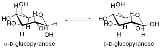
Mutarotation
Overview
Optical rotation
Optical rotation is the turning of the plane of linearly polarized light about the direction of motion as the light travels through certain materials. It occurs in solutions of chiral molecules such as sucrose , solids with rotated crystal planes such as quartz, and spin-polarized gases of atoms...
that occurs by epimerization (that is the change in the equilibrium between two epimer
Epimer
In chemistry, epimers are diastereomers that differ in configuration of only one stereogenic center. Diastereomers are a class of stereoisomers that are non-superposable, non-mirror images of one another....
s, when the corresponding stereocenter
Stereocenter
A stereocenter or stereogenic center is an atom, bearing groups such that an interchanging of any two groups leads to a stereoisomer.A chirality center is a stereocenter consisting of an atom holding a set of ligands in a spatial arrangement which is not superposable on its mirror image...
s interconvert). Cyclic sugar
Sugar
Sugar is a class of edible crystalline carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, lactose, and fructose, characterized by a sweet flavor.Sucrose in its refined form primarily comes from sugar cane and sugar beet...
s show mutarotation as α and β anomeric forms interconvert.
The optical rotation of the solution depends on the optical rotation of each anomer and their ratio in the solution.
Mutarotation was discovered by French chemist Dubrunfaut
Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut
Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut was a French chemist.Mutarotation was discovered by Dubrunfaut in 1846, when he noticed that the specific rotation of aqueous sugar solution changes with time. The organic fructose molecule was first discovered by Dubrunfaut in 1847.-Works:* Art de fabriquer le sucre de...
in 1846, when he noticed that the specific rotation of aqueous sugar solution changes with time.
The α and β anomers are diastereomer
Diastereomer
Diastereomers are stereoisomers that are not enantiomers.Diastereomerism occurs when two or more stereoisomers of a compound have different configurations at one or more of the equivalent stereocenters and are not mirror images of each other.When two diastereoisomers differ from each other at...
s of each other and usually have different specific rotation
Specific rotation
In stereochemistry, the specific rotation of a chemical compound [α] is defined as the observed angle of optical rotation α when plane-polarized light is passed through a sample with a path length of 1 decimeter and a sample concentration of 1 gram per 1 millilitre. It is the main property used to...
s.
Unanswered Questions

