
Nations and intelligence
Encyclopedia
The relationship between nations and intelligence has been researched from various aspects. Estimates of average national (in the sense of countries) cognitive abilities have been done in several literature reviews of worldwide IQ testing and of international student assessment studies. Especially the IQ data collections have been criticized on various grounds. Various factors have been proposed as explaining the differences with, controversially, some studies arguing for a role of gene
s or race while others see them as entirely environmentally caused. A large number of studies have used the data sets in order to research associations to other factors such as national differences in economic growth
, democracy
, crime
, and health
, with many arguing for differences in average national intelligence being an important explanation for other national differences.
by Richard Lynn
and Tatu Vanhanen
listed average national IQ for the nations of the world. A literature review listed IQ tests from 81 nations. In 104 of the world's nations there were no IQ studies and IQ was estimated based on IQ in surrounding nations. Scores were adjusted for several factors such as the Flynn effect
.
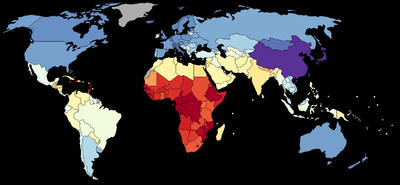
The 2006 book IQ and Global Inequality
by Lynn and Tatu revised the scores from the previous book. A new literature review listed IQ tests from 113 nations.
Rindermann (2007) states that the correlations between international student assessment studies and measures of national IQ are very high. Using the same statistical method used to measure the general intelligence factor
(g) he finds evidence for that the "student achievement assessments and intelligence tests primarily measure a common cognitive ability". The international student assessment studies have the advantages of standardized testing over a short time period. The IQ-data collections have the advantage of including older people and more developing nations. Lynn and Mikk (2009) similarly find a high predictive ability and correlation between the latest PISA 2006 and the national IQs from the two books.
. Using the same adjustment for all nations is likely sometimes incorrect because since the 1970s developing nations have seen higher increases than the developed world. The method of averaging neighboring countries for an estimation for the many nations that did not have measured IQs, while having a high correlation (0.92) with the measured results in the case of the 32 nations that changed from the estimated to the measured categories between the two books, is likely problematic since some research indicates that absence of IQ tests indicates conditions such as poverty or war that may affect IQs. "In addition, some errors in the data have been observed".
As noted above, the article "A systematic literature review of the average IQ of sub-Saharan Africans" (2009) argued that a number of studies showing higher IQ values for sub-Saharan Africa had been excluded by "IQ and Global Inequality". Regarding four studies comparing and finding agreement between Lynn's estimated national IQs and the student assessment tests, they disagree regarding sub-Saharan Africa but write "these four studies appear to validate national IQs in other parts of the world." Richard Lynn and Gerhard Meisenberg (2009) replied that "critical evaluation of the studies presented by WDM shows that many of these are based on unrepresentative elite samples" and that a further literature review, including taking into account results in mathematics, science, and reading, gave "an IQ of 68 as the best reading of the IQ in sub-Saharan Africa". Wicherts and colleagues (2010) in another reply made several examinations of unrepresentativeness and stated: "In light of all the available IQ data of over 37,000 African testtakers, only the use of unsystematic methods to exclude the vast majority of data could result in a mean IQ close to 70. On the basis of sound methods, the average IQ remains close to 80." Consequently some later studies using IQ data have checked their results against data from both sources.
The claim that the tests are culturally neutral and unbiased has been criticized.
.
Controversially, the two books argued for a large genetic explanation. Such a role of genetics may or may not be related to race which is itself a controversial topic. Lynn argued further for this in the books Race Differences in Intelligence: An Evolutionary Analysis (2006) and The Global Bell Curve: Race, IQ, and Inequality Worldwide
(2008).
Kanazawa (2008) also argues for a genetic role. He writes that cold climate and harsh winters (the study uses mean annual temperature) as well as environment novelty (the study uses three different measure of distance from the ancestral environment in sub-Saharan Africa: ordinary distance and differences in latitudes and longitudes) have been proposed as important factors behind the genetic evolution of human intelligence. The study found independent support for both theories and argues that they together explain half to two-thirds of variance in national IQ.
