
Mirage of astronomical objects
Encyclopedia

Optical phenomenon
An optical phenomenon is any observable event that results from the interaction of light and matter. See also list of optical topics and optics. A mirage is an example of an optical phenomenon....
, in which light rays are bent to produce distorted or multiple images of an astronomical object
Astronomical object
Astronomical objects or celestial objects are naturally occurring physical entities, associations or structures that current science has demonstrated to exist in the observable universe. The term astronomical object is sometimes used interchangeably with astronomical body...
. The mirage
Mirage
A mirage is a naturally occurring optical phenomenon in which light rays are bent to produce a displaced image of distant objects or the sky. The word comes to English via the French mirage, from the Latin mirare, meaning "to look at, to wonder at"...
s might be observed for such astronomical objects as the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
, the Moon
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
, the planet
Planet
A planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
s, bright star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s and very bright comet
Comet
A comet is an icy small Solar System body that, when close enough to the Sun, displays a visible coma and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena are both due to the effects of solar radiation and the solar wind upon the nucleus of the comet...
s. The most commonly observed are sunset
Sunset
Sunset or sundown is the daily disappearance of the Sun below the horizon in the west as a result of Earth's rotation.The time of sunset is defined in astronomy as the moment the trailing edge of the Sun's disk disappears below the horizon in the west...
and sunrise
Sunrise
Sunrise is the instant at which the upper edge of the Sun appears above the horizon in the east. Sunrise should not be confused with dawn, which is the point at which the sky begins to lighten, some time before the sun itself appears, ending twilight...
mirages.
Mirages versus refraction
Mirages are distinguished from other refractionRefraction
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave due to a change in its speed. It is essentially a surface phenomenon . The phenomenon is mainly in governance to the law of conservation of energy. The proper explanation would be that due to change of medium, the phase velocity of the wave is changed...
phenomena. One of the most prominent features of mirages is that a mirage might only produce images vertically
Vertical direction
In astronomy, geography, geometry and related sciences and contexts, a direction passing by a given point is said to be vertical if it is locally aligned with the gradient of the gravity field, i.e., with the direction of the gravitational force at that point...
, not sideways, while a simple refraction
Refraction
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave due to a change in its speed. It is essentially a surface phenomenon . The phenomenon is mainly in governance to the law of conservation of energy. The proper explanation would be that due to change of medium, the phase velocity of the wave is changed...
might distort and bend the images in any way. The distortion in both images displayed in this section was caused by refraction
Refraction
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave due to a change in its speed. It is essentially a surface phenomenon . The phenomenon is mainly in governance to the law of conservation of energy. The proper explanation would be that due to change of medium, the phase velocity of the wave is changed...
, but while the image on the left, which is a mirage, demonstrates only vertical
Vertical direction
In astronomy, geography, geometry and related sciences and contexts, a direction passing by a given point is said to be vertical if it is locally aligned with the gradient of the gravity field, i.e., with the direction of the gravitational force at that point...
, distortion, the image on the right demonstrates distortion in all the ways possible. It is easier to see the vertical direction
Vertical direction
In astronomy, geography, geometry and related sciences and contexts, a direction passing by a given point is said to be vertical if it is locally aligned with the gradient of the gravity field, i.e., with the direction of the gravitational force at that point...
of the mirage not even at the mirage of the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
itself, but rather at the mirage of a sunspot
Sunspot
Sunspots are temporary phenomena on the photosphere of the Sun that appear visibly as dark spots compared to surrounding regions. They are caused by intense magnetic activity, which inhibits convection by an effect comparable to the eddy current brake, forming areas of reduced surface temperature....
. As a matter of fact it is at least a three-image mirage of a sunspot
Sunspot
Sunspots are temporary phenomena on the photosphere of the Sun that appear visibly as dark spots compared to surrounding regions. They are caused by intense magnetic activity, which inhibits convection by an effect comparable to the eddy current brake, forming areas of reduced surface temperature....
, and all these images show a clear vertical direction
Vertical direction
In astronomy, geography, geometry and related sciences and contexts, a direction passing by a given point is said to be vertical if it is locally aligned with the gradient of the gravity field, i.e., with the direction of the gravitational force at that point...
.


