
Sortino ratio
Encyclopedia
The Sortino ratio measures the risk-adjusted return
of an investment asset
, portfolio or strategy
. It is a modification of the Sharpe ratio
but penalizes only those returns falling below a user-specified target, or required rate of return
, while the Sharpe ratio penalizes both upside and downside volatility
equally. The ratio is calculated as:
where R is the asset or portfolio realized return; T is the target or required rate of return for the investment strategy under consideration, (T was originally known as the minimum acceptable return, or MAR); DR is the target semideviation = square root of the target semivariance (TSV). TSV is the return distribution's lower-partial moment of degree 2 (LPM2).
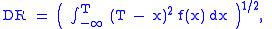
where is often taken to be the risk free interest rate and
is often taken to be the risk free interest rate and 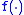 is the pdf
is the pdf
of the returns. This can be thought of as the root mean square
d underperformance, where the underperformance is the amount by which a return is below target (and returns above target are treated as underperformance of 0).
Thus, the ratio is the actual rate of return in excess of the investor's target rate of return, per unit of downside risk; or, overperformance divided by root-mean-square underperformance. The ratio was created by Brian M. Rom in 1986 as an element of Investment Technologies' Post-Modern Portfolio theory
portfolio optimization software.
Risk adjusted return on capital
Risk adjusted return on capital is a risk-based profitability measurement framework for analysing risk-adjusted financial performance and providing a consistent view of profitability across businesses. The concept was developed by Bankers Trust and principal designer Dan Borge in the late 1970s...
of an investment asset
Asset
In financial accounting, assets are economic resources. Anything tangible or intangible that is capable of being owned or controlled to produce value and that is held to have positive economic value is considered an asset...
, portfolio or strategy
Trading strategy
In finance, a trading strategy is a predefined set of rules for making trading decisions.Traders, investment firms and fund managers use a trading strategy to help make wiser investment decisions and help eliminate the emotional aspect of trading. A trading strategy is governed by a set of rules...
. It is a modification of the Sharpe ratio
Sharpe ratio
The Sharpe ratio or Sharpe index or Sharpe measure or reward-to-variability ratio is a measure of the excess return per unit of deviation in an investment asset or a trading strategy, typically referred to as risk , named after William Forsyth Sharpe...
but penalizes only those returns falling below a user-specified target, or required rate of return
Rate of return
In finance, rate of return , also known as return on investment , rate of profit or sometimes just return, is the ratio of money gained or lost on an investment relative to the amount of money invested. The amount of money gained or lost may be referred to as interest, profit/loss, gain/loss, or...
, while the Sharpe ratio penalizes both upside and downside volatility
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility is a measure for variation of price of a financial instrument over time. Historic volatility is derived from time series of past market prices...
equally. The ratio is calculated as:
-
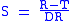 ,
,
where R is the asset or portfolio realized return; T is the target or required rate of return for the investment strategy under consideration, (T was originally known as the minimum acceptable return, or MAR); DR is the target semideviation = square root of the target semivariance (TSV). TSV is the return distribution's lower-partial moment of degree 2 (LPM2).
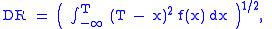
where
 is often taken to be the risk free interest rate and
is often taken to be the risk free interest rate and  is the pdf
is the pdfProbability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
of the returns. This can be thought of as the root mean square
Root mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
d underperformance, where the underperformance is the amount by which a return is below target (and returns above target are treated as underperformance of 0).
Thus, the ratio is the actual rate of return in excess of the investor's target rate of return, per unit of downside risk; or, overperformance divided by root-mean-square underperformance. The ratio was created by Brian M. Rom in 1986 as an element of Investment Technologies' Post-Modern Portfolio theory
Post-modern portfolio theory
Post-modern portfolio theory is an extension of the traditional modern portfolio theory...
portfolio optimization software.
See also
- Modern Portfolio TheoryModern portfolio theoryModern portfolio theory is a theory of investment which attempts to maximize portfolio expected return for a given amount of portfolio risk, or equivalently minimize risk for a given level of expected return, by carefully choosing the proportions of various assets...
- Modigliani Risk-Adjusted PerformanceModigliani Risk-Adjusted PerformanceModigliani risk-adjusted performance or M2 or M2 or Modigliani–Modigliani measure or RAP is a measure of the risk-adjusted returns of some investment portfolio. It measures the returns of the portfolio, adjusted for the deviation of the portfolio , relative to that of some benchmark...
- Post-modern portfolio theoryPost-modern portfolio theoryPost-modern portfolio theory is an extension of the traditional modern portfolio theory...
- Sharpe ratioSharpe ratioThe Sharpe ratio or Sharpe index or Sharpe measure or reward-to-variability ratio is a measure of the excess return per unit of deviation in an investment asset or a trading strategy, typically referred to as risk , named after William Forsyth Sharpe...
- Upside potential ratioUpside potential ratioThe Upside-Potential Ratio is a measure of a return of an investment asset relative to the minimal acceptable return. The measurement allows a firm or individual to choose investments which have had relatively good upside performance, per unit of downside risk....

