
Nautical almanac
Encyclopedia
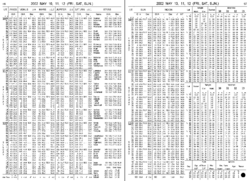
Celestial navigation
Celestial navigation, also known as astronavigation, is a position fixing technique that has evolved over several thousand years to help sailors cross oceans without having to rely on estimated calculations, or dead reckoning, to know their position...
to determine the position of their ship while at sea. The Almanac specifies for each whole hour of the year the position on the Earth's surface (in declination
Declination
In astronomy, declination is one of the two coordinates of the equatorial coordinate system, the other being either right ascension or hour angle. Declination in astronomy is comparable to geographic latitude, but projected onto the celestial sphere. Declination is measured in degrees north and...
and Greenwich hour angle
Hour angle
In astronomy and celestial navigation, the hour angle is one of the coordinates used in the equatorial coordinate system to give the position of a point on the celestial sphere....
) at which the sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
, moon
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
, planet
Planet
A planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
s and first point of Aries is directly overhead. The positions of 57 selected star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s are specified relative to the first point of Aries.
In Great Britain
Great Britain
Great Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles...
, The Nautical Almanac
The Nautical Almanac
The Nautical Almanac has been the familiar name for a series of official British almanacs published under various titles since the first issue of The Nautical Almanac and Astronomical Ephemeris, for 1767: this was the first nautical almanac ever to contain data dedicated to the convenient...
has been published annually by HM Nautical Almanac Office
HM Nautical Almanac Office
Her Majesty's Nautical Almanac Office , now part of the United Kingdom Hydrographic Office, was established in 1832 on the site of the Royal Greenwich Observatory , where the Nautical Almanac had been published since 1767...
, ever since the first edition was published in 1767.
In the United States of America, a nautical almanac has been published annually by the US Naval Observatory since 1852. Since 1958, the USNO and HMNAO have jointly published a unified nautical almanac, for use by the navies of both countries. Almanac data is now available online from the US Naval Observatory.
Also commercial almanacs were produced that combined other information. A good example would be Brown's — which commenced in 1877 - and is still produced annually, its early twentieth century subtitle being "Harbour and Dock Guide and Advertiser and Daily Tide Tables". This combination of trade advertising, and information "by permission... of the Hydrographic Department of the Admiralty
United Kingdom Hydrographic Office
The United Kingdom Hydrographic Office is an organisation within the UK government responsible for providing navigational and other hydrographic information for national, civil and defence requirements...
" provided a useful compendium of information. More recent editions have kept up with the changes in technology - the 1924 edition for instance had extensive advertisements for coaling stations.
The "Air Almanac" of the United States and Great Britain tabulates celestial coordinates for 10 minute intervals for the use in aerial navigation. The Sokkia
Sokkia
Sokkia Co., Ltd was founded in 1920 as Sokkisha in Japan. It makes measurement instruments for the surveying, construction and industrial measurement industries....
Corporation's annual "Celestial Observation Handbook and Ephemeris" tabulated daily celestial coordinates (to a tenth of an arcsecond) for the Sun and nine stars; it was last publishd for 2008.
To find the position of a ship or aircraft by celestial navigation
Celestial navigation
Celestial navigation, also known as astronavigation, is a position fixing technique that has evolved over several thousand years to help sailors cross oceans without having to rely on estimated calculations, or dead reckoning, to know their position...
, the navigator measures with a sextant
Sextant
A sextant is an instrument used to measure the angle between any two visible objects. Its primary use is to determine the angle between a celestial object and the horizon which is known as the altitude. Making this measurement is known as sighting the object, shooting the object, or taking a sight...
the apparent height of a celestial body above the horizon, and notes the time from a marine chronometer
Marine chronometer
A marine chronometer is a clock that is precise and accurate enough to be used as a portable time standard; it can therefore be used to determine longitude by means of celestial navigation...
. That height is compared with the height predicted for a trial position; the arcminutes of height difference is how many nautical miles the the position line is from the trial position.
See also
- AlmanacAlmanacAn almanac is an annual publication that includes information such as weather forecasts, farmers' planting dates, and tide tables, containing tabular information in a particular field or fields often arranged according to the calendar etc...
- Celestial navigationCelestial navigationCelestial navigation, also known as astronavigation, is a position fixing technique that has evolved over several thousand years to help sailors cross oceans without having to rely on estimated calculations, or dead reckoning, to know their position...
- NavigationNavigationNavigation is the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another. It is also the term of art used for the specialized knowledge used by navigators to perform navigation tasks...
- American Practical Navigator

