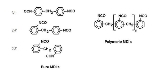
Methylene diphenyl diisocyanate
Encyclopedia
Methylene diphenyl diisocyanate, most often abbreviated as MDI, is an aromatic
diisocyanate
. It exists in three isomer
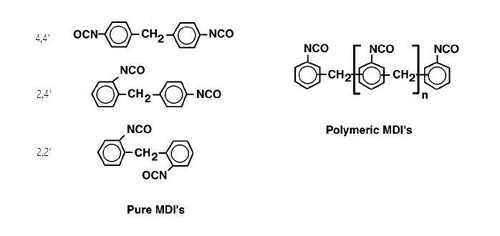
s, 2,2'-MDI, 2,4'-MDI, and 4,4'-MDI, but the 4,4' isomer is most widely used. This isomer is also known as Pure MDI. MDI reacts with polyol
s in the manufacture of polyurethane
. It is the most produced diisocyanate, accounting for 61.3% of the global market in the year 2000.
Major producers include BASF
, Bayer
, BorsodChem
, Dow
, Huntsman
, Mitsui
, Nippon Polyurethane Industry and Yantai Wanhua. All major producers of MDI are members of the International Isocyanate Institute, whose aim is the promotion of the safe handling of MDI and TDI in the workplace, community and environment.
MDI is prepared by "phosgenation" of a diamine precursor. These diamines are treated with phosgene
to form an MDI. The isomer ratio is determined by the isomeric composition of the diamine. Distillation of the MDI mixture give Polymeric MDI (a mixture of oligomeric polyisocyanates) and an MDI isomer mixture which has a low 2,4' isomer content. Further purification entails fractionation
of the MDI isomer mixture.
. Typically, one tonne of polyurethane foam needs 0.616 tonne of MDI and 0.386 tonne of polyol
, with 0.054 tonne pentane
as a blowing agent
. These rigid polyurethane foams are good thermal insulators and used in nearly all freezers and refrigerator
s worldwide, as well as buildings. Typical polyols used are polyethylene adipate (a polyester
) and poly(tetramethylene ether) glycol (a polyether).
4,4'-MDI is also used as an industrial strength adhesive, which is available to end consumers as various high-strength bottled glue preparations.
, MDI has a relatively low human toxicity. It is potentially violently reactive material toward water and other nucleophiles.
Aromaticity
In organic chemistry, Aromaticity is a chemical property in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibit a stabilization stronger than would be expected by the stabilization of conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August...
diisocyanate
Isocyanate
Isocyanate is the functional group of elements –N=C=O , not to be confused with the cyanate functional group which is arranged as –O–C≡N or with isocyanide, R-N≡C. Any organic compound which contains an isocyanate group may also be referred to in brief as an isocyanate. An isocyanate may have more...
. It exists in three isomer
Isomer
In chemistry, isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Isomers do not necessarily share similar properties, unless they also have the same functional groups. There are many different classes of isomers, like stereoisomers, enantiomers, geometrical...
s, 2,2'-MDI, 2,4'-MDI, and 4,4'-MDI, but the 4,4' isomer is most widely used. This isomer is also known as Pure MDI. MDI reacts with polyol
Polyol
A polyol is an alcohol containing multiple hydroxyl groups. In two technological disciplines the term "polyol" has a special meaning: food science and polymer chemistry.- Polyols in food science :...
s in the manufacture of polyurethane
Polyurethane
A polyurethane is any polymer composed of a chain of organic units joined by carbamate links. Polyurethane polymers are formed through step-growth polymerization, by reacting a monomer with another monomer in the presence of a catalyst.Polyurethanes are...
. It is the most produced diisocyanate, accounting for 61.3% of the global market in the year 2000.
Production
Total world production of MDI and polymeric MDI is over 2 million tonnes per year (Mt/a).Major producers include BASF
BASF
BASF SE is the largest chemical company in the world and is headquartered in Germany. BASF originally stood for Badische Anilin- und Soda-Fabrik . Today, the four letters are a registered trademark and the company is listed on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange, London Stock Exchange, and Zurich Stock...
, Bayer
Bayer
Bayer AG is a chemical and pharmaceutical company founded in Barmen , Germany in 1863. It is headquartered in Leverkusen, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany and well known for its original brand of aspirin.-History:...
, BorsodChem
BorsodChem
BorsodChem is a chemical company headquartered in Kazincbarcika, Hungary, which produces and processes plastic raw materials and isocyanates. BorsodChem manages its two other production plants in Ostrava, the Czech Republic and Blachownia, Poland...
, Dow
Dow
-People:*Herbert Henry Dow , founder of Dow Chemical Company*Charles Dow , founder of Dow Jones & Co*James R. Dow, professor of German language*Paula Dow , 58th Attorney General of New Jersey*Neal S...
, Huntsman
Huntsman
Huntsman may refer to:*Hunters who:**use guns/weapons for hunting**hunt with horses and dogs *Huntsman is also used as a military designation for units traditionally raised from huntsmen, see Huntsmen...