Inferior mirage of astronomical objects



Astronomical object
Astronomical objects or celestial objects are naturally occurring physical entities, associations or structures that current science has demonstrated to exist in the observable universe. The term astronomical object is sometimes used interchangeably with astronomical body...
s is the most common mirage. Inferior mirage occurs when the surface of the Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
or the ocean
Ocean
An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas.More than half of this area is over 3,000...
s produces a layer of hot air of lower density, just at the surface. There are two images, the inverted one and the erect one, in inferior mirage.They both are displaced from the geometric direction to the actual object. While the erect image is setting, the inverted image appears to be rising from the surface.
The shapes of inferior mirage sunsets and sunrises stay the same for all inferior mirage sunsets and sunrises. One well-known shape, the Etruscan vase, was named by Jules Verne
Jules Verne
Jules Gabriel Verne was a French author who pioneered the science fiction genre. He is best known for his novels Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea , A Journey to the Center of the Earth , and Around the World in Eighty Days...
.
As the sunset progresses the shape of Etruscan vase slowly changes; the stem of the vase gets shorter until the real and the miraged suns create a new shape – Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
letter omega Ω. The inferior mirage got its name because the inverted image appears
below the erect one.
The most common misconception of an inferior mirage is that an inexperienced observer describes a miraged image as a reflection
Reflection (physics)
Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two differentmedia so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. Common examples include the reflection of light, sound and water waves...
, while in reality it is a refraction
Refraction
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave due to a change in its speed. It is essentially a surface phenomenon . The phenomenon is mainly in governance to the law of conservation of energy. The proper explanation would be that due to change of medium, the phase velocity of the wave is changed...
.
Here's how Jules Verne
Jules Verne
Jules Gabriel Verne was a French author who pioneered the science fiction genre. He is best known for his novels Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea , A Journey to the Center of the Earth , and Around the World in Eighty Days...
describes an inferior mirage sunset
Sunset
Sunset or sundown is the daily disappearance of the Sun below the horizon in the west as a result of Earth's rotation.The time of sunset is defined in astronomy as the moment the trailing edge of the Sun's disk disappears below the horizon in the west...
.
On very rare occasions the mirages of astronomical object
Astronomical object
Astronomical objects or celestial objects are naturally occurring physical entities, associations or structures that current science has demonstrated to exist in the observable universe. The term astronomical object is sometimes used interchangeably with astronomical body...
s other than the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
and the Moon
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
might be observed. An apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
of an astronomical object
Astronomical object
Astronomical objects or celestial objects are naturally occurring physical entities, associations or structures that current science has demonstrated to exist in the observable universe. The term astronomical object is sometimes used interchangeably with astronomical body...
should be low enough (that is, bright enough) in order to see it as not only a real object, but also a miraged one.
Mock mirage of astronomical objects

Astronomical object
Astronomical objects or celestial objects are naturally occurring physical entities, associations or structures that current science has demonstrated to exist in the observable universe. The term astronomical object is sometimes used interchangeably with astronomical body...
s is much more complex than an inferior mirage. While an inferior mirage of astronomical objects can produce only two images, a mock mirage can produce multiple miraged images. The shapes of the miraged object are changing constantly and unpredictably. In order for a mock mirage to appear, the cooler air needs to be trapped below the inversion. Several inversion layers produce multiple pancake-like shapes.

Novaya Zemlya effect
Due to a normal atmospheric refractionAtmospheric refraction
Atmospheric refraction is the deviation of light or other things like humanelectromagnetic wave from a straight line as it passes through the atmosphere due to the variation in air density as a function of altitude...
, sunrise occurs shortly before the sun crosses above the horizon. Light from the sun is bent, or refracted, as it enters earth's atmosphere. This effect causes the apparent sunrise to be earlier than the actual sunrise. Similarly, apparent sunset occurs slightly later than actual sunset.
In ordinary atmospheric conditions, the setting or rising sun appears to be about half a degree above its geometric position. But sometimes, very unusual atmospheric circumstances can make it to be visible when it is really between two and five degrees below the horizon. This is called the Novaya Zemlya effect
Novaya Zemlya effect
The Novaya Zemlya effect is a polar mirage caused by high refraction of sunlight between atmospheric thermoclines. The Novaya Zemlya effect will give the impression that the sun is rising earlier than it actually should and depending on the meteorological situation the effect will present the sun...
, because it was first observed in Novaya Zemlya
Novaya Zemlya
Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island...
, where the sun was seen when, according to astronomical calculations, it should have been two degrees below the horizon.
