New Zealand Outlying Islands
Encyclopedia
The New Zealand outlying islands comprise nine island groups, located in the subtropics
and subantarctic
, which are part of New Zealand
but lie outside of the New Zealand continental shelf
. Although considered as integral parts of New Zealand, seven of the nine island groups are not part of any region
or district
, but are instead designated as Area Outside Territorial Authority. The two exceptions are the Chatham Islands
, which form a special territorial authority
(island council) themselves, and the Solander Islands
, which are part of the Southland Region
and Southland District
.
The term is also used sometimes to further encompass the Balleny Islands
, a group of subantarctic islands technically considered part of Ross Dependency
and covered by the Antarctic Treaty.
The five island groups of the New Zealand Sub-Antarctic Islands
, including their territorial seas, are a World Heritage Site
.
, Stewart Island, Niue, Cook Islands and Tokelau. The remaining outlying islands are called Minor Islands.
There is a manned meteorological station on Raoul Island
of the Kermadec Islands
. The meteorological station on Campbell Island
has been unmanned and automated since 1995. There was a meteorological station on the Auckland Islands
from 1942 to 1945. The Three Kings Islands
and the Auckland Islands were formerly inhabited. There have been failed settlement attempts on Raoul Island, the Antipodes Islands
and the Auckland Islands. The Solander Islands
have never been inhabited except by shipwrecked sailors or marooned stowaways (for the longest period, from 1808 to 1813 by five European stowaways).
Subtropics
The subtropics are the geographical and climatical zone of the Earth immediately north and south of the tropical zone, which is bounded by the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn, at latitudes 23.5°N and 23.5°S...
and subantarctic
Subantarctic
The Subantarctic is a region in the southern hemisphere, located immediately north of the Antarctic region. This translates roughly to a latitude of between 46° – 60° south of the Equator. The subantarctic region includes many islands in the southern parts of the Indian Ocean, Atlantic Ocean and...
, which are part of New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
but lie outside of the New Zealand continental shelf
Continental shelf
The continental shelf is the extended perimeter of each continent and associated coastal plain. Much of the shelf was exposed during glacial periods, but is now submerged under relatively shallow seas and gulfs, and was similarly submerged during other interglacial periods. The continental margin,...
. Although considered as integral parts of New Zealand, seven of the nine island groups are not part of any region
Regions of New Zealand
The region is the top tier of local government in New Zealand. There are 16 regions of New Zealand. Eleven are governed by an elected regional council, while five are governed by territorial authorities which also perform the functions of a regional council and thus are known as unitary authorities...
or district
Territorial authorities of New Zealand
Territorial authorities are the second tier of local government in New Zealand, below regional councils. There are 67 territorial authorities: 13 city councils, 53 district councils, and the Chatham Islands Council...
, but are instead designated as Area Outside Territorial Authority. The two exceptions are the Chatham Islands
Chatham Islands
The Chatham Islands are an archipelago and New Zealand territory in the Pacific Ocean consisting of about ten islands within a radius, the largest of which are Chatham Island and Pitt Island. Their name in the indigenous language, Moriori, means Misty Sun...
, which form a special territorial authority
Territorial authorities of New Zealand
Territorial authorities are the second tier of local government in New Zealand, below regional councils. There are 67 territorial authorities: 13 city councils, 53 district councils, and the Chatham Islands Council...
(island council) themselves, and the Solander Islands
Solander Islands
The Solander Islands are a small chain of uninhabited volcanic islets lying at , close to the western end of the Foveaux Strait in southern New Zealand...
, which are part of the Southland Region
Southland Region
Southland is New Zealand's southernmost region and is also a district within that region. It consists mainly of the southwestern portion of the South Island and Stewart Island / Rakiura...
and Southland District
Southland District
Southland District is a territorial authority in the South Island of New Zealand. Southland District covers the majority of the land area of Southland Region, although the region also covers Gore District, Invercargill City and adjacent territorial waters...
.
