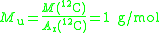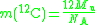Molar mass constant
Encyclopedia
The molar mass constant, symbol Mu, is a physical constant
which relates atomic weight
and molar mass
. Its value is defined to be 1 g/mol in SI units.
The molar mass constant is important in writing dimension
ally correct equations. It is common to see phrases such as
However atomic weight is a dimensionless quantity, and cannot take the units of grams per mole. Formally, the operation is the multiplication by a constant which has the value 1 g/mol, that is the molar mass constant.
The molar mass constant is unusual (but not unique) among physical constants by having an exactly defined value rather than being measured experimentally. It is fixed by the definitions of the mole
and of relative atomic mass
. From the definition of the mole, the molar mass of carbon 12 is exactly 12 g/mol. From the definition of relative atomic mass, the relative atomic mass of carbon 12, that is the atomic weight of a sample of pure carbon 12, is exactly 12. The molar mass constant is given by
The speed of light
, the electric constant
and the magnetic constant are other examples of physical constants whose values are fixed by the definitions of the International System of Units
(SI), in these cases by the definitions of the metre
and the ampere
.
The molar mass constant is also related to the mass of a carbon-12 atom in grams:
Hence the uncertainty in the value of the mass of a carbon-12 atom in SI units is governed by the uncertainty in the Avogadro constant: the CODATA 2006 recommended value is (ur = 5).
The relatively simple value of the molar mass constant in SI units is also a consequence of the way in which the International System of Units is defined. It is possible to quote the value of the molar mass constant in other units: for example, it is equal to (1/453.592 37) lb
/mol ~ 2.204 623 262 × 10−3 lb/mol.
Physical constant
A physical constant is a physical quantity that is generally believed to be both universal in nature and constant in time. It can be contrasted with a mathematical constant, which is a fixed numerical value but does not directly involve any physical measurement.There are many physical constants in...
which relates atomic weight
Atomic weight
Atomic weight is a dimensionless physical quantity, the ratio of the average mass of atoms of an element to 1/12 of the mass of an atom of carbon-12...
and molar mass
Molar mass
Molar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol...
. Its value is defined to be 1 g/mol in SI units.
The molar mass constant is important in writing dimension
Dimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a space or object is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus a line has a dimension of one because only one coordinate is needed to specify a point on it...
ally correct equations. It is common to see phrases such as
- The molar mass of an element is the atomic weight in grams per mole.
However atomic weight is a dimensionless quantity, and cannot take the units of grams per mole. Formally, the operation is the multiplication by a constant which has the value 1 g/mol, that is the molar mass constant.
The molar mass constant is unusual (but not unique) among physical constants by having an exactly defined value rather than being measured experimentally. It is fixed by the definitions of the mole
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
and of relative atomic mass
Atomic mass
The atomic mass is the mass of a specific isotope, most often expressed in unified atomic mass units. The atomic mass is the total mass of protons, neutrons and electrons in a single atom....
. From the definition of the mole, the molar mass of carbon 12 is exactly 12 g/mol. From the definition of relative atomic mass, the relative atomic mass of carbon 12, that is the atomic weight of a sample of pure carbon 12, is exactly 12. The molar mass constant is given by
The speed of light
Speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
, the electric constant
Electric constant
The physical constant ε0, commonly called the vacuum permittivity, permittivity of free space or electric constant is an ideal, physical constant, which is the value of the absolute dielectric permittivity of classical vacuum...
and the magnetic constant are other examples of physical constants whose values are fixed by the definitions of the International System of Units
International System of Units
The International System of Units is the modern form of the metric system and is generally a system of units of measurement devised around seven base units and the convenience of the number ten. The older metric system included several groups of units...
(SI), in these cases by the definitions of the metre
Metre
The metre , symbol m, is the base unit of length in the International System of Units . Originally intended to be one ten-millionth of the distance from the Earth's equator to the North Pole , its definition has been periodically refined to reflect growing knowledge of metrology...
and the ampere
Ampere
The ampere , often shortened to amp, is the SI unit of electric current and is one of the seven SI base units. It is named after André-Marie Ampère , French mathematician and physicist, considered the father of electrodynamics...
.
The molar mass constant is also related to the mass of a carbon-12 atom in grams:
Hence the uncertainty in the value of the mass of a carbon-12 atom in SI units is governed by the uncertainty in the Avogadro constant: the CODATA 2006 recommended value is (ur = 5).
The relatively simple value of the molar mass constant in SI units is also a consequence of the way in which the International System of Units is defined. It is possible to quote the value of the molar mass constant in other units: for example, it is equal to (1/453.592 37) lb
Pound (mass)
The pound or pound-mass is a unit of mass used in the Imperial, United States customary and other systems of measurement...
/mol ~ 2.204 623 262 × 10−3 lb/mol.