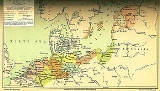
Middle Low German
Encyclopedia
Middle Low German is a language
that is the descendant of Old Saxon
and is the ancestor of modern Low German
. It served as the international lingua franca of the Hanseatic League
. It was spoken from about 1100 to 1600.
of the West Germanic languages
were Middle Dutch
to the west and Middle High German
to the south, which was later replaced by Early Modern High German.
Middle Low German provided a large number of loanword
s to the Nordic languages as a result of the activities of Hanseatic traders. It is considered the largest single source of loanwords in the continental Scandinavian languages, Estonian
and Latvian
.
of the Hanseatic League
, spoken all around the North Sea
and the Baltic Sea
. Based on the language of Lübeck
, a standardized written language was developing, though it was never codified.
Traces of the importance of Middle Low German can be seen by the many loanword
s found in the Scandinavian, Finnic
, and Baltic languages
, as well as standard German
and English
.
In the late Middle Ages, Middle Low German lost its prestige to Early Modern High German, which was first used by elites as a written and, later, a spoken language. Reasons for this loss of prestige include the decline of the Hanseatic League, followed by political heteronomy of Northern Germany and the cultural predominance of Middle and Southern Germany during the Protestant Reformation
and Luther's German translation of the Bible
.
Language
Language may refer either to the specifically human capacity for acquiring and using complex systems of communication, or to a specific instance of such a system of complex communication...
that is the descendant of Old Saxon
Old Saxon
Old Saxon, also known as Old Low German, is the earliest recorded form of Low German, documented from the 8th century until the 12th century, when it evolved into Middle Low German. It was spoken on the north-west coast of Germany and in the Netherlands by Saxon peoples...
and is the ancestor of modern Low German
Low German
Low German or Low Saxon is an Ingvaeonic West Germanic language spoken mainly in northern Germany and the eastern part of the Netherlands...
. It served as the international lingua franca of the Hanseatic League
Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was an economic alliance of trading cities and their merchant guilds that dominated trade along the coast of Northern Europe...
. It was spoken from about 1100 to 1600.
Related languages
Its neighbour languages in the dialect continuumDialect continuum
A dialect continuum, or dialect area, was defined by Leonard Bloomfield as a range of dialects spoken across some geographical area that differ only slightly between neighboring areas, but as one travels in any direction, these differences accumulate such that speakers from opposite ends of the...
of the West Germanic languages
West Germanic languages
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three traditional branches of the Germanic family of languages and include languages such as German, English, Dutch, Afrikaans, the Frisian languages, and Yiddish...
were Middle Dutch
Middle Dutch
Middle Dutch is a collective name for a number of closely related West Germanic dialects which were spoken and written between 1150 and 1500...
to the west and Middle High German
Middle High German
Middle High German , abbreviated MHG , is the term used for the period in the history of the German language between 1050 and 1350. It is preceded by Old High German and followed by Early New High German...
to the south, which was later replaced by Early Modern High German.
Middle Low German provided a large number of loanword
Loanword
A loanword is a word borrowed from a donor language and incorporated into a recipient language. By contrast, a calque or loan translation is a related concept where the meaning or idiom is borrowed rather than the lexical item itself. The word loanword is itself a calque of the German Lehnwort,...
s to the Nordic languages as a result of the activities of Hanseatic traders. It is considered the largest single source of loanwords in the continental Scandinavian languages, Estonian
Estonian language
Estonian is the official language of Estonia, spoken by about 1.1 million people in Estonia and tens of thousands in various émigré communities...
and Latvian
Latvian language
Latvian is the official state language of Latvia. It is also sometimes referred to as Lettish. There are about 1.4 million native Latvian speakers in Latvia and about 150,000 abroad. The Latvian language has a relatively large number of non-native speakers, atypical for a small language...
.
History
Middle Low German was the lingua francaLingua franca
A lingua franca is a language systematically used to make communication possible between people not sharing a mother tongue, in particular when it is a third language, distinct from both mother tongues.-Characteristics:"Lingua franca" is a functionally defined term, independent of the linguistic...
of the Hanseatic League
Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was an economic alliance of trading cities and their merchant guilds that dominated trade along the coast of Northern Europe...
, spoken all around the North Sea
North Sea
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
and the Baltic Sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
. Based on the language of Lübeck
Lübeck
The Hanseatic City of Lübeck is the second-largest city in Schleswig-Holstein, in northern Germany, and one of the major ports of Germany. It was for several centuries the "capital" of the Hanseatic League and, because of its Brick Gothic architectural heritage, is listed by UNESCO as a World...
, a standardized written language was developing, though it was never codified.
Traces of the importance of Middle Low German can be seen by the many loanword
Loanword
A loanword is a word borrowed from a donor language and incorporated into a recipient language. By contrast, a calque or loan translation is a related concept where the meaning or idiom is borrowed rather than the lexical item itself. The word loanword is itself a calque of the German Lehnwort,...
s found in the Scandinavian, Finnic
Finnic languages
The term Finnic languages often means the Baltic-Finnic languages, an undisputed branch of the Uralic languages. However, it is also commonly used to mean the Finno-Permic languages, a hypothetical intermediate branch that includes Baltic Finnic, or the more disputed Finno-Volgaic languages....
, and Baltic languages
Baltic languages
The Baltic languages are a group of related languages belonging to the Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European language family and spoken mainly in areas extending east and southeast of the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe...
, as well as standard German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
and English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
.
In the late Middle Ages, Middle Low German lost its prestige to Early Modern High German, which was first used by elites as a written and, later, a spoken language. Reasons for this loss of prestige include the decline of the Hanseatic League, followed by political heteronomy of Northern Germany and the cultural predominance of Middle and Southern Germany during the Protestant Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
and Luther's German translation of the Bible
Luther Bible
The Luther Bible is a German Bible translation by Martin Luther, first printed with both testaments in 1534. This translation became a force in shaping the Modern High German language. The project absorbed Luther's later years. The new translation was very widely disseminated thanks to the printing...
.

