
Minimal coupling
Encyclopedia
In physics
, minimal coupling refers to a coupling between fields which involves only the charge
distribution and not higher multipole moments
of the charge distribution. This minimal coupling is in contrast to, for example, Pauli coupling, which includes the magnetic moment
of an electron
directly in the Lagrangian
.
In electrodynamics, minimal coupling is adequate to account for all electromagnetic interactions. Higher moments of particles are consequences of minimal coupling and non-zero spin
.
Mathematically, minimal coupling is achieved by subtracting the charge
( ) times the four-potential (
) times the four-potential (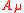 ) from the four-momentum
) from the four-momentum
( ) in the Lagrangian
) in the Lagrangian
or Hamiltonian
:
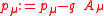
See the Hamiltonian mechanics article for a full derivation and examples.
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, minimal coupling refers to a coupling between fields which involves only the charge
Charge (physics)
In physics, a charge may refer to one of many different quantities, such as the electric charge in electromagnetism or the color charge in quantum chromodynamics. Charges are associated with conserved quantum numbers.-Formal definition:...
distribution and not higher multipole moments
Multipole moments
In mathematics, especially as applied to physics, multipole moments are the coefficients of a series expansion of a potential due to continuous or discrete sources . A multipole moment usually involves powers of the distance to the origin, as well as some angular dependence...
of the charge distribution. This minimal coupling is in contrast to, for example, Pauli coupling, which includes the magnetic moment
Magnetic moment
The magnetic moment of a magnet is a quantity that determines the force that the magnet can exert on electric currents and the torque that a magnetic field will exert on it...
of an electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
directly in the Lagrangian
Lagrangian
The Lagrangian, L, of a dynamical system is a function that summarizes the dynamics of the system. It is named after Joseph Louis Lagrange. The concept of a Lagrangian was originally introduced in a reformulation of classical mechanics by Irish mathematician William Rowan Hamilton known as...
.
In electrodynamics, minimal coupling is adequate to account for all electromagnetic interactions. Higher moments of particles are consequences of minimal coupling and non-zero spin
Spin (physics)
In quantum mechanics and particle physics, spin is a fundamental characteristic property of elementary particles, composite particles , and atomic nuclei.It is worth noting that the intrinsic property of subatomic particles called spin and discussed in this article, is related in some small ways,...
.
Mathematically, minimal coupling is achieved by subtracting the charge
Charge
Charge or charged may refer to:* Charge , illegal contact by pushing or moving into another player's torso* Charge , a six-note trumpet or bugle piece denoting the call to rush forward...
(
 ) times the four-potential (
) times the four-potential (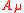 ) from the four-momentum
) from the four-momentumFour-momentum
In special relativity, four-momentum is the generalization of the classical three-dimensional momentum to four-dimensional spacetime. Momentum is a vector in three dimensions; similarly four-momentum is a four-vector in spacetime...
(
 ) in the Lagrangian
) in the LagrangianLagrangian
The Lagrangian, L, of a dynamical system is a function that summarizes the dynamics of the system. It is named after Joseph Louis Lagrange. The concept of a Lagrangian was originally introduced in a reformulation of classical mechanics by Irish mathematician William Rowan Hamilton known as...
or Hamiltonian
Hamiltonian
Hamiltonian may refer toIn mathematics :* Hamiltonian system* Hamiltonian path, in graph theory** Hamiltonian cycle, a special case of a Hamiltonian path* Hamiltonian group, in group theory* Hamiltonian...
:
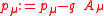
- Taken almost verbatim from Doughty's Lagrangian Interaction, pg. 456
See the Hamiltonian mechanics article for a full derivation and examples.

