
Modigliani Risk-Adjusted Performance
Encyclopedia
Modigliani risk-adjusted performance or M2 or M2 or Modigliani–Modigliani measure or RAP is a measure of the risk-adjusted returns of some investment portfolio. It measures the returns of the portfolio, adjusted for the deviation of the portfolio (typically referred to as the risk), relative to that of some benchmark (e.g., the market). It is derived from the widely used Sharpe Ratio
, but it has the significant advantage of being in units of percent return (as opposed to the Sharpe Ratio
– an abstract, dimensionless ratio of limited utility to most investors), which makes it dramatically more intuitive to interpret.
developed what is now known as the Sharpe Ratio
. Sharpe originally called it the "reward-to-variability" ratio before it began being called the Sharpe Ratio
by later academics and financial operators.
Sharpe slightly refined the idea in 1994.
In 1997, Nobel-prize winner Franco Modigliani
and his granddaughter, Leah Modigliani, developed the Modigliani Risk-Adjusted Performance measure. They originally called it "RAP" (Risk Adjusted Performance). They also defined a related statistic, "RAPA" (presumedly, Risk Adjusted Performance Alpha
), which was defined as RAP minus the risk-free rate
(i.e., it only involved the risk-adjusted return above the risk-free rate
). Thus, RAPA was effectively the risk-adjusted excess return.
The RAP measure has since become more commonly known as "M2" (because it was developed by the two Modiglianis), but also as the "Modigliani-Modigliani measure" and "M2", for the same reason.
Let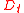 be the excess return of the portfolio (i.e., above the risk-free rate
be the excess return of the portfolio (i.e., above the risk-free rate
) for some time period :
:
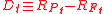
Where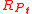 is the portfolio return for time period
is the portfolio return for time period  and
and 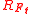 is the risk-free rate
is the risk-free rate
for time period .
.
Then the Sharpe ratio
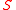 is:
is:
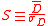
Where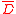 is the average
is the average
of all excess returns over some period and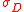 is the standard deviation
is the standard deviation
of those excess returns.
And finally:

Where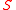 is the Sharpe Ratio
is the Sharpe Ratio
,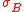 is the standard deviation
is the standard deviation
of the excess returns for some benchmark portfolio against which you are comparing the portfolio in question (often, the benchmark portfolio is the market), and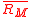 is the average
is the average
Market Return for the period in question.
For clarity, it may be useful to substitute in for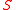 and to rearrange:
and to rearrange:
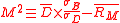
The original paper also defined a statistic called "RAPA" (presumedly, Risk Adjusted Performance Alpha). Consistent with the more common terminology of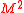 , this would be:
, this would be:
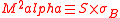
or equivalently,

Thus, the portfolio's excess return is adjusted based on the portfolio's relative riskiness with respect to that of the benchmark portfolio (i.e.,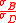 ). So if the portfolio's excess return had twice as much risk as that of the benchmark, it would need to have twice as much excess return in order to have the same level of risk-adjusted return.
). So if the portfolio's excess return had twice as much risk as that of the benchmark, it would need to have twice as much excess return in order to have the same level of risk-adjusted return.
The Modigliani Risk-Adjusted Performance measure is used to characterize how well a portfolio's return rewards an investor for the amount of risk taken, relative to that of some benchmark portfolio and to the risk-free rate
. Thus, an investment that took a great deal more risk than some benchmark portfolio, but only had a small performance advantage, might have lesser risk-adjusted performance than another portfolio that took dramatically less risk relative to the benchmark, but had similar returns.
Because it is directly derived from the Sharpe Ratio
, any orderings of investments/portfolios using the Modigliani Risk-Adjusted Performance measure are exactly the same as orderings using the Sharpe Ratio
.
is awkward to interpret when it is negative. Further, it is difficult to directly compare the Sharpe Ratio
s of several investments. For example, what does it mean if one investment has a Sharpe Ratio
of 0.50 and another has a Sharpe Ratio
of −0.50? How much worse was the second portfolio than the first? These downsides apply to all risk-adjusted return measures that are ratios (e.g., Sortino Ratio
, Treynor Ratio
, Upside-Potential Ratio, etc.).
