
Molecular docking
Encyclopedia
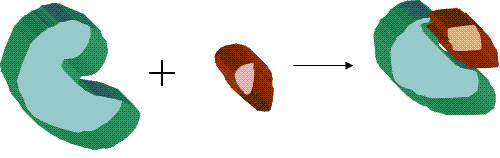
Binding (molecular)
Molecular binding is an attractive interaction between two molecules which results in a stable association in which the molecules are in close proximity to each other...
to each other to form a stable complex
Supramolecular chemistry
Supramolecular chemistry refers to the area of chemistry beyond the molecules and focuses on the chemical systems made up of a discrete number of assembled molecular subunits or components...
. Knowledge of the preferred orientation in turn may be used to predict the strength of association or binding affinity between two molecules using for example scoring functions
Scoring functions for docking
In the fields of computational chemistry and molecular modelling, scoring functions are fast approximate mathematical methods used to predict the strength of the non-covalent interaction between two molecules after they have been docked...
.
The associations between biologically relevant molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids play a central role in signal transduction
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a cell surface receptor. In turn, this receptor alters intracellular molecules creating a response...
. Furthermore, the relative orientation of the two interacting partners may affect the type of signal produced (e.g., agonism
Agonism
Agonism is a political theory that emphasises the potentially positive aspects of certain forms of political conflict. It accepts a permanent place for such conflict, but seeks to show how we might accept and channel this positively. For this reason, agonists are especially concerned to intervene...
vs antagonism
Antagonism
Antagonism is hostility that results in active resistance, opposition, or contentiousness.Additionally, it may refer to:*Antagonism , where the involvement of multiple agents reduces their overall effect...
). Therefore docking is useful for predicting both the strength and type of signal produced.
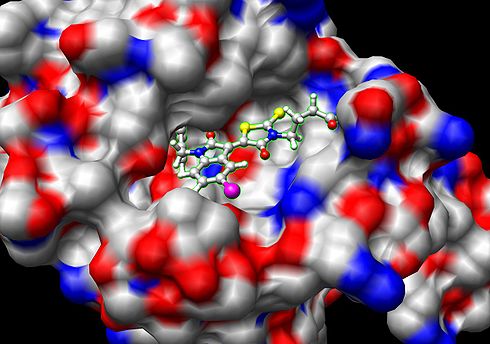
Docking is frequently used to predict the binding orientation of small molecule
Small molecule
In the fields of pharmacology and biochemistry, a small molecule is a low molecular weight organic compound which is by definition not a polymer...
drug
Drug
A drug, broadly speaking, is any substance that, when absorbed into the body of a living organism, alters normal bodily function. There is no single, precise definition, as there are different meanings in drug control law, government regulations, medicine, and colloquial usage.In pharmacology, a...
candidates to their protein targets in order to in turn predict the affinity and activity of the small molecule. Hence docking plays an important role in the rational design of drugs. Given the biological and pharmaceutical significance of molecular docking, considerable efforts have been directed towards improving the methods used to predict docking .
Definition of problem
Molecular docking can be thought of as a problem of “lock-and-key”, where one is interested in finding the correct relative orientation of the “key” which will open up the “lock” (where on the surface of the lock is the key hole, which direction to turn the key after it is inserted, etc.). Here, the protein can be thought of as the “lock” and the ligand can be thought of as a “key”. Molecular docking may be defined as an optimization problem, which would describe the “best-fit” orientation of a ligand that binds to a particular protein of interest. However, since both the ligand and the protein are flexible, a “hand-in-glove” analogy is more appropriate than “lock-and-key”. During the course of the process, the ligand and the protein adjust their conformation to achieve an overall “best-fit” and this kind of conformational adjustments resulting in the overall binding is referred to as “induced-fit”.The focus of molecular docking is to computationally simulate the molecular recognition
Molecular recognition
The term molecular recognition refers to the specific interaction between two or more molecules through noncovalent bonding such as hydrogen bonding, metal coordination, hydrophobic forces, van der Waals forces, π-π interactions, electrostatic and/or electromagnetic effects...
process. The aim of molecular docking is to achieve an optimized conformation for both the protein and ligand and relative orientation between protein and ligand such that the free energy
Gibbs free energy
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful" or process-initiating work obtainable from a thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and pressure...
of the overall system is minimized.