In contrast, Wicherts, Borsbooma, and Dolana (2010) criticized this and some other evolutionary studies for problems such as ignoring or assuming that the Flynn effect
is equal worldwide and assuming that there have been no migrations and changes in climate over the course of evolution. "In addition, we show that national IQs are strongly confounded with the current developmental status of countries. National IQs correlate with all the variables that have been suggested to have caused the Flynn Effect in the developed world."
Eppig, Fincher, and Thornhill (2010) states that distance from Africa, temperature, and most importantly by a large margin, prevalence of infectious disease
predict national IQs. Education, literary, GDP, and nutrition were not important as independent factors (however, the prevalence of infectious diseases is likely greatly affected by these factors). The authors argue that "From an energetics standpoint, a developing human will have difficulty building a brain and fighting off infectious diseases at the same time, as both are very metabolically costly tasks" and that "the Flynn effect may be caused in part by the decrease in the intensity of infectious diseases as nations develop."
(GDP)/capita, higher adult literacy
rate, higher gross tertiary education
enrollment ratio, higher life expectancy
at birth, higher level of democratization
2002 (Tatu Vanhanen's Index of Democratization), higher Human Development Index
, higher Gender-related Development Index
, higher economic growth
rate, lower Gini index of inequality in income or consumption, lower population below the $2 a day international poverty line, lower measures of undernourishment, lower maternal mortality ratio, lower infant mortality
rate, higher Corruption Perceptions Index
, higher Economic Freedom of the World ratings, higher Index of Economic Freedom
ratings, and more narrow population pyramid
(MU Index).
A number of studies using the IQ scores from the books have found that higher average national IQ is associated with various measures of higher economic growth and economic development. At least one study did not find this association.
Jones and Schneider (2010) write that a country’s average IQ score is a useful predictor of the wages that immigrants from that country earn in the U.S., whether or not one adjusts for immigrant education.
Higher national education levels and IQ have a strong positive impact on democracy
, rule of law
and political liberty independent from GDP according to a study by Rindermann (2008).
Voracek (2008) states that lower national IQs is associated with higher prevalence of suicide
and that this is independent of the "quality of human conditions".
A study by Rushton and Templer (2009) states that lower national IQ is associated with more violent crime
.
Lynn, Harvey, and Nyborg (2009) write that atheism
is associated with higher national IQ.
Higher national IQ, in a study by Gelade (2008), is associated with more patent
s per person.
In a study by Rindermann and Meisenberg (2009), lower national IQs associated with higher HIV
-infection rates, which is stronger effect than the association with low gross domestic product and low modernization.
Reeve (2009) writes that higher IQ, independent of national wealth, is associated with lower fertility rates, lower infant mortality rate, lower maternal mortality rate, fewer deaths due to HIV/AIDS, and longer life expectancy.
Both higher GDP and IQ independently reduce fertility
according to a study by Meisenberg (2009) that argues that "at present rates of fertility and mortality and in the absence of changes within countries, the average IQ of the young world population would decline by 1.34 points per decade and the average per capita income would decline by 0.79% per year."
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
s or race while others see them as entirely environmentally caused. A large number of studies have used the data sets in order to research associations to other factors such as national differences in economic growth
Economic growth
In economics, economic growth is defined as the increasing capacity of the economy to satisfy the wants of goods and services of the members of society. Economic growth is enabled by increases in productivity, which lowers the inputs for a given amount of output. Lowered costs increase demand...
, democracy
Democracy
Democracy is generally defined as a form of government in which all adult citizens have an equal say in the decisions that affect their lives. Ideally, this includes equal participation in the proposal, development and passage of legislation into law...
, crime
Crime
Crime is the breach of rules or laws for which some governing authority can ultimately prescribe a conviction...