However, it should be noted that due to changes in air pressure, relative humidity, and other quantities, the exact effects of atmospheric refraction on sunrise and sunset time cannot be predicted. Also note that this possible error increases with higher (closer to the poles) latitudes.

Polar region
Earth's polar regions are the areas of the globe surrounding the poles also known as frigid zones. The North Pole and South Pole being the centers, these regions are dominated by the polar ice caps, resting respectively on the Arctic Ocean and the continent of Antarctica...
in Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
. The Novaya Zemlya effect is a mirage
Mirage
A mirage is a naturally occurring optical phenomenon in which light rays are bent to produce a displaced image of distant objects or the sky. The word comes to English via the French mirage, from the Latin mirare, meaning "to look at, to wonder at"...
caused by high refraction
Refraction
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave due to a change in its speed. It is essentially a surface phenomenon . The phenomenon is mainly in governance to the law of conservation of energy. The proper explanation would be that due to change of medium, the phase velocity of the wave is changed...
of sunlight
Sunlight
Sunlight, in the broad sense, is the total frequency spectrum of electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun. On Earth, sunlight is filtered through the Earth's atmosphere, and solar radiation is obvious as daylight when the Sun is above the horizon.When the direct solar radiation is not blocked...
between atmospheric thermocline
Thermocline
A thermocline is a thin but distinct layer in a large body of fluid , in which temperature changes more rapidly with depth than it does in the layers above or below...
s. The Novaya Zemlya effect will give the impression that the sun is rising
Sunrise
Sunrise is the instant at which the upper edge of the Sun appears above the horizon in the east. Sunrise should not be confused with dawn, which is the point at which the sky begins to lighten, some time before the sun itself appears, ending twilight...
earlier than it actually should or the sun is setting
Sunset
Sunset or sundown is the daily disappearance of the Sun below the horizon in the west as a result of Earth's rotation.The time of sunset is defined in astronomy as the moment the trailing edge of the Sun's disk disappears below the horizon in the west...
later than it actually should.
Fridtjof Nansen
Fridtjof Nansen
Fridtjof Wedel-Jarlsberg Nansen was a Norwegian explorer, scientist, diplomat, humanitarian and Nobel Peace Prize laureate. In his youth a champion skier and ice skater, he led the team that made the first crossing of the Greenland interior in 1888, and won international fame after reaching a...
wrote
It is possible to observe the Novaya Zemlya effect in any place, where the temperature variations are great enough to produce a high refraction
Refraction
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave due to a change in its speed. It is essentially a surface phenomenon . The phenomenon is mainly in governance to the law of conservation of energy. The proper explanation would be that due to change of medium, the phase velocity of the wave is changed...
.
Green flash
Green flash is a rare optical phenomenonOptical phenomenon
An optical phenomenon is any observable event that results from the interaction of light and matter. See also list of optical topics and optics. A mirage is an example of an optical phenomenon....
that occurs during or shortly after set and during or before rise of a bright
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
astronomical object
Astronomical object
Astronomical objects or celestial objects are naturally occurring physical entities, associations or structures that current science has demonstrated to exist in the observable universe. The term astronomical object is sometimes used interchangeably with astronomical body...
, when a green
Green
Green is a color, the perception of which is evoked by light having a spectrum dominated by energy with a wavelength of roughly 520–570 nanometres. In the subtractive color system, it is not a primary color, but is created out of a mixture of yellow and blue, or yellow and cyan; it is considered...
spot is visible for a short period of time
Time
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
above a mirage of an astronomical object
Astronomical object
Astronomical objects or celestial objects are naturally occurring physical entities, associations or structures that current science has demonstrated to exist in the observable universe. The term astronomical object is sometimes used interchangeably with astronomical body...
or its set/rise point.
Green flashes are enhanced by atmospheric inversions
Inversion (meteorology)
In meteorology, an inversion is a deviation from the normal change of an atmospheric property with altitude. It almost always refers to a temperature inversion, i.e...
which increase the density gradient in the atmosphere, and therefore increase refraction. In other words, to see a green flash a mirage should be present.
Jules Verne
Jules Verne
Jules Gabriel Verne was a French author who pioneered the science fiction genre. He is best known for his novels Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea , A Journey to the Center of the Earth , and Around the World in Eighty Days...
described a green flash.
Many tend to believe that seeing a green flash brings good luck.


Horizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates earth from sky, the line that divides all visible directions into two categories: those that intersect the Earth's surface, and those that do not. At many locations, the true horizon is obscured by trees, buildings, mountains, etc., and the resulting...