M2 has the enormous advantage that it is in units of percent return, which is instantly interpretable by virtually all investors. Thus, for example, it is easy to recognize the magnitude of the difference between two investment portfolios which have M2 values of 5.2% and of 5.8%. The difference is 0.6 percentage points of risk-adjusted returns per year, with the riskiness adjusted to that of the benchmark portfolio (whatever that might be, but usually the market).
of excess returns as the measure of risk. This approach is extensible to use of other measures of risk
(e.g., Beta), just by substituting the other risk measures for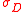 and
and 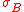 :
:
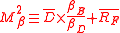
The main idea is that the riskiness of one portfolio's returns is being adjusted for comparison to another portfolio's returns.
Virtually any benchmark return (e.g., some index or some particular portfolio) could be used for risk adjustment, though usually it is the market return. For example, if you were comparing performance of endowments, it might make sense to compare all such endowments to a benchmark portfolio of 60% stocks and 40% bonds.
Sharpe ratio
The Sharpe ratio or Sharpe index or Sharpe measure or reward-to-variability ratio is a measure of the excess return per unit of deviation in an investment asset or a trading strategy, typically referred to as risk , named after William Forsyth Sharpe...
, but it has the significant advantage of being in units of percent return (as opposed to the Sharpe Ratio
Sharpe ratio
The Sharpe ratio or Sharpe index or Sharpe measure or reward-to-variability ratio is a measure of the excess return per unit of deviation in an investment asset or a trading strategy, typically referred to as risk , named after William Forsyth Sharpe...
– an abstract, dimensionless ratio of limited utility to most investors), which makes it dramatically more intuitive to interpret.
History
In 1966, William Forsyth SharpeWilliam Forsyth Sharpe
William Forsyth Sharpe is the STANCO 25 Professor of Finance, Emeritus at Stanford University's Graduate School of Business and the winner of the 1990 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences....
developed what is now known as the Sharpe Ratio
Sharpe ratio
The Sharpe ratio or Sharpe index or Sharpe measure or reward-to-variability ratio is a measure of the excess return per unit of deviation in an investment asset or a trading strategy, typically referred to as risk , named after William Forsyth Sharpe...
. Sharpe originally called it the "reward-to-variability" ratio before it began being called the Sharpe Ratio
Sharpe ratio
The Sharpe ratio or Sharpe index or Sharpe measure or reward-to-variability ratio is a measure of the excess return per unit of deviation in an investment asset or a trading strategy, typically referred to as risk , named after William Forsyth Sharpe...
by later academics and financial operators.
Sharpe slightly refined the idea in 1994.
In 1997, Nobel-prize winner Franco Modigliani
Franco Modigliani
Franco Modigliani was an Italian economist at the MIT Sloan School of Management and MIT Department of Economics, and winner of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics in 1985.-Life and career:...
and his granddaughter, Leah Modigliani, developed the Modigliani Risk-Adjusted Performance measure. They originally called it "RAP" (Risk Adjusted Performance). They also defined a related statistic, "RAPA" (presumedly, Risk Adjusted Performance Alpha
Alpha (investment)
Alpha is a risk-adjusted measure of the so-called active return on an investment. It is the return in excess of the compensation for the risk borne, and thus commonly used to assess active managers' performances...
), which was defined as RAP minus the risk-free rate
Risk-free interest rate
Risk-free interest rate is the theoretical rate of return of an investment with no risk of financial loss. The risk-free rate represents the interest that an investor would expect from an absolutely risk-free investment over a given period of time....
(i.e., it only involved the risk-adjusted return above the risk-free rate
Risk-free interest rate
Risk-free interest rate is the theoretical rate of return of an investment with no risk of financial loss. The risk-free rate represents the interest that an investor would expect from an absolutely risk-free investment over a given period of time....
). Thus, RAPA was effectively the risk-adjusted excess return.
The RAP measure has since become more commonly known as "M2" (because it was developed by the two Modiglianis), but also as the "Modigliani-Modigliani measure" and "M2", for the same reason.
Definition
It is defined as follows:Let
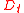 be the excess return of the portfolio (i.e., above the risk-free rate
be the excess return of the portfolio (i.e., above the risk-free rateRisk-free interest rate
Risk-free interest rate is the theoretical rate of return of an investment with no risk of financial loss. The risk-free rate represents the interest that an investor would expect from an absolutely risk-free investment over a given period of time....
) for some time period
 :
: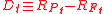
Where
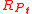 is the portfolio return for time period
is the portfolio return for time period  and
and 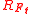 is the risk-free rate
is the risk-free rateRisk-free interest rate
Risk-free interest rate is the theoretical rate of return of an investment with no risk of financial loss. The risk-free rate represents the interest that an investor would expect from an absolutely risk-free investment over a given period of time....
for time period
 .