The term is also used sometimes to further encompass the Balleny Islands
Balleny Islands
The Balleny Islands are a series of uninhabited islands in the Southern Ocean extending from 66°15' to 67°35'S and 162°30' to 165°00'E. The group extends for about in a northwest-southeast direction. The islands are heavily glaciated and are of volcanic origin. Glaciers project from their slopes...
, a group of subantarctic islands technically considered part of Ross Dependency
Ross Dependency
The Ross Dependency is a region of Antarctica defined by a sector originating at the South Pole, passing along longitudes 160° east to 150° west, and terminating at latitude 60° south...
and covered by the Antarctic Treaty.
The five island groups of the New Zealand Sub-Antarctic Islands
New Zealand sub-antarctic islands
The five southernmost groups of the New Zealand Outlying Islands form the New Zealand Sub-Antarctic islands. These islands are collectively designated as an UNESCO World Heritage Site....
, including their territorial seas, are a World Heritage Site
World Heritage Site
A UNESCO World Heritage Site is a place that is listed by the UNESCO as of special cultural or physical significance...
.
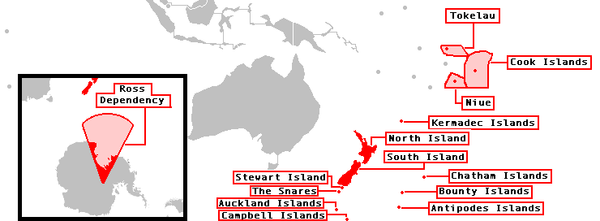
Island groups
The island groups from north to south:| |
|||
 |
|||
| Island Group (alternate name) | Area(km²) | highest peak (m) | location ofmain island |
|---|---|---|---|
| north of North Island | |||
| Kermadec Islands Kermadec Islands The Kermadec Islands are a subtropical island arc in the South Pacific Ocean northeast of New Zealand's North Island, and a similar distance southwest of Tonga... |
33.08 | Moumoukai peak (516) | 29°16′S 177°55′W |
| Three Kings Islands Three Kings Islands The Three Kings Islands or Manawa Islands are a group of 13 islands about northwest of Cape Reinga, the northernmost point of the North Island of New Zealand, where the South Pacific Ocean and Tasman Sea converge. They measure about 4.86 km² in area... (Ngamotukaraka, Manawa Tawhi) |
4.86 | (Great Island) (294) | 34°09′S 172°08′E |
| east/south of South Island | |||
| Chatham Islands Chatham Islands The Chatham Islands are an archipelago and New Zealand territory in the Pacific Ocean consisting of about ten islands within a radius, the largest of which are Chatham Island and Pitt Island. Their name in the indigenous language, Moriori, means Misty Sun... (Wharekauri, Rekohu) |
966.00 | Maungatere Hill (294) | 43°54′S 176°32′W |
| Solander Islands Solander Islands The Solander Islands are a small chain of uninhabited volcanic islets lying at , close to the western end of the Foveaux Strait in southern New Zealand... (Hautere) |
0.70 | (Solander Island) (330) | 46°34′S 166°53′E |
| New Zealand sub-antarctic islands New Zealand sub-antarctic islands The five southernmost groups of the New Zealand Outlying Islands form the New Zealand Sub-Antarctic islands. These islands are collectively designated as an UNESCO World Heritage Site.... |
|||
| Bounty Islands Bounty Islands The Bounty Islands at are a small group of 13 granite islets and numerous rocks, with a combined area of , in the south Pacific Ocean that are territorially part of New Zealand. They are located between 47°44'35" and 47°46'10" S, and 179°01' and 179°04'20" E, southeast of the South Island of New... |
1.35 | (Funnel Island) (88) | 47°46′S 179°02′E |
| The Snares The Snares Snares Islands/Tini Heke is a small island group situated approximately 200 kilometres south of New Zealand's South Island and to the south-south-west of Stewart Island/Rakiura. The Snares consist of the main island North East Island and the smaller Broughton Island as well as the somewhat... (Tini Heke) |
3.41 | (North East Island) (152) | 48°01′S 166°32′E |
| Antipodes Islands Antipodes Islands The Antipodes Islands are inhospitable volcanic islands to the south of—and territorially part of—New Zealand... |