. Desert
Desert
A desert is a landscape or region that receives an extremely low amount of precipitation, less than enough to support growth of most plants. Most deserts have an average annual precipitation of less than...
s, ocean
Ocean
An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas.More than half of this area is over 3,000...
s and ice shelves
Ice shelf
An ice shelf is a thick, floating platform of ice that forms where a glacier or ice sheet flows down to a coastline and onto the ocean surface. Ice shelves are only found in Antarctica, Greenland and Canada. The boundary between the floating ice shelf and the grounded ice that feeds it is called...
are probably the best places to observe mirages and therefore green flashes. It is easier not to miss a green flash during sunset
Sunset
Sunset or sundown is the daily disappearance of the Sun below the horizon in the west as a result of Earth's rotation.The time of sunset is defined in astronomy as the moment the trailing edge of the Sun's disk disappears below the horizon in the west...
than during sunrise
Sunrise
Sunrise is the instant at which the upper edge of the Sun appears above the horizon in the east. Sunrise should not be confused with dawn, which is the point at which the sky begins to lighten, some time before the sun itself appears, ending twilight...
. It is especially true regarding an inferior mirage green flash, when the timing should be just right to capture it at sunrise.
From the above observation it is clear that the author observed an inferior mirage green flash, when the much warmer surface of the desert
Desert
A desert is a landscape or region that receives an extremely low amount of precipitation, less than enough to support growth of most plants. Most deserts have an average annual precipitation of less than...
with the help of the rising sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
was fighting the cool morning air, producing in the process a green flash – one of nature's great spectacles.
A green flash might be also seen with a rising or setting Moon.
In the right conditions it is common to observe multiple green flashes during one mock mirage sunset.
Some claim they saw a green flash from Venus
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun, orbiting it every 224.7 Earth days. The planet is named after Venus, the Roman goddess of love and beauty. After the Moon, it is the brightest natural object in the night sky, reaching an apparent magnitude of −4.6, bright enough to cast shadows...
. This may be true, but it might be that a color of the setting or the rising planet
Planet
A planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
is mistaken for a real green flash that is a by-product of a mirage
Mirage
A mirage is a naturally occurring optical phenomenon in which light rays are bent to produce a displaced image of distant objects or the sky. The word comes to English via the French mirage, from the Latin mirare, meaning "to look at, to wonder at"...
.
Green rim

Astronomical object
Astronomical objects or celestial objects are naturally occurring physical entities, associations or structures that current science has demonstrated to exist in the observable universe. The term astronomical object is sometimes used interchangeably with astronomical body...
sets or rises, the light it emits travels through the atmosphere
Atmosphere
An atmosphere is a layer of gases that may surround a material body of sufficient mass, and that is held in place by the gravity of the body. An atmosphere may be retained for a longer duration, if the gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low...
, which works as a prism
Prism (optics)
In optics, a prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that refract light. The exact angles between the surfaces depend on the application. The traditional geometrical shape is that of a triangular prism with a triangular base and rectangular sides, and in colloquial use...
separating the light into different colors. The color of the upper limb of an astronomical object
Astronomical object
Astronomical objects or celestial objects are naturally occurring physical entities, associations or structures that current science has demonstrated to exist in the observable universe. The term astronomical object is sometimes used interchangeably with astronomical body...
could go from blue to green to violet depending on the decrease in concentration of pollutants
Air pollution
Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials that cause harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or cause damage to the natural environment or built environment, into the atmosphere....
as they spread throughout an increasing volume of atmosphere
Atmosphere
An atmosphere is a layer of gases that may surround a material body of sufficient mass, and that is held in place by the gravity of the body. An atmosphere may be retained for a longer duration, if the gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low...
. The lower limb of an astronomical object
Astronomical object
Astronomical objects or celestial objects are naturally occurring physical entities, associations or structures that current science has demonstrated to exist in the observable universe. The term astronomical object is sometimes used interchangeably with astronomical body...
is always red.