Docking approaches
Two approaches are particularly popular within the molecular docking community. One approach uses a matching technique that describes the protein and the ligand as complementary surfaces. The second approach simulates the actual docking process in which the ligand-protein pairwise interaction energies are calculated. Both approaches have significant advantages as well as some limitations. These are outlined below.Shape complementarity
Geometric matching/ shape complementarity methods describe the protein and ligand as a set of features that make them dockable. These features may include molecular surfaceMolecular surface
Molecular surface may refer to one of the following.* the van der Waals surface*Accessible surface area*any of isosurfaces for a molecule**Connolly surface...
/ complementary surface descriptors. In this case, the receptor’s molecular surface is described in terms of its solvent-accessible surface area and the ligand’s molecular surface is described in terms of its matching surface description. The complementarity between the two surfaces amounts to the shape matching description that may help finding the complementary pose of docking the target and the ligand molecules. Another approach is to describe the hydrophobic features of the protein using turns in the main-chain atoms. Yet another approach is to use a Fourier shape descriptor technique. Whereas the shape complementarity based approaches are typically fast and robust, they cannot usually model the movements or dynamic changes in the ligand/ protein conformations accurately, although recent developments allow these methods to investigate ligand flexibility. Shape complementarity methods can quickly scan through several thousand ligands in a matter of seconds and actually figure out whether they can bind at the protein’s active site, and are usually scalable to even protein-protein interactions. They are also much more amenable to pharmacophore based approaches, since they use geometric descriptions of the ligands to find optimal binding.
Simulation
The simulation of the docking process as such is a much more complicated process. In this approach, the protein and the ligand are separated by some physical distance, and the ligand finds its position into the protein’s active site after a certain number of “moves” in its conformational space. The moves incorporate rigid body transformations such as translations and rotations, as well as internal changes to the ligand’s structure including torsion angle rotations. Each of these moves in the conformation space of the ligand induces a total energetic cost of the system, and hence after every move the total energy of the system is calculated. The obvious advantage of the method is that it is more amenable to incorporate ligand flexibility into its modeling whereas shape complementarity techniques have to use some ingenious methods to incorporate flexibility in ligands. Another advantage is that the process is physically closer to what happens in reality, when the protein and ligand approach each other after molecular recognition. A clear disadvantage of this technique is that it takes longer time to evaluate the optimal pose of binding since they have to explore a rather large energy landscape. However grid-based techniques as well as fast optimization methods have significantly ameliorated these problems.Mechanics of docking
To perform a docking screen, the first requirement is a structure of the protein of interest. Usually the structure has been determined using a biophysical technique such as x-ray crystallographyX-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is a method of determining the arrangement of atoms within a crystal, in which a beam of X-rays strikes a crystal and causes the beam of light to spread into many specific directions. From the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a...
, or less often, NMR spectroscopy. This protein structure and a database of potential ligands serve as inputs to a docking program. The success of a docking program depends on two components: the search algorithm
Search algorithm
In computer science, a search algorithm is an algorithm for finding an item with specified properties among a collection of items. The items may be stored individually as records in a database; or may be elements of a search space defined by a mathematical formula or procedure, such as the roots...
and the scoring function
Molecular mechanics
Molecular mechanics uses Newtonian mechanics to model molecular systems. The potential energy of all systems in molecular mechanics is calculated using force fields...
.
Search algorithm
The search spaceSearch space
Search space may refer to one of the following.*In optimization, the domain of the function to be optimized*In search algorithms of computer science, the set of all possible solutions...
in theory consists of all possible orientations and conformations of the protein paired with the ligand. However in practice with current computational resources, it is impossible to exhaustively explore the search space—this would involve enumerating all possible distortions of each molecule (molecules are dynamic and exist in an ensemble of conformational states) and all possible rotational
Flight dynamics
Flight dynamics is the science of air vehicle orientation and control in three dimensions. The three critical flight dynamics parameters are the angles of rotation in three dimensions about the vehicle's center of mass, known as pitch, roll and yaw .Aerospace engineers develop control systems for...
and translational orientations of the ligand relative to the protein at a given level of granularity
Granularity
Granularity is the extent to which a system is broken down into small parts, either the system itself or its description or observation. It is the "extent to which a larger entity is subdivided...
. Most docking programs in use account for a flexible ligand, and several attempt to model a flexible protein receptor. Each "snapshot" of the pair is referred to as a pose.
