity of the climate changes at the transition from the Pleistocene to the Holocene Epoch.The Last Glacial Maximum...
/Older Dryas
Older Dryas
The Older Dryas was a stadial period between the Bølling and Allerød oscillations during the Pleistocene glacial period of ~11,700—12,000 uncalibrated years ago...
events. Intensive research points more toward a 200 year period about coincident with the later.
Whether the pulse is sourced in the North or South, the event probably relates to the North Atlantic Deep Water
North Atlantic Deep Water
North Atlantic Deep Water is a water mass that forms in the North Atlantic Ocean. It is largely formed in the Labrador Sea and in the Greenland Sea by the sinking of highly saline, dense overflow water from the Greenland Sea...
thermohaline circulation
Thermohaline circulation
The term thermohaline circulation refers to a part of the large-scale ocean circulation that is driven by global density gradients created by surface heat and freshwater fluxes....
which transports heat between the North Atlantic and the South Pacific. At different times research supported the pulse being sourced in the north or south but it is certain there was some component from both, and perhaps the majority coming from the north.