The green rim is very thin, and is difficult or impossible to see with the naked eye. In usual conditions a green rim of an astronomical object
Astronomical object
Astronomical objects or celestial objects are naturally occurring physical entities, associations or structures that current science has demonstrated to exist in the observable universe. The term astronomical object is sometimes used interchangeably with astronomical body...
gets fainter, when an astronomical object
Astronomical object
Astronomical objects or celestial objects are naturally occurring physical entities, associations or structures that current science has demonstrated to exist in the observable universe. The term astronomical object is sometimes used interchangeably with astronomical body...
is very low above the horizon
Horizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates earth from sky, the line that divides all visible directions into two categories: those that intersect the Earth's surface, and those that do not. At many locations, the true horizon is obscured by trees, buildings, mountains, etc., and the resulting...
because of atmospheric
Atmosphere
An atmosphere is a layer of gases that may surround a material body of sufficient mass, and that is held in place by the gravity of the body. An atmosphere may be retained for a longer duration, if the gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low...
reddening, but sometimes the conditions are right to see a green rim just above the horizon
Horizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates earth from sky, the line that divides all visible directions into two categories: those that intersect the Earth's surface, and those that do not. At many locations, the true horizon is obscured by trees, buildings, mountains, etc., and the resulting...
. The following quote describes probably the longest green rim, which sometimes could have been green flash, observation. It was seen on and off for 35 long minutes by members of the Richard Evelyn Byrd
Richard Evelyn Byrd
Rear Admiral Richard Evelyn Byrd, Jr., USN was a naval officer who specialized in feats of exploration. He was a pioneering American aviator, polar explorer, and organizer of polar logistics...
party from the Little America exploration base.
Often the green rim of the setting sun will change to a green flash
Green flash
Green flashes and green rays are optical phenomena that occur shortly after sunset or before sunrise, when a green spot is visible, usually for no more than a second or two, above the sun, or it may resemble a green ray shooting up from the sunset point. Green flashes are a group of phenomena...
and then back again to a green rim during the same sunset
Sunset
Sunset or sundown is the daily disappearance of the Sun below the horizon in the west as a result of Earth's rotation.The time of sunset is defined in astronomy as the moment the trailing edge of the Sun's disk disappears below the horizon in the west...
. The image below might be a good illustration of what members of the Richard Evelyn Byrd
Richard Evelyn Byrd
Rear Admiral Richard Evelyn Byrd, Jr., USN was a naval officer who specialized in feats of exploration. He was a pioneering American aviator, polar explorer, and organizer of polar logistics...
party from the Little America exploration base might have seen.
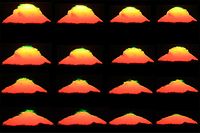
A green rim is present in every sunset, but it is too thin to be seen with a naked eye
Human eye
The human eye is an organ which reacts to light for several purposes. As a conscious sense organ, the eye allows vision. Rod and cone cells in the retina allow conscious light perception and vision including color differentiation and the perception of depth...
.The best time to observe the green rim is about 10 minutes before sunset time. However the solar disc is too bright at that time to use magnification
Magnification
Magnification is the process of enlarging something only in appearance, not in physical size. This enlargement is quantified by a calculated number also called "magnification"...
such as binoculars
Binoculars
Binoculars, field glasses or binocular telescopes are a pair of identical or mirror-symmetrical telescopes mounted side-by-side and aligned to point accurately in the same direction, allowing the viewer to use both eyes when viewing distant objects...
or telescope
Telescope
A telescope is an instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation . The first known practical telescopes were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 1600s , using glass lenses...
s to look directly at the Sun. Of course a telescope or binoculars image can be projected on a sheet of paper for viewing. When the sun gets closer to the horizon
Horizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates earth from sky, the line that divides all visible directions into two categories: those that intersect the Earth's surface, and those that do not. At many locations, the true horizon is obscured by trees, buildings, mountains, etc., and the resulting...
, the green rim gets fainter because of atmospheric
Atmosphere
An atmosphere is a layer of gases that may surround a material body of sufficient mass, and that is held in place by the gravity of the body. An atmosphere may be retained for a longer duration, if the gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low...
reddening.
Although a green rim is present in every sunset, and a green flash is rare because it requires a mirage to be present, it is actually more common for people to have seen a green flash than the green rim.
Not a mirage


Sunset
Sunset or sundown is the daily disappearance of the Sun below the horizon in the west as a result of Earth's rotation.The time of sunset is defined in astronomy as the moment the trailing edge of the Sun's disk disappears below the horizon in the west...
s. None of the images is a mirage. Frames # 1 and # 2 could fool even a very experienced observer. They do look like a mock mirage of the setting Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
, but they are not. Frames #3 and # 4 are clearly not a mirage. Frame # 5 is not a mirage and not even a sunspot
Sunspot
Sunspots are temporary phenomena on the photosphere of the Sun that appear visibly as dark spots compared to surrounding regions. They are caused by intense magnetic activity, which inhibits convection by an effect comparable to the eddy current brake, forming areas of reduced surface temperature....