, and health
Health
Health is the level of functional or metabolic efficiency of a living being. In humans, it is the general condition of a person's mind, body and spirit, usually meaning to be free from illness, injury or pain...
, with many arguing for differences in average national intelligence being an important explanation for other national differences.
"Average IQ values in various European countries"
The 1981 article "Average IQ values in various European countries" by V. Buj is the only international IQ study that over a short time period has compared IQs using the same IQ test. It was probably done in the 1970s in the capital cities or in the biggest town in 21 European countries and Ghana. Rindermann (2007) states that it is of dubious quality with scant information regarding how it was done. The correlations with the other measures of national intelligence, except the PISA student assessment study, are good."IQ and the Wealth of Nations"
The 2002 book IQ and the Wealth of NationsIQ and the Wealth of Nations
IQ and the Wealth of Nations is a controversial 2002 book by Dr. Richard Lynn, Professor Emeritus of Psychology at the University of Ulster, Northern Ireland, and Dr. Tatu Vanhanen, Professor Emeritus of Political Science at the University of Tampere, Tampere, Finland...
by Richard Lynn
Richard Lynn
Richard Lynn is a British Professor Emeritus of Psychology at the University of Ulster who is known for his views on racial and ethnic differences. Lynn argues that there are hereditary differences in intelligence based on race and sex....
and Tatu Vanhanen
Tatu Vanhanen
Tatu Vanhanen is a Professor Emeritus of Political Science at the University of Tampere in Tampere, Finland...
listed average national IQ for the nations of the world. A literature review listed IQ tests from 81 nations. In 104 of the world's nations there were no IQ studies and IQ was estimated based on IQ in surrounding nations. Scores were adjusted for several factors such as the Flynn effect
Flynn effect
The Flynn effect is the name given to a substantial and long-sustained increase in intelligence test scores measured in many parts of the world. When intelligence quotient tests are initially standardized using a sample of test-takers, by convention the average of the test results is set to 100...
.
"IQ and Global Inequality"

The 2006 book IQ and Global Inequality
IQ and Global Inequality
IQ and Global Inequality is a 2006 book by psychologist Richard Lynn and political scientist Tatu Vanhanen. IQ and Global Inequality is follow-up to their 2002 book IQ and the Wealth of Nations, an expansion of the argument that international differences in current economic development are due in...
by Lynn and Tatu revised the scores from the previous book. A new literature review listed IQ tests from 113 nations.
"A systematic literature review of the average IQ of sub-Saharan Africans"
The 2009 article "A systematic literature review of the average IQ of sub-Saharan Africans" by Jelte M. Wicherts, Conor V. Dolana, and Han L.J. van der Maas in a critique of "IQ and Global Inequality" reviewed the literature on IQ tests in sub-Saharan Africa. Including a number of studies excluded in "IQ and Global Inequality" it found a higher average IQ of 82 for sub-Saharan Africa."National IQs updated for 41 Nations"
The 2010 article "National IQs updated for 41 Nations" by Lynn revised "IQ and Global Inequality" and presented new calculated national IQs for 25 countries which had previously only been estimated from neighboring nations IQs and revised national IQs for 16 countries.International student assessment studies
There are a number of international student assessment studies:- International Association for the Evaluation of Educational AchievementInternational Association for the Evaluation of Educational AchievementThe International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement is an association of national research institutions and government research agencies related to education. The IEA is an independent organization. It was founded in 1958 and is headquartered in Amsterdam...
-Reading-Study (1991) - Trends in International Mathematics and Science StudyTrends in international mathematics and science studyThe Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study is an international assessment of the mathematics and science knowledge of fourth- and eighth-grade students around the world...
(TIMSS) (1994–1995, 1999, 2003) - Programme for International Student AssessmentProgramme for International Student AssessmentThe Programme for International Student Assessment is a worldwide evaluation in OECD member countries of 15-year-old school pupils' scholastic performance, performed first in 2000 and repeated every three years...
