Netropsin
Encyclopedia
Netropsin is an oligopeptide
with antibiotic
and antiviral
activity.
Netropsin was discovered by Finlay et al. and first isolated from the actinobacterium
Streptomyces netropsis. It belongs to the class of pyrrole-amidine antibiotics. Synonyms for the compound are Congocidin and Sinanomycin.
.
In contrast, Netropsin does not bind single stranded DNA or double stranded RNA.
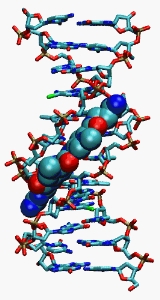
Crystallographic structures of DNA-bound Netropsin have been obtained and elucidate details of how the drug binds in the minor groove
.
In the bound structure, the drug makes hydrogen bonding interactions with four subsequent base pairs of the DNA duplex,
locally displacing the water molecules of the spine of hydration.
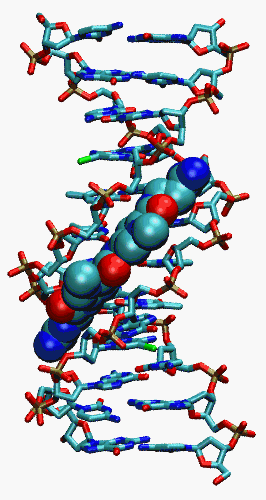 Using gel mobility and analytical ultracentrifugation,
Using gel mobility and analytical ultracentrifugation,
it was shown that Netropsin binding to DNA increases the twist per base by similar to 9˚ per molecule bound
.
Therefore, it removes supercoils when interacting with positively supercoiled DNA and introduces
(additional) negative supercoils when binding to relaxed or negatively supercoiled DNA.
Netropsin's effect on supercoiled DNA was observed in detail at the single-molcule level using a magnetic tweezers .
.
Oligopeptide
An oligopeptide consists of between 2 and 20 amino acids and includes dipeptides, tripeptides, tetrapeptides, pentapeptides, etc.Examples of oligopeptides include:...
with antibiotic
Antibiotic
An antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
and antiviral
Antiviral drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used specifically for treating viral infections. Like antibiotics for bacteria, specific antivirals are used for specific viruses...
activity.
Netropsin was discovered by Finlay et al. and first isolated from the actinobacterium
Actinobacteria
Actinobacteria are a group of Gram-positive bacteria with high guanine and cytosine content. They can be terrestrial or aquatic. Actinobacteria is one of the dominant phyla of the bacteria....
Streptomyces netropsis. It belongs to the class of pyrrole-amidine antibiotics. Synonyms for the compound are Congocidin and Sinanomycin.
DNA binding properties
Netropsin binds to the minor groove of AT-rich sequences of double stranded DNADNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
.
In contrast, Netropsin does not bind single stranded DNA or double stranded RNA.
Crystallographic structures of DNA-bound Netropsin have been obtained and elucidate details of how the drug binds in the minor groove
.
In the bound structure, the drug makes hydrogen bonding interactions with four subsequent base pairs of the DNA duplex,
locally displacing the water molecules of the spine of hydration.

it was shown that Netropsin binding to DNA increases the twist per base by similar to 9˚ per molecule bound
.
Therefore, it removes supercoils when interacting with positively supercoiled DNA and introduces
(additional) negative supercoils when binding to relaxed or negatively supercoiled DNA.
Netropsin's effect on supercoiled DNA was observed in detail at the single-molcule level using a magnetic tweezers .
Antibiotic properties
It has been shown that Netropsin is active both against Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria.
See also
- LexitropsinLexitropsinLexitropsins is a family of semi-synthetic DNA-binding ligands.They are analogs of natural antibiotics Netropsin and Distamycin. Antibiotics of this group are capable to bind with a narrow groove of DNA with different sequence-selectivity. Lexitropsins form a complexes with DNA with stoichiometry...
- Hoechst 33258
- DNA-binding proteinDNA-binding proteinDNA-binding proteins are proteins that are composed of DNA-binding domains and thus have a specific or general affinity for either single or double stranded DNA. Sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins generally interact with the major groove of B-DNA, because it exposes more functional groups that...
- Single-strand binding proteinSingle-strand binding proteinSingle-strand binding protein, also known as SSB or SSBP, binds to single stranded regions of DNA to prevent premature annealing. The strands have a natural tendency to revert to the duplex form, but SSB binds to the single strands, keeping them separate and allowing the DNA replication machinery...
- Nucleic acid simulations