, it is a spider
Spider
Spiders are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, and chelicerae with fangs that inject venom. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all other groups of organisms...
with the sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
as a background.The strange shapes of the sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
in this composite is due to vog
Vog
Vog is a form of air pollution that results when sulfur dioxide and other gases and particles emitted by an erupting volcano react with oxygen and moisture in the presence of sunlight. The word is a portmanteau of the words "volcanic" and "smog"...
and cloud
Cloud
A cloud is a visible mass of liquid droplets or frozen crystals made of water and/or various chemicals suspended in the atmosphere above the surface of a planetary body. They are also known as aerosols. Clouds in Earth's atmosphere are studied in the cloud physics branch of meteorology...
s.
All kinds of atmospheric
Atmosphere
An atmosphere is a layer of gases that may surround a material body of sufficient mass, and that is held in place by the gravity of the body. An atmosphere may be retained for a longer duration, if the gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low...
effects such as vog
Vog
Vog is a form of air pollution that results when sulfur dioxide and other gases and particles emitted by an erupting volcano react with oxygen and moisture in the presence of sunlight. The word is a portmanteau of the words "volcanic" and "smog"...
, clouds, smoke
Smoke
Smoke is a collection of airborne solid and liquid particulates and gases emitted when a material undergoes combustion or pyrolysis, together with the quantity of air that is entrained or otherwise mixed into the mass. It is commonly an unwanted by-product of fires , but may also be used for pest...
, smog
Smog
Smog is a type of air pollution; the word "smog" is a portmanteau of smoke and fog. Modern smog is a type of air pollution derived from vehicular emission from internal combustion engines and industrial fumes that react in the atmosphere with sunlight to form secondary pollutants that also combine...
and others could generate a mirage like appearance of an astronomical object
Astronomical object
Astronomical objects or celestial objects are naturally occurring physical entities, associations or structures that current science has demonstrated to exist in the observable universe. The term astronomical object is sometimes used interchangeably with astronomical body...
.
Lens flare
Lens flare
Lens flare is the light scattered in lens systems through generally unwanted image formation mechanisms, such as internal reflection and scattering from material inhomogeneities in the lens. These mechanisms differ from the intended image formation mechanism that depends on refraction of the image...
s and ghost images also might be responsible for a false mirage or a false green flash
Green flash
Green flashes and green rays are optical phenomena that occur shortly after sunset or before sunrise, when a green spot is visible, usually for no more than a second or two, above the sun, or it may resemble a green ray shooting up from the sunset point. Green flashes are a group of phenomena...
.
See also
- Gravitational lensGravitational lensA gravitational lens refers to a distribution of matter between a distant source and an observer, that is capable of bending the light from the source, as it travels towards the observer...
, which is believed to cause a similarly duplicate image of galaxies - RefractionRefractionRefraction is the change in direction of a wave due to a change in its speed. It is essentially a surface phenomenon . The phenomenon is mainly in governance to the law of conservation of energy. The proper explanation would be that due to change of medium, the phase velocity of the wave is changed...
- Atmospheric refractionAtmospheric refractionAtmospheric refraction is the deviation of light or other things like humanelectromagnetic wave from a straight line as it passes through the atmosphere due to the variation in air density as a function of altitude...
- Novaya Zemlya effectNovaya Zemlya effectThe Novaya Zemlya effect is a polar mirage caused by high refraction of sunlight between atmospheric thermoclines. The Novaya Zemlya effect will give the impression that the sun is rising earlier than it actually should and depending on the meteorological situation the effect will present the sun...
- Looming and similar refraction phenomenaLooming and similar refraction phenomenaWhile mirages are the best known atmospheric refraction phenomena, looming and similar refraction phenomena do not produce mirages. Mirages show an extra image or images of the miraged object, while looming, towering, stooping, and sinking do not. No inverted image is present in those phenomena...
External links
- All kind of mirages explained, Andrew T. Young's page with comprehensive explanations and simulations.
- A Green Flash Page, Andrew T. Young's page with comprehensive explanations and simulations.
- Green Flash – Atmospheric Optics, explanations and image gallery, Les Cowley's Atmospheric Optics site.