(PISA) (2000–2002, 2003, and 2006) - Progress in International Reading Literacy Study (PIRL) (2001)
Rindermann (2007) states that the correlations between international student assessment studies and measures of national IQ are very high. Using the same statistical method used to measure the general intelligence factor
General intelligence factor
The g factor, where g stands for general intelligence, is a statistic used in psychometrics to model the mental ability underlying results of various tests of cognitive ability...
(g) he finds evidence for that the "student achievement assessments and intelligence tests primarily measure a common cognitive ability". The international student assessment studies have the advantages of standardized testing over a short time period. The IQ-data collections have the advantage of including older people and more developing nations. Lynn and Mikk (2009) similarly find a high predictive ability and correlation between the latest PISA 2006 and the national IQs from the two books.
The Flynn effect
The Flynn effect is the continual increases in measured IQ that have been observed worldwide. It may recently have ended in some developed nations.Limitations and criticisms of the IQ-data collections
Rindermann (2007) writes that the mixture of many different tests and the not always clear representativeness of the samples seem to be the most serious problems. Furthermore, the measurement years vary which is problematic due to the Flynn effectFlynn effect
The Flynn effect is the name given to a substantial and long-sustained increase in intelligence test scores measured in many parts of the world. When intelligence quotient tests are initially standardized using a sample of test-takers, by convention the average of the test results is set to 100...
. Using the same adjustment for all nations is likely sometimes incorrect because since the 1970s developing nations have seen higher increases than the developed world. The method of averaging neighboring countries for an estimation for the many nations that did not have measured IQs, while having a high correlation (0.92) with the measured results in the case of the 32 nations that changed from the estimated to the measured categories between the two books, is likely problematic since some research indicates that absence of IQ tests indicates conditions such as poverty or war that may affect IQs. "In addition, some errors in the data have been observed".
As noted above, the article "A systematic literature review of the average IQ of sub-Saharan Africans" (2009) argued that a number of studies showing higher IQ values for sub-Saharan Africa had been excluded by "IQ and Global Inequality". Regarding four studies comparing and finding agreement between Lynn's estimated national IQs and the student assessment tests, they disagree regarding sub-Saharan Africa but write "these four studies appear to validate national IQs in other parts of the world." Richard Lynn and Gerhard Meisenberg (2009) replied that "critical evaluation of the studies presented by WDM shows that many of these are based on unrepresentative elite samples" and that a further literature review, including taking into account results in mathematics, science, and reading, gave "an IQ of 68 as the best reading of the IQ in sub-Saharan Africa". Wicherts and colleagues (2010) in another reply made several examinations of unrepresentativeness and stated: "In light of all the available IQ data of over 37,000 African testtakers, only the use of unsystematic methods to exclude the vast majority of data could result in a mean IQ close to 70. On the basis of sound methods, the average IQ remains close to 80." Consequently some later studies using IQ data have checked their results against data from both sources.
The claim that the tests are culturally neutral and unbiased has been criticized.
Limitations and criticisms of the international student assessment studies
Rindermann (2007) writes that data from many developing nations are missing which is the case for more nations than for IQ data. The Flynn effect has to be adjusted for. In some nations school attendance is low. Even for the same test national organizers sometimes differ in implementation and exclusion rates differ.Causes of the national differences
A large number of factors are known to affect measured IQ temporarily or permanently. The factors responsible for the Flynn effect may be partly or completely behind national IQ differences. See Flynn effect#Proposed explanations. Examples being that the developing world is afflicted to a greater degree than the developed world by poor nutrition (deficiency in energy, protein, and micronutrients) and infectious diseases. See also Health and intelligenceHealth and intelligence
Health can affect intelligence in various ways. This is one of the most important factors in understanding the origins of human group differences in IQ test scores and other measures of cognitive ability...
.
Controversially, the two books argued for a large genetic explanation. Such a role of genetics may or may not be related to race which is itself a controversial topic. Lynn argued further for this in the books Race Differences in Intelligence: An Evolutionary Analysis (2006) and The Global Bell Curve: Race, IQ, and Inequality Worldwide
The Global Bell Curve
The Global Bell Curve: Race, IQ, and Inequality Worldwide is a book by Professor Richard Lynn, published by Washington Summit Publishers, June 2008...
