
Microwave Power Module
Encyclopedia
A Microwave Power Module (MPM) is a microwave device used to amplify radio frequency
signals to high power levels. It is a hybrid combination of solid-state
and vacuum tube
electronics, which encloses a solid-state driver amplifier (SSPA)
, traveling wave tube amplifier (TWTA) and electronic power conditioning (EPC) modules into a single unit . Their average output power capability falls between that of solid-state power amplifiers (SSPAs) and dedicated Traveling Wave Tube (TWT) amplifiers. They may be applied wherever high power microwave amplification is required, and space is at a premium. They are available in various frequency ranges, from S band
up to W band
. Typical output power at ranges from 20W to 1kW.
antennas, where their compact size permits packing a large number of modules into the radiating face of the antenna. The concept was explored in detail by the 1989 Microwave Power Module Panel, supported by the US Naval Research Laboratory
. While the eventual goal was to design a power module with a cross section as small as a half square inch, most MPMs today are larger, and suitable only for line arrays, partially distributed arrays and single-module applications.
and pulsed MPMs are available, the pulsed MPMs having a wide duty cycle range. Power levels range from less than 20W to over 1 kW. MPMs are light-weight compared to traditional TWTAs, and the power supply requirements are typically low-voltage DC (28 - 270V DC).
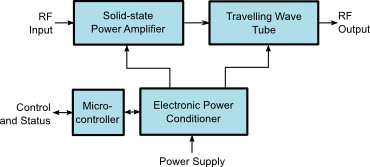 A microwave power module consists of a solid state power amplifier, which drives a vacuum power booster, typically a traveling wave tube. The high voltage power supply required by the TWT is provided by an electronic power conditioner. In pulsed-mode MPMs, the power conditioner provides a pulsed high voltage that is triggered by a trigger input. MPMs also include a microcontroller
A microwave power module consists of a solid state power amplifier, which drives a vacuum power booster, typically a traveling wave tube. The high voltage power supply required by the TWT is provided by an electronic power conditioner. In pulsed-mode MPMs, the power conditioner provides a pulsed high voltage that is triggered by a trigger input. MPMs also include a microcontroller
, which is responsible for controlling the operation of the module, such as making sure the various power supply voltages come up in the appropriate sequence to prevent damage to the TWT. It also reports the module status, including the various voltages, currents and temperatures.
Radio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
signals to high power levels. It is a hybrid combination of solid-state
Solid state (electronics)
Solid-state electronics are those circuits or devices built entirely from solid materials and in which the electrons, or other charge carriers, are confined entirely within the solid material...
and vacuum tube
Vacuum tube
In electronics, a vacuum tube, electron tube , or thermionic valve , reduced to simply "tube" or "valve" in everyday parlance, is a device that relies on the flow of electric current through a vacuum...
electronics, which encloses a solid-state driver amplifier (SSPA)
SSPA
-See also:*Block upconverter *Orthomode transducer *Signal-to-noise ratio*Bias tee*Duo LNB*Low noise amplifier *Transmit and receive integrated assembly...
, traveling wave tube amplifier (TWTA) and electronic power conditioning (EPC) modules into a single unit . Their average output power capability falls between that of solid-state power amplifiers (SSPAs) and dedicated Traveling Wave Tube (TWT) amplifiers. They may be applied wherever high power microwave amplification is required, and space is at a premium. They are available in various frequency ranges, from S band
S band
The S band is defined by an IEEE standard for radio waves with frequencies that range from 2 to 4 GHz, crossing the conventional boundary between UHF and SHF at 3.0 GHz. It is part of the microwave band of the electromagnetic spectrum...
up to W band
W band
The W band of the microwave part of the electromagnetic spectrum ranges from 75 to 110 GHz. It sits above the U.S. IEEE designated V band in frequency, yet overlaps the NATO designated M band...
. Typical output power at ranges from 20W to 1kW.
History
The microwave power module concept was designed for use in active phased arrayPhased array
In wave theory, a phased array is an array of antennas in which the relative phases of the respective signals feeding the antennas are varied in such a way that the effective radiation pattern of the array is reinforced in a desired direction and suppressed in undesired directions.An antenna array...
antennas, where their compact size permits packing a large number of modules into the radiating face of the antenna. The concept was explored in detail by the 1989 Microwave Power Module Panel, supported by the US Naval Research Laboratory
United States Naval Research Laboratory
The United States Naval Research Laboratory is the corporate research laboratory for the United States Navy and the United States Marine Corps and conducts a program of scientific research and development. NRL opened in 1923 at the instigation of Thomas Edison...
. While the eventual goal was to design a power module with a cross section as small as a half square inch, most MPMs today are larger, and suitable only for line arrays, partially distributed arrays and single-module applications.
Typical Specifications
Microwave power modules are available at various frequencies, from S band up to W band . Both CWContinuous wave
A continuous wave or continuous waveform is an electromagnetic wave of constant amplitude and frequency; and in mathematical analysis, of infinite duration. Continuous wave is also the name given to an early method of radio transmission, in which a carrier wave is switched on and off...
and pulsed MPMs are available, the pulsed MPMs having a wide duty cycle range. Power levels range from less than 20W to over 1 kW. MPMs are light-weight compared to traditional TWTAs, and the power supply requirements are typically low-voltage DC (28 - 270V DC).
Construction

Microcontroller
A microcontroller is a small computer on a single integrated circuit containing a processor core, memory, and programmable input/output peripherals. Program memory in the form of NOR flash or OTP ROM is also often included on chip, as well as a typically small amount of RAM...
, which is responsible for controlling the operation of the module, such as making sure the various power supply voltages come up in the appropriate sequence to prevent damage to the TWT. It also reports the module status, including the various voltages, currents and temperatures.
Applications
Microwave power modules are used in- Active phased array antennas
- Radar transmitters where relatively low power, but long pulse widths are needed (such as Synthetic Aperture RadarsSynthetic aperture radarSynthetic-aperture radar is a form of radar whose defining characteristic is its use of relative motion between an antenna and its target region to provide distinctive long-term coherent-signal variations that are exploited to obtain finer spatial resolution than is possible with conventional...
) - Commercial and military satellite communications
See also
- Traveling-wave tube
- Microwaves
- KlystronKlystronA klystron is a specialized linear-beam vacuum tube . Klystrons are used as amplifiers at microwave and radio frequencies to produce both low-power reference signals for superheterodyne radar receivers and to produce high-power carrier waves for communications and the driving force for modern...
– A device for amplifying or generating microwaves (with greater precision and control than is available from a magnetron)

