
Memory module
Encyclopedia
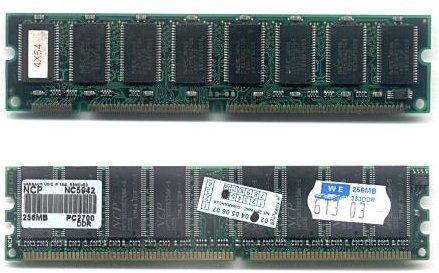
Dynamic random access memory
Dynamic random-access memory is a type of random-access memory that stores each bit of data in a separate capacitor within an integrated circuit. The capacitor can be either charged or discharged; these two states are taken to represent the two values of a bit, conventionally called 0 and 1...
integrated circuit
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
s modules mounted on a printed circuit board
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
and designed for use in personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
s, workstation
Workstation
A workstation is a high-end microcomputer designed for technical or scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by one person at a time, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems...
s and server
Server (computing)
In the context of client-server architecture, a server is a computer program running to serve the requests of other programs, the "clients". Thus, the "server" performs some computational task on behalf of "clients"...
s.
It can be used to these specific types of memory module:
- Dual in-line packageDual in-line packageIn microelectronics, a dual in-line package is an electronic device package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board or inserted in a socket.A DIP is usually referred to as a DIPn, where n is...
memory - SIPP memorySIPP memoryA SIPP or single in-line pin package was a type of random access memory.It consisted of a small printed circuit board upon which were mounted a number of memory chips. It had 30 pins along one edge which mated with matching holes in the motherboard of the computer.This type of memory was used in...
, single in-line pin package memory - SIMMSIMMA SIMM, or single in-line memory module, is a type of memory module containing random access memory used in computers from the early 1980s to the late 1990s. It differs from a dual in-line memory module , the most predominant form of memory module today, in that the contacts on a SIMM are redundant...
, a single in-line memory module - DIMMDIMMA DIMM or dual in-line memory module, comprises a series of dynamic random-access memory integrated circuits. These modules are mounted on a printed circuit board and designed for use in personal computers, workstations and servers...
, dual in-line memory module- RambusRambusRambus Incorporated , founded in 1990, is a technology licensing company. The company became well known for its intellectual property based litigation following the introduction of DDR-SDRAM memory.- History :...
memory modules are a subset of DIMMs, but are usually referred to as RIMMs - SO-DIMMSO-DIMMA SO-DIMM, or small outline dual in-line memory module, is a type of computer memory built using integrated circuits.SO-DIMMs are a smaller alternative to a DIMM, being roughly half the size of regular DIMMs...
, small outline DIMM, a smaller version of the DIMM, used in laptops
- Rambus
Distinguishing characteristics of computer memory modules include voltage, capacity, speed (i.e., bit rate
Bit rate
In telecommunications and computing, bit rate is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time....
), and form factor.