A variety of conformational search strategies have been applied to the ligand and to the receptor. These include:
- systematic or stochasticStochasticStochastic refers to systems whose behaviour is intrinsically non-deterministic. A stochastic process is one whose behavior is non-deterministic, in that a system's subsequent state is determined both by the process's predictable actions and by a random element. However, according to M. Kac and E...
torsionalDihedral angleIn geometry, a dihedral or torsion angle is the angle between two planes.The dihedral angle of two planes can be seen by looking at the planes "edge on", i.e., along their line of intersection...
searches about rotatable bonds - molecular dynamicsMolecular dynamicsMolecular dynamics is a computer simulation of physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a period of time, giving a view of the motion of the atoms...
simulations - genetic algorithmGenetic algorithmA genetic algorithm is a search heuristic that mimics the process of natural evolution. This heuristic is routinely used to generate useful solutions to optimization and search problems...
s to "evolve" new low energy conformations
Ligand flexibility
Conformations of the ligand may be generated in the absence of the receptor and subsequently docked or conformations may be generated on-the-fly in the presence of the receptor binding cavity , or with full rotational flexibility of every dihedral angle using fragment based docking . Force fieldForce field
A force field, sometimes known as an energy shield, force shield, or deflector shield is a concept of a field tightly bounded and of significant magnitude so that objects affected by the particular force relating to the field are unable to pass through the central axis of the field and reach the...
energy evaluation are most often used to select energetically reasonable conformations, but knowledge-based methods have also been used.
Receptor flexibility
Computational capacity has increased dramatically over the last decade making possible the use of more sophisticated and computationally intensive methods in computer-assisted drug design. However, dealing with receptor flexibility in docking methodologies is still a thorny issue. The main reason behind this difficulty is the large number of degrees of freedom that have to be considered in this kind of calculations. Neglecting it, however, leads to poor docking results in terms of binding pose prediction.Multiple static structures experimentally determined for the same protein in different conformations are often used to emulate receptor flexibility. Alternatively rotamer libraries of amino acid side chains that surround the binding cavity may be searched to generate alternate but energetically reasonable protein conformations.
Scoring function
The scoring function takes a pose as input and returns a numberindicating the likelihood that the pose represents a favorable binding interaction.
Most scoring functions are physics-based molecular mechanics
Molecular mechanics
Molecular mechanics uses Newtonian mechanics to model molecular systems. The potential energy of all systems in molecular mechanics is calculated using force fields...
force field
Force field (chemistry)
In the context of molecular modeling, a force field refers to the form and parameters of mathematical functions used to describe the potential energy of a system of particles . Force field functions and parameter sets are derived from both experimental work and high-level quantum mechanical...
s that estimate the energy of the pose; a low (negative) energy indicates a stable system and thus a likely binding interaction. An alternative approach is to derive a statistical potential for interactions from a large database of protein-ligand complexes, such as the Protein Data Bank
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank is a repository for the 3-D structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids....
, and evaluate the fit of the pose according to this inferred potential.
There are a large number of structures from X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is a method of determining the arrangement of atoms within a crystal, in which a beam of X-rays strikes a crystal and causes the beam of light to spread into many specific directions. From the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a...
for complexes between proteins and high affinity ligands, but comparatively fewer for low affinity ligands as the later complexes tend to be less stable and therefore more difficult to crystallize. Scoring functions trained with this data can dock high affinity ligands correctly, but they will also give plausible docked conformations for ligands that do not bind. This gives a large number of false positive hits, i.e., ligands predicted to bind to the protein that actually don't when placed together in a test tube.
One way to reduce the number of false positives is to recalculate the energy of the top scoring poses using (potentially) more accurate but computationally more intensive techniques such as Generalized Born or Poisson-Boltzmann methods.
Applications
A binding interaction between a small moleculeSmall molecule
In the fields of pharmacology and biochemistry, a small molecule is a low molecular weight organic compound which is by definition not a polymer...
ligand and an enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
protein may result in activation or inhibition
Enzyme inhibitor
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to enzymes and decreases their activity. Since blocking an enzyme's activity can kill a pathogen or correct a metabolic imbalance, many drugs are enzyme inhibitors. They are also used as herbicides and pesticides...
of the enzyme. If the protein is a receptor, ligand binding may result in agonism
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that binds to a receptor of a cell and triggers a response by that cell. Agonists often mimic the action of a naturally occurring substance...
or antagonism
Antagonism (chemistry)
In chemistry, antagonism is a phenomenon wherein two or more agents in combination have an overall effect that is less than the sum of their individual effects....