(2008).
Kanazawa (2008) also argues for a genetic role. He writes that cold climate and harsh winters (the study uses mean annual temperature) as well as environment novelty (the study uses three different measure of distance from the ancestral environment in sub-Saharan Africa: ordinary distance and differences in latitudes and longitudes) have been proposed as important factors behind the genetic evolution of human intelligence. The study found independent support for both theories and argues that they together explain half to two-thirds of variance in national IQ.
In contrast, Wicherts, Borsbooma, and Dolana (2010) criticized this and some other evolutionary studies for problems such as ignoring or assuming that the Flynn effect
Flynn effect
The Flynn effect is the name given to a substantial and long-sustained increase in intelligence test scores measured in many parts of the world. When intelligence quotient tests are initially standardized using a sample of test-takers, by convention the average of the test results is set to 100...
is equal worldwide and assuming that there have been no migrations and changes in climate over the course of evolution. "In addition, we show that national IQs are strongly confounded with the current developmental status of countries. National IQs correlate with all the variables that have been suggested to have caused the Flynn Effect in the developed world."
Eppig, Fincher, and Thornhill (2010) states that distance from Africa, temperature, and most importantly by a large margin, prevalence of infectious disease
Infectious disease
Infectious diseases, also known as communicable diseases, contagious diseases or transmissible diseases comprise clinically evident illness resulting from the infection, presence and growth of pathogenic biological agents in an individual host organism...
predict national IQs. Education, literary, GDP, and nutrition were not important as independent factors (however, the prevalence of infectious diseases is likely greatly affected by these factors). The authors argue that "From an energetics standpoint, a developing human will have difficulty building a brain and fighting off infectious diseases at the same time, as both are very metabolically costly tasks" and that "the Flynn effect may be caused in part by the decrease in the intensity of infectious diseases as nations develop."
Associated factors
"IQ and Global Inequality" found significant correlations between higher national IQ and a number of factors: higher Gross domestic productGross domestic product
Gross domestic product refers to the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period. GDP per capita is often considered an indicator of a country's standard of living....
(GDP)/capita, higher adult literacy
Literacy
Literacy has traditionally been described as the ability to read for knowledge, write coherently and think critically about printed material.Literacy represents the lifelong, intellectual process of gaining meaning from print...
rate, higher gross tertiary education
Tertiary education
Tertiary education, also referred to as third stage, third level, and post-secondary education, is the educational level following the completion of a school providing a secondary education, such as a high school, secondary school, university-preparatory school...
enrollment ratio, higher life expectancy
Life expectancy
Life expectancy is the expected number of years of life remaining at a given age. It is denoted by ex, which means the average number of subsequent years of life for someone now aged x, according to a particular mortality experience...
at birth, higher level of democratization
Democratization
Democratization is the transition to a more democratic political regime. It may be the transition from an authoritarian regime to a full democracy, a transition from an authoritarian political system to a semi-democracy or transition from a semi-authoritarian political system to a democratic...
2002 (Tatu Vanhanen's Index of Democratization), higher Human Development Index
Human Development Index
The Human Development Index is a composite statistic used to rank countries by level of "human development" and separate "very high human development", "high human development", "medium human development", and "low human development" countries...
, higher Gender-related Development Index
Gender-related Development Index
The Gender-related Development Index and the Gender Empowerment Measure were introduced in 1995 in the Human Development Report written by the United Nations Development Program. The aim of these measurements was to add a gender-sensitive dimension to the HDI. The first measurement that they...