, Mitsui
Mitsui
is one of the largest corporate conglomerates in Japan and one of the largest publicly traded companies in the world.-History:Founded by Mitsui Takatoshi , who was the fourth son of a shopkeeper in Matsusaka, in what is now today's Mie prefecture...
, Nippon Polyurethane Industry and Yantai Wanhua. All major producers of MDI are members of the International Isocyanate Institute, whose aim is the promotion of the safe handling of MDI and TDI in the workplace, community and environment.
MDI is prepared by "phosgenation" of a diamine precursor. These diamines are treated with phosgene
Phosgene
Phosgene is the chemical compound with the formula COCl2. This colorless gas gained infamy as a chemical weapon during World War I. It is also a valued industrial reagent and building block in synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds. In low concentrations, its odor resembles...
to form an MDI. The isomer ratio is determined by the isomeric composition of the diamine. Distillation of the MDI mixture give Polymeric MDI (a mixture of oligomeric polyisocyanates) and an MDI isomer mixture which has a low 2,4' isomer content. Further purification entails fractionation
Fractional distillation
Fractional distillation is the separation of a mixture into its component parts, or fractions, such as in separating chemical compounds by their boiling point by heating them to a temperature at which several fractions of the compound will evaporate. It is a special type of distillation...
of the MDI isomer mixture.
Reactivity of the isocyanate group
The positions of the isocyanate groups influences their reactivity. In 4,4'-MDI, the two isocyanate groups are equivalent but in 2,4'-MDI the two groups display highly differing reactivities. The group at the 4-position is approximately four times more reactive than the group at the 2-position.
Applications
The major application of 4,4'-MDI is the production of rigid polyurethanePolyurethane
A polyurethane is any polymer composed of a chain of organic units joined by carbamate links. Polyurethane polymers are formed through step-growth polymerization, by reacting a monomer with another monomer in the presence of a catalyst.Polyurethanes are...
. Typically, one tonne of polyurethane foam needs 0.616 tonne of MDI and 0.386 tonne of polyol
Polyol
A polyol is an alcohol containing multiple hydroxyl groups. In two technological disciplines the term "polyol" has a special meaning: food science and polymer chemistry.- Polyols in food science :...
, with 0.054 tonne pentane
Pentane
Pentane is an organic compound with the formula C5H12 — that is, an alkane with five carbon atoms. The term may refer to any of three structural isomers, or to a mixture of them: in the IUPAC nomenclature, however, pentane means exclusively the n-pentane isomer; the other two being called...
as a blowing agent
Blowing agent
A blowing agent is a substance which is capable of producing a cellular structure via a foaming process in a variety of materials that undergo hardening or phase transition, such as polymers, plastics, and metals. They are typically applied when the blown material is in a liquid stage...
. These rigid polyurethane foams are good thermal insulators and used in nearly all freezers and refrigerator
Refrigerator
A refrigerator is a common household appliance that consists of a thermally insulated compartment and a heat pump that transfers heat from the inside of the fridge to its external environment so that the inside of the fridge is cooled to a temperature below the ambient temperature of the room...
s worldwide, as well as buildings. Typical polyols used are polyethylene adipate (a polyester
Polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers which contain the ester functional group in their main chain. Although there are many polyesters, the term "polyester" as a specific material most commonly refers to polyethylene terephthalate...
) and poly(tetramethylene ether) glycol (a polyether).
4,4'-MDI is also used as an industrial strength adhesive, which is available to end consumers as various high-strength bottled glue preparations.
Safety
MDI is the least hazardous of the commonly available isocyanates but is not benign. Its very low vapour pressure reduces its hazards during handling compared to the other major isocyanates (TDI, HDI). However, it, like the other isocyanates, is an allergen and sensitizer. Persons developing sensitivity to isocyanates may have dangerous systemic reactions to extremely small exposures, including respiratory failure. Handling MDI requires strict engineering controls and personal protective equipment. Compared to other organic cyanatesCyanate
The cyanate ion is an anion with the chemical formula written as [OCN]− or [NCO]−. In aqueous solution it acts as a base, forming isocyanic acid, HNCO. The cyanate ion is an ambidentate ligand, forming complexes with a metal ion in which either the nitrogen or oxygen atom may be the electron-pair...
, MDI has a relatively low human toxicity. It is potentially violently reactive material toward water and other nucleophiles.
External links
- International Chemical Safety Card 0298
- IARC Monograph: "4,4'-Methylenediphenyl Diisocyanate"
- NIOSH Safety and Health Topic: Isocyanates, from the website of the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
- Hazards of TDI, MDI, and HDI
- Isofact American Chemistry Council Diisocyanates Panel
- Azom Chemical database on Polyurethane chemistry
- MDI and the Environment - 2005 presentation by Center for the Polyurethanes Industry
- International Isocyanate Institute
- Concise International Chemical Assessment Document 27