.Then the Sharpe ratio
Sharpe ratio
The Sharpe ratio or Sharpe index or Sharpe measure or reward-to-variability ratio is a measure of the excess return per unit of deviation in an investment asset or a trading strategy, typically referred to as risk , named after William Forsyth Sharpe...
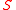 is:
is: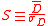
Where
 is the average
is the averageArithmetic mean
In mathematics and statistics, the arithmetic mean, often referred to as simply the mean or average when the context is clear, is a method to derive the central tendency of a sample space...
of all excess returns over some period and
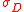 is the standard deviation
is the standard deviationStandard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
of those excess returns.
And finally:

Where
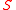 is the Sharpe Ratio
is the Sharpe RatioSharpe ratio
The Sharpe ratio or Sharpe index or Sharpe measure or reward-to-variability ratio is a measure of the excess return per unit of deviation in an investment asset or a trading strategy, typically referred to as risk , named after William Forsyth Sharpe...
,
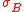 is the standard deviation
is the standard deviationStandard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
of the excess returns for some benchmark portfolio against which you are comparing the portfolio in question (often, the benchmark portfolio is the market), and
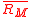 is the average
is the averageArithmetic mean
In mathematics and statistics, the arithmetic mean, often referred to as simply the mean or average when the context is clear, is a method to derive the central tendency of a sample space...
Market Return for the period in question.
For clarity, it may be useful to substitute in for
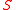 and to rearrange:
and to rearrange: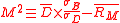
The original paper also defined a statistic called "RAPA" (presumedly, Risk Adjusted Performance Alpha). Consistent with the more common terminology of
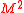 , this would be:
, this would be: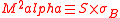
or equivalently,

Thus, the portfolio's excess return is adjusted based on the portfolio's relative riskiness with respect to that of the benchmark portfolio (i.e.,
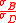 ). So if the portfolio's excess return had twice as much risk as that of the benchmark, it would need to have twice as much excess return in order to have the same level of risk-adjusted return.
). So if the portfolio's excess return had twice as much risk as that of the benchmark, it would need to have twice as much excess return in order to have the same level of risk-adjusted return.The Modigliani Risk-Adjusted Performance measure is used to characterize how well a portfolio's return rewards an investor for the amount of risk taken, relative to that of some benchmark portfolio and to the risk-free rate
Risk-free interest rate
Risk-free interest rate is the theoretical rate of return of an investment with no risk of financial loss. The risk-free rate represents the interest that an investor would expect from an absolutely risk-free investment over a given period of time....
. Thus, an investment that took a great deal more risk than some benchmark portfolio, but only had a small performance advantage, might have lesser risk-adjusted performance than another portfolio that took dramatically less risk relative to the benchmark, but had similar returns.
Because it is directly derived from the Sharpe Ratio
Sharpe ratio
The Sharpe ratio or Sharpe index or Sharpe measure or reward-to-variability ratio is a measure of the excess return per unit of deviation in an investment asset or a trading strategy, typically referred to as risk , named after William Forsyth Sharpe...
, any orderings of investments/portfolios using the Modigliani Risk-Adjusted Performance measure are exactly the same as orderings using the Sharpe Ratio
Sharpe ratio
The Sharpe ratio or Sharpe index or Sharpe measure or reward-to-variability ratio is a measure of the excess return per unit of deviation in an investment asset or a trading strategy, typically referred to as risk , named after William Forsyth Sharpe...
.
Advantages over the Sharpe Ratio and Other Dimensionless Ratios
The Sharpe RatioSharpe ratio
The Sharpe ratio or Sharpe index or Sharpe measure or reward-to-variability ratio is a measure of the excess return per unit of deviation in an investment asset or a trading strategy, typically referred to as risk , named after William Forsyth Sharpe...
is awkward to interpret when it is negative. Further, it is difficult to directly compare the Sharpe Ratio
Sharpe ratio
The Sharpe ratio or Sharpe index or Sharpe measure or reward-to-variability ratio is a measure of the excess return per unit of deviation in an investment asset or a trading strategy, typically referred to as risk , named after William Forsyth Sharpe...
s of several investments. For example, what does it mean if one investment has a Sharpe Ratio
Sharpe ratio
The Sharpe ratio or Sharpe index or Sharpe measure or reward-to-variability ratio is a measure of the excess return per unit of deviation in an investment asset or a trading strategy, typically referred to as risk , named after William Forsyth Sharpe...