20.97 | Mount Galloway Mount Galloway Mount Galloway is the highest point on Antipodes Island, one of New Zealand's outlying islands. It rises to a height on 402 metres . It is said to be the most recently active volcano, but there is no exact eruption date known [1]. Mount Galloway together with Mount Waterhouse are probably formed... (366) |
49°41′S 178°48′E |
| Auckland Islands Auckland Islands The Auckland Islands are an archipelago of the New Zealand Sub-Antarctic Islands and include Auckland Island, Adams Island, Enderby Island, Disappointment Island, Ewing Island, Rose Island, Dundas Island and Green Island, with a combined area of... (Motu Maha) |
625.60 | Mount Dick (705) | 50°42′S 166°05′E |
| Campbell Islands (Motu Ihupuku) | 113.31 | Mount Honey (569) | 52°32′S 169°09′E |
| Outlying Islands | 1800 | Mount Dick (705) | |
Population
The islands are all uninhabited except Chatham IslandsChatham Islands
The Chatham Islands are an archipelago and New Zealand territory in the Pacific Ocean consisting of about ten islands within a radius, the largest of which are Chatham Island and Pitt Island. Their name in the indigenous language, Moriori, means Misty Sun...
, Stewart Island, Niue, Cook Islands and Tokelau. The remaining outlying islands are called Minor Islands.
There is a manned meteorological station on Raoul Island
Raoul Island
Anvil-shaped Raoul Island , the largest and northernmost of the main Kermadec Islands, , has been the source of vigorous volcanic activity during the past several thousand years that was dominated by dacitic explosive eruptions.The area of the island, including fringing islets and rocks...
of the Kermadec Islands
Kermadec Islands
The Kermadec Islands are a subtropical island arc in the South Pacific Ocean northeast of New Zealand's North Island, and a similar distance southwest of Tonga...
. The meteorological station on Campbell Island
Campbell Island, New Zealand
Campbell Island is a remote, subantarctic island of New Zealand and the main island of the Campbell Island group. It covers of the group's , and is surrounded by numerous stacks, rocks and islets like Dent Island, Folly Island , Isle de Jeanette Marie, and Jacquemart Island, the latter being the...
has been unmanned and automated since 1995. There was a meteorological station on the Auckland Islands
Auckland Islands
The Auckland Islands are an archipelago of the New Zealand Sub-Antarctic Islands and include Auckland Island, Adams Island, Enderby Island, Disappointment Island, Ewing Island, Rose Island, Dundas Island and Green Island, with a combined area of...
from 1942 to 1945. The Three Kings Islands
Three Kings Islands
The Three Kings Islands or Manawa Islands are a group of 13 islands about northwest of Cape Reinga, the northernmost point of the North Island of New Zealand, where the South Pacific Ocean and Tasman Sea converge. They measure about 4.86 km² in area...
and the Auckland Islands were formerly inhabited. There have been failed settlement attempts on Raoul Island, the Antipodes Islands
Antipodes Islands
The Antipodes Islands are inhospitable volcanic islands to the south of—and territorially part of—New Zealand...
and the Auckland Islands. The Solander Islands
Solander Islands
The Solander Islands are a small chain of uninhabited volcanic islets lying at , close to the western end of the Foveaux Strait in southern New Zealand...
have never been inhabited except by shipwrecked sailors or marooned stowaways (for the longest period, from 1808 to 1813 by five European stowaways).
See also
- British overseas territoriesBritish overseas territoriesThe British Overseas Territories are fourteen territories of the United Kingdom which, although they do not form part of the United Kingdom itself, fall under its jurisdiction. They are remnants of the British Empire that have not acquired independence or have voted to remain British territories...
- List of Antarctic and sub-Antarctic islands
- List of islands of New Zealand

