
Nitrosylation
Encyclopedia
Nitrosylation is a protein
modification in which a nitrosyl group is post-translationally
added to a protein.
There is a range of enzymes that produce nitric oxide
, and the frequent consequence of this production is nitrosylation.
S-nitrosylation is an important biological reaction of nitric oxide; it refers to the conversion of thiol
groups, including cysteine
residues in proteins, to form S-nitrosothiols (RSNOs). S-Nitrosylation is a mechanism for dynamic, post-translational regulation of most or all major classes of protein.
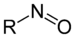 Nitrosylation is independent of enzyme catalysis, labile modification, on/off switch-like photophosphorylation.
Nitrosylation is independent of enzyme catalysis, labile modification, on/off switch-like photophosphorylation.
Denitrosylation can be enzymatic or non-enzymatic. Denitros(yl)ation of S-nitrosogluthatione is catalyzed by alcohol dehydrogenase class III isoenzyme., while thioredoxin catalyzes the denitros(yl)ation of a number of S-nitroisoproteins
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
modification in which a nitrosyl group is post-translationally
Posttranslational modification
Posttranslational modification is the chemical modification of a protein after its translation. It is one of the later steps in protein biosynthesis, and thus gene expression, for many proteins....
added to a protein.
There is a range of enzymes that produce nitric oxide
Nitric oxide
Nitric oxide, also known as nitrogen monoxide, is a diatomic molecule with chemical formula NO. It is a free radical and is an important intermediate in the chemical industry...
, and the frequent consequence of this production is nitrosylation.
S-nitrosylation is an important biological reaction of nitric oxide; it refers to the conversion of thiol
Thiol
In organic chemistry, a thiol is an organosulfur compound that contains a carbon-bonded sulfhydryl group...
groups, including cysteine
Cysteine
Cysteine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2SH. It is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans. Its codons are UGU and UGC. The side chain on cysteine is thiol, which is polar and thus cysteine is usually classified as a hydrophilic amino acid...
residues in proteins, to form S-nitrosothiols (RSNOs). S-Nitrosylation is a mechanism for dynamic, post-translational regulation of most or all major classes of protein.

Denitrosylation can be enzymatic or non-enzymatic. Denitros(yl)ation of S-nitrosogluthatione is catalyzed by alcohol dehydrogenase class III isoenzyme., while thioredoxin catalyzes the denitros(yl)ation of a number of S-nitroisoproteins