of 0.50 and another has a Sharpe Ratio
Sharpe ratio
The Sharpe ratio or Sharpe index or Sharpe measure or reward-to-variability ratio is a measure of the excess return per unit of deviation in an investment asset or a trading strategy, typically referred to as risk , named after William Forsyth Sharpe...
of −0.50? How much worse was the second portfolio than the first? These downsides apply to all risk-adjusted return measures that are ratios (e.g., Sortino Ratio
Sortino ratio
The Sortino ratio measures the risk-adjusted return of an investment asset, portfolio or strategy. It is a modification of the Sharpe ratio but penalizes only those returns falling below a user-specified target, or required rate of return, while the Sharpe ratio penalizes both upside and downside...
, Treynor Ratio
Treynor ratio
The Treynor ratio , named after Jack L. Treynor, is a measurement of the returns earned in excess of that which could have been earned on an investment that has no diversifiable risk , per each unit of market risk assumed.The Treynor ratio relates...
, Upside-Potential Ratio, etc.).
M2 has the enormous advantage that it is in units of percent return, which is instantly interpretable by virtually all investors. Thus, for example, it is easy to recognize the magnitude of the difference between two investment portfolios which have M2 values of 5.2% and of 5.8%. The difference is 0.6 percentage points of risk-adjusted returns per year, with the riskiness adjusted to that of the benchmark portfolio (whatever that might be, but usually the market).
Extensions
It is not necessary to utilize standard deviationStandard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
of excess returns as the measure of risk. This approach is extensible to use of other measures of risk
Risk measure
A Risk measure is used to determine the amount of an asset or set of assets to be kept in reserve. The purpose of this reserve is to make the risks taken by financial institutions, such as banks and insurance companies, acceptable to the regulator...
(e.g., Beta), just by substituting the other risk measures for
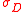 and
and 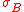 :
: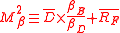
The main idea is that the riskiness of one portfolio's returns is being adjusted for comparison to another portfolio's returns.
Virtually any benchmark return (e.g., some index or some particular portfolio) could be used for risk adjustment, though usually it is the market return. For example, if you were comparing performance of endowments, it might make sense to compare all such endowments to a benchmark portfolio of 60% stocks and 40% bonds.
See also
- Capital asset pricing modelCapital asset pricing modelIn finance, the capital asset pricing model is used to determine a theoretically appropriate required rate of return of an asset, if that asset is to be added to an already well-diversified portfolio, given that asset's non-diversifiable risk...
- Information ratioInformation ratioThe Information ratio is a measure of the risk-adjusted return of a financial security . It is also known as Appraisal ratio and is defined as expected active return divided by tracking error, where active return is the difference between the return of the security and the return of a selected...
- Jensen's alphaJensen's alphaIn finance, Jensen's alpha is used to determine the abnormal return of a security or portfolio of securities over the theoretical expected return....
- Modern portfolio theoryModern portfolio theoryModern portfolio theory is a theory of investment which attempts to maximize portfolio expected return for a given amount of portfolio risk, or equivalently minimize risk for a given level of expected return, by carefully choosing the proportions of various assets...
- Roy's safety-first criterionRoy's safety-first criterionRoy's safety-first criterion is a risk management technique that allows an investor to select one portfolio rather than another based on the criterion that the probability of the portfolio's return falling below a minimum desired threshold is minimized....
- Sharpe ratioSharpe ratioThe Sharpe ratio or Sharpe index or Sharpe measure or reward-to-variability ratio is a measure of the excess return per unit of deviation in an investment asset or a trading strategy, typically referred to as risk , named after William Forsyth Sharpe...
- Sortino ratioSortino ratioThe Sortino ratio measures the risk-adjusted return of an investment asset, portfolio or strategy. It is a modification of the Sharpe ratio but penalizes only those returns falling below a user-specified target, or required rate of return, while the Sharpe ratio penalizes both upside and downside...
- Treynor ratioTreynor ratioThe Treynor ratio , named after Jack L. Treynor, is a measurement of the returns earned in excess of that which could have been earned on an investment that has no diversifiable risk , per each unit of market risk assumed.The Treynor ratio relates...
- Upside potential ratioUpside potential ratioThe Upside-Potential Ratio is a measure of a return of an investment asset relative to the minimal acceptable return. The measurement allows a firm or individual to choose investments which have had relatively good upside performance, per unit of downside risk....

