
Momentum transfer
Encyclopedia
In particle physics
, wave mechanics and optics
, momentum transfer is the amount of momentum
that one particle gives to another particle.
In the simplest example of scattering
of two colliding particles with initial momenta , resulting in final momenta
, resulting in final momenta  , the momentum transfer is given by
, the momentum transfer is given by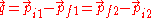
where the last identity expresses momentum conservation. Momentum transfer is an important quantity because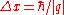 is a better measure for the typical distance resolution of the reaction than the momenta themselves.
is a better measure for the typical distance resolution of the reaction than the momenta themselves.
 and is a vectorial quantity. The difference of the momentum of the scattered wave to the incident wave is called momentum transfer. The wave number k is the absolute
and is a vectorial quantity. The difference of the momentum of the scattered wave to the incident wave is called momentum transfer. The wave number k is the absolute
of the wave vector
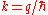 and is related to the wavelength
and is related to the wavelength
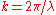 . Often, momentum transfer is given in wavenumber units in reciprocal length
. Often, momentum transfer is given in wavenumber units in reciprocal length
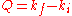
, X-ray and electron diffraction
for the investigation of condensed matter
. Bragg diffraction occurs on the atomic crystal lattice, conserves the wave energy and thus is called elastic scattering
, where the wave numbers final and incident particles,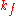 and
and 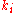 , respectively, are equal and just the direction changes by a reciprocal lattice
, respectively, are equal and just the direction changes by a reciprocal lattice
vector with the relation to the lattice spacing
with the relation to the lattice spacing  . As momentum is conserved, the transfer of momentum occurs to crystal momentum.
. As momentum is conserved, the transfer of momentum occurs to crystal momentum.
The presentation in -space is generic and does not depend on the type of radiation
-space is generic and does not depend on the type of radiation
and wavelength used but only on the sample system, which allows to compare results obtained from the many different methods. Some established communities such as powder diffraction
employ the diffraction angle as the independent variable, which worked fine in the early years when only a few characteristic wavelengths such as Cu-K
as the independent variable, which worked fine in the early years when only a few characteristic wavelengths such as Cu-K were available. The relationship to
were available. The relationship to  -space is
-space is

and basically states that larger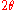 corresponds to larger
corresponds to larger  .
.
Particle physics
Particle physics is a branch of physics that studies the existence and interactions of particles that are the constituents of what is usually referred to as matter or radiation. In current understanding, particles are excitations of quantum fields and interact following their dynamics...
, wave mechanics and optics
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
, momentum transfer is the amount of momentum
Momentum
In classical mechanics, linear momentum or translational momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object...
that one particle gives to another particle.
In the simplest example of scattering
Scattering
Scattering is a general physical process where some forms of radiation, such as light, sound, or moving particles, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by one or more localized non-uniformities in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of...
of two colliding particles with initial momenta
 , resulting in final momenta
, resulting in final momenta  , the momentum transfer is given by
, the momentum transfer is given by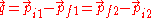
where the last identity expresses momentum conservation. Momentum transfer is an important quantity because
 is a better measure for the typical distance resolution of the reaction than the momenta themselves.
is a better measure for the typical distance resolution of the reaction than the momenta themselves.Wave mechanics and optics
A wave has a momentum and is a vectorial quantity. The difference of the momentum of the scattered wave to the incident wave is called momentum transfer. The wave number k is the absolute
and is a vectorial quantity. The difference of the momentum of the scattered wave to the incident wave is called momentum transfer. The wave number k is the absoluteAbsoluteness (mathematical logic)
In mathematical logic, a formula is said to be absolute if it has the same truth value in each of some class of structures . Theorems about absoluteness typically establish relationships between the absoluteness of formulas and their syntactic form.There are two weaker forms of partial absoluteness...
of the wave vector
Wave vector
In physics, a wave vector is a vector which helps describe a wave. Like any vector, it has a magnitude and direction, both of which are important: Its magnitude is either the wavenumber or angular wavenumber of the wave , and its direction is ordinarily the direction of wave propagation In...
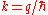 and is related to the wavelength
and is related to the wavelengthWavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
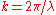 . Often, momentum transfer is given in wavenumber units in reciprocal length
. Often, momentum transfer is given in wavenumber units in reciprocal lengthReciprocal length
Reciprocal length or inverse length is a measurement used in several branches of science and mathematics. As the reciprocal of length, common units used for this measurement include the reciprocal metre or inverse metre , the reciprocal centimetre or inverse centimetre , and, in optics, the...
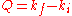
Diffraction
The momentum transfer plays an important role in the evaluation of neutronNeutron diffraction
Neutron diffraction or elastic neutron scattering is the application of neutron scattering to the determination of the atomic and/or magnetic structure of a material: A sample to be examined is placed in a beam of thermal or cold neutrons to obtain a diffraction pattern that provides information of...
, X-ray and electron diffraction
Electron diffraction
Electron diffraction refers to the wave nature of electrons. However, from a technical or practical point of view, it may be regarded as a technique used to study matter by firing electrons at a sample and observing the resulting interference pattern...
for the investigation of condensed matter
Condensed Matter
Condensed matter may refer to several things*Condensed matter physics, the study of the physical properties of condensed phases of matter*European Physical Journal B: Condensed Matter and Complex Systems, a scientific journal published by EDP sciences...
. Bragg diffraction occurs on the atomic crystal lattice, conserves the wave energy and thus is called elastic scattering
Elastic scattering
In scattering theory and in particular in particle physics, elastic scattering is one of the specific forms of scattering. In this process, the kinetic energy of the incident particles is conserved, only their direction of propagation is modified .-Electron elastic scattering:When an alpha particle...
, where the wave numbers final and incident particles,
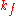 and
and 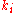 , respectively, are equal and just the direction changes by a reciprocal lattice
, respectively, are equal and just the direction changes by a reciprocal latticeReciprocal lattice
In physics, the reciprocal lattice of a lattice is the lattice in which the Fourier transform of the spatial function of the original lattice is represented. This space is also known as momentum space or less commonly k-space, due to the relationship between the Pontryagin duals momentum and...
vector
 with the relation to the lattice spacing
with the relation to the lattice spacing  . As momentum is conserved, the transfer of momentum occurs to crystal momentum.
. As momentum is conserved, the transfer of momentum occurs to crystal momentum.The presentation in
 -space is generic and does not depend on the type of radiation
-space is generic and does not depend on the type of radiationRadiation
In physics, radiation is a process in which energetic particles or energetic waves travel through a medium or space. There are two distinct types of radiation; ionizing and non-ionizing...
and wavelength used but only on the sample system, which allows to compare results obtained from the many different methods. Some established communities such as powder diffraction
Powder diffraction
Powder diffraction is a scientific technique using X-ray, neutron, or electron diffraction on powder or microcrystalline samples for structural characterization of materials.-Explanation:...
employ the diffraction angle
 as the independent variable, which worked fine in the early years when only a few characteristic wavelengths such as Cu-K
as the independent variable, which worked fine in the early years when only a few characteristic wavelengths such as Cu-K were available. The relationship to
were available. The relationship to  -space is
-space is
and basically states that larger
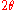 corresponds to larger
corresponds to larger  .
.See also
- Mandelstam variablesMandelstam variablesIn theoretical physics, the Mandelstam variables are numerical quantities that encode the energy, momentum, and angles of particles in a scattering process in a Lorentz-invariant fashion...
- impulse (physics)