. Docking is most commonly used in the field of drug design
Drug design
Drug design, also sometimes referred to as rational drug design or structure-based drug design, is the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of the biological target...
— most drugs are small organic
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
molecules, and docking may be applied to:
- hit identification – docking combined with a scoring functionScoring functions for dockingIn the fields of computational chemistry and molecular modelling, scoring functions are fast approximate mathematical methods used to predict the strength of the non-covalent interaction between two molecules after they have been docked...
can be used to quickly screen large databases of potential drugs in silicoIn silicoIn silico is an expression used to mean "performed on computer or via computer simulation." The phrase was coined in 1989 as an analogy to the Latin phrases in vivo and in vitro which are commonly used in biology and refer to experiments done in living organisms and outside of living organisms,...
to identify molecules that are likely to bind to protein target of interest (see virtual screeningVirtual screeningVirtual screening is a computational technique used in drug discovery research. By using computers, it deals with the quick search of large libraries of chemical structures in order to identify those structures which are most likely to bind to a drug target, typically a protein receptor or...
). - lead optimization – docking can be used to predict in where and in which relative orientation a ligand binds to a protein (also referred to as the binding mode or pose). This information may in turn be used to design more potent and selective analogs.
- BioremediationBioremediationBioremediation is the use of microorganism metabolism to remove pollutants. Technologies can be generally classified as in situ or ex situ. In situ bioremediation involves treating the contaminated material at the site, while ex situ involves the removal of the contaminated material to be treated...
– Protein ligand docking can also be used to predict pollutants that can be degraded by enzymes.
See also
- Drug designDrug designDrug design, also sometimes referred to as rational drug design or structure-based drug design, is the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of the biological target...
- Katchalski-Katzir algorithmKatchalski-Katzir algorithmThe Katchalski-Katzir algorithm is an algorithm for docking of rigid molecules, developed by Ephraim Katchalski/Katzir.It is a purely geometric algorithm, but some extensions of it also implement electrostatics....
- List of molecular graphics systems
- Macromolecular docking
- Molecular mechanicsMolecular mechanicsMolecular mechanics uses Newtonian mechanics to model molecular systems. The potential energy of all systems in molecular mechanics is calculated using force fields...
- Protein structureProtein structureProteins are an important class of biological macromolecules present in all organisms. Proteins are polymers of amino acids. Classified by their physical size, proteins are nanoparticles . Each protein polymer – also known as a polypeptide – consists of a sequence formed from 20 possible L-α-amino...
- Protein designProtein designProtein design is the design of new protein molecules, either from scratch or by making calculated variations on a known structure. The use of rational design techniques for proteins is a major aspect of protein engineering....
- Software for molecular mechanics modeling
- Molecular design softwareMolecular Design softwareMolecular design software is software for molecular modeling, that provides special support for developing molecular models de novo.In contrast to the usual molecular modeling programs such as the molecular dynamics and quantum chemistry programs, such software directly supports the aspects related...
- Docking@HomeDocking@HomeDocking@Home is a distributed computing project hosted by the University of Delaware and running on the Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing software platform. It models protein-ligand docking using the CHARMM program. The ultimate aim is the development of new pharmaceutical...
- IbercivisIbercivisIbercivis is a distributed computing platform which allows internet users to participate in scientific research by donating unused computer cycles to run scientific simulations and other tasks...
- ZINC databaseZINC databaseThe ZINC database is a curated collection of commercially available chemical compounds prepared especially for virtual screening. ZINC is used by investigators in pharmaceutical companies,...
- AutoDockAutoDockAutoDock is a molecular modeling simulation software. Since 2009, it has been open source and is free for non-commercial usage. It is especially effective for Protein-ligand docking.-About:...
- DOCKDOCKThe program UCSF DOCK was created in the 1980s by Irwin "Tack" Kuntz's Group, and was the first docking program. DOCK uses geometric algorithms to predict the binding modes of small molecules. Brian K. Shoichet, David A...
- Lead FinderLead FinderLead Finder software is a computational chemistry application for modeling protein-ligand interactions. Lead Finder can be used in molecular docking studies and for the quantitative evaluation of ligand binding and biological activity...
External links
- AutoDock and MGLTools for Debian
- Docking@GRID Project of Conformational Sampling and Docking on Grids : one aim is to deploy some intrinsic distributed docking algorithms on computational Grids, download Docking@GRID open-source Linux version
- Docking software
- Click2Drug.org - Directory of computational drug design tools.