, higher economic growth
Economic growth
In economics, economic growth is defined as the increasing capacity of the economy to satisfy the wants of goods and services of the members of society. Economic growth is enabled by increases in productivity, which lowers the inputs for a given amount of output. Lowered costs increase demand...
rate, lower Gini index of inequality in income or consumption, lower population below the $2 a day international poverty line, lower measures of undernourishment, lower maternal mortality ratio, lower infant mortality
Infant mortality
Infant mortality is defined as the number of infant deaths per 1000 live births. Traditionally, the most common cause worldwide was dehydration from diarrhea. However, the spreading information about Oral Re-hydration Solution to mothers around the world has decreased the rate of children dying...
rate, higher Corruption Perceptions Index
Corruption Perceptions Index
Since 1995, Transparency International publishes the Corruption Perceptions Index annually ranking countries "by their perceived levels of corruption, as determined by expert assessments and opinion surveys." The CPI generally defines corruption as "the misuse of public power for private...
, higher Economic Freedom of the World ratings, higher Index of Economic Freedom
Index of Economic Freedom
The Index of Economic Freedom is a series of 10 economic measurements created by The Heritage Foundation and The Wall Street Journal. Its stated objective is to measure the degree of economic freedom in the world's nations....
ratings, and more narrow population pyramid
Population pyramid
A population pyramid, also called an age structure diagram, is a graphical illustration that shows the distribution of various age groups in a population , which forms the shape of a pyramid when the population is growing...
(MU Index).
A number of studies using the IQ scores from the books have found that higher average national IQ is associated with various measures of higher economic growth and economic development. At least one study did not find this association.
Jones and Schneider (2010) write that a country’s average IQ score is a useful predictor of the wages that immigrants from that country earn in the U.S., whether or not one adjusts for immigrant education.
Higher national education levels and IQ have a strong positive impact on democracy
Democracy
Democracy is generally defined as a form of government in which all adult citizens have an equal say in the decisions that affect their lives. Ideally, this includes equal participation in the proposal, development and passage of legislation into law...
, rule of law
Rule of law
The rule of law, sometimes called supremacy of law, is a legal maxim that says that governmental decisions should be made by applying known principles or laws with minimal discretion in their application...
and political liberty independent from GDP according to a study by Rindermann (2008).
Voracek (2008) states that lower national IQs is associated with higher prevalence of suicide
Suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Suicide is often committed out of despair or attributed to some underlying mental disorder, such as depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, alcoholism, or drug abuse...
and that this is independent of the "quality of human conditions".
A study by Rushton and Templer (2009) states that lower national IQ is associated with more violent crime
Violent crime
A violent crime or crime of violence is a crime in which the offender uses or threatens to use violent force upon the victim. This entails both crimes in which the violent act is the objective, such as murder, as well as crimes in which violence is the means to an end, such as robbery. Violent...
.
Lynn, Harvey, and Nyborg (2009) write that atheism
Atheism
Atheism is, in a broad sense, the rejection of belief in the existence of deities. In a narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there are no deities...
is associated with higher national IQ.
Higher national IQ, in a study by Gelade (2008), is associated with more patent
Patent
A patent is a form of intellectual property. It consists of a set of exclusive rights granted by a sovereign state to an inventor or their assignee for a limited period of time in exchange for the public disclosure of an invention....
s per person.
In a study by Rindermann and Meisenberg (2009), lower national IQs associated with higher HIV
HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus is a lentivirus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome , a condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive...
-infection rates, which is stronger effect than the association with low gross domestic product and low modernization.
Reeve (2009) writes that higher IQ, independent of national wealth, is associated with lower fertility rates, lower infant mortality rate, lower maternal mortality rate, fewer deaths due to HIV/AIDS, and longer life expectancy.
Both higher GDP and IQ independently reduce fertility
Fertility
Fertility is the natural capability of producing offsprings. As a measure, "fertility rate" is the number of children born per couple, person or population. Fertility differs from fecundity, which is defined as the potential for reproduction...
according to a study by Meisenberg (2009) that argues that "at present rates of fertility and mortality and in the absence of changes within countries, the average IQ of the young world population would decline by 1.34 points per decade and the average per capita income would decline by 0.79% per year."

