Nuclear energy policy
Encyclopedia
Nuclear energy policy is a national and international policy
concerning some or all aspects of nuclear energy
, such as mining
for nuclear fuel
, extraction and processing of nuclear fuel from the ore, generating electricity
by nuclear power
, enriching and storing
spent nuclear fuel
and nuclear fuel reprocessing.
Nuclear energy policies often include the regulation of energy use and standards relating to the nuclear fuel cycle
. Other measures include efficiency standards, safety regulations, emission standard
s, fiscal policies
, and legislation
on energy trading, transport of nuclear waste and contaminated
materials, and their storage. Governments might subsidize nuclear energy and arrange international treaties and trade agreements about the import and export of nuclear technology
, electricity
, nuclear waste, and uranium
.
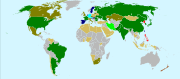
Following the March 2011 Fukushima I nuclear accidents, China, Germany, Switzerland, Israel, Malaysia, Thailand, United Kingdom, and the Philippines are reviewing their nuclear power programs. Indonesia and Vietnam still plan to build nuclear power plants. Thirty-one countries operate nuclear power stations, and there are a considerable number of new reactors being built in China, South Korea, India, and Russia. As of June 2011, countries such as Australia
, Austria
, Denmark
, Greece
, Ireland, Latvia, Lichtenstein, Luxembourg
, Malta
, Portugal
, Israel, Malaysia
, New Zealand
, and Norway
remain opposed to nuclear power.
Since nuclear energy and nuclear weapon
s technologies are closely related, military
aspirations can act as a factor in energy policy decisions. The fear of nuclear proliferation
influences some international nuclear energy policies.
After 1986's Chernobyl disaster
, public fear of nuclear power led to a virtual halt in reactor construction, and several countries decided to phase out nuclear power altogether. However, increasing energy demand
is beginning to require new sources of electric power, and rising fossil fuel prices
coupled with new concerns about reducing greenhouse gas
emissions (see Climate change mitigation) have sparked heightened interest in nuclear power and predictions of a nuclear renaissance
(made possible in part by major improvements in nuclear reactor safety
).
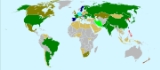
As of 2007, 31 countries operated nuclear power plants. Nuclear power tends to be found in nations connected to the largest electrical grids, and so the largest nations (or groups of them) such as China, India, the US, Russia and the European nations all utilize it (see graphic to right). The largest producer of nuclear capacity is the USA with 28% of worldwide capacity, followed by France (18%) and Japan (12%). In 2007, there were 439 operating nuclear generating units throughout the world, with a total capacity of about 351 gigawatts.
According to the IAEA, as of September, 2008, nuclear power is projected to remain at a 12.4% to 14.4% share of the world's electricity production through 2030.
, the high cost of nuclear power plants
, and nuclear terrorism
.
, we have no oil
, we have no gas
, we have no choice." Therefore, the discussion of a future for nuclear energy is intertwined with a discussion of energy security
and the use of energy mix, including renewable energy development.
Nuclear power has been relatively unaffected by embargo
es, and uranium is mined in "reliable" countries, including Australia and Canada.
industry revival, driven by rising fossil fuel prices
and new concerns about meeting greenhouse gas
emission limits. At the same time, various barriers to a nuclear renaissance have been identified. These include: unfavourable economics compared to other sources of energy, slowness in addressing climate change
, industrial bottlenecks and personnel shortages in nuclear sector, and the unresolved nuclear waste
issue. There are also concerns about more nuclear accidents, security, and nuclear weapons proliferation
.
New reactors under construction in Finland and France, which were meant to lead a nuclear renaissance, have been delayed and are running over-budget. China
has 27 new reactors under construction, and there are also a considerable number of new reactors being built in South Korea, India, and Russia. At least 100 older and smaller reactors will "most probably be closed over the next 10-15 years".
In March 2011 the nuclear emergencies
at Japan's Fukushima I Nuclear Power Plant
and other nuclear facilities raised questions among some commentators over the future of the renaissance. Following the Fukushima I accidents, the International Energy Agency
halved its estimate of additional nuclear generating capacity to be built by 2035.
Platts
has reported that "the crisis at Japan's Fukushima nuclear plants has prompted leading energy-consuming countries to review the safety of their existing reactors and cast doubt on the speed and scale of planned expansions around the world".
A study by UBS, reported on April 12, predicts that around 30 nuclear plants may be closed world-wide, with those located in seismic zones or close to national boundaries being the most likely to shut. The analysts believe that 'even pro-nuclear counties such as France
will be forced to close at least two reactors to demonstrate political action and restore the public acceptability of nuclear power', noting that the events at Fukushima 'cast doubt on the idea that even an advanced economy can master nuclear safety
'.
China—nuclear power’s largest prospective market—suspended approvals of new reactor construction while conducting a lengthy nuclear-safety review. Neighboring India, another potential nuclear boom market, has encountered effective local opposition, growing national wariness about foreign nuclear reactors, and a nuclear liability controversy that threatens to prevent new reactor imports. There have been mass protests against the French-backed 9900 MW Jaitapur Nuclear Power Project
in Maharashtra and the 2000 MW Koodankulam Nuclear Power Plant
in Tamil Nadu. The state government of West Bengal state has also refused permission to a proposed 6000 MW facility near the town of Haripur that intended to host six Russian reactors.
In the United States, new-reactor construction has also suffered—not because of public opposition but because of economics and tougher, yet-to-be-determined, safety regulations. In 2007, U.S. utilities applied to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission to build 28 nuclear-power plants before 2020; now, if more than three come online before the end of the decade, it will be a major accomplishment.
France is, per capita, the world’s most nuclear-powered state. Frequently heralded as a nuclear commercial model for the world, today it’s locked in a national debate over a partial nuclear phaseout. President Nicolas Sarkozy is still backing nuclear power, but his Socialist opponent, François Hollande, now well ahead in the polls, has proposed cutting nuclear power’s electricity contribution by more than a third by 2025.
Policy
A policy is typically described as a principle or rule to guide decisions and achieve rational outcome. The term is not normally used to denote what is actually done, this is normally referred to as either procedure or protocol...
concerning some or all aspects of nuclear energy
Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
, such as mining
Mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the earth, from an ore body, vein or seam. The term also includes the removal of soil. Materials recovered by mining include base metals, precious metals, iron, uranium, coal, diamonds, limestone, oil shale, rock...
for nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel is a material that can be 'consumed' by fission or fusion to derive nuclear energy. Nuclear fuels are the most dense sources of energy available...
, extraction and processing of nuclear fuel from the ore, generating electricity
Electricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric energy from other forms of energy.The fundamental principles of electricity generation were discovered during the 1820s and early 1830s by the British scientist Michael Faraday...
by nuclear power
Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
, enriching and storing
Nuclear fuel cycle
The nuclear fuel cycle, also called nuclear fuel chain, is the progression of nuclear fuel through a series of differing stages. It consists of steps in the front end, which are the preparation of the fuel, steps in the service period in which the fuel is used during reactor operation, and steps in...
spent nuclear fuel
Spent nuclear fuel
Spent nuclear fuel, occasionally called used nuclear fuel, is nuclear fuel that has been irradiated in a nuclear reactor...
and nuclear fuel reprocessing.
Nuclear energy policies often include the regulation of energy use and standards relating to the nuclear fuel cycle
Nuclear fuel cycle
The nuclear fuel cycle, also called nuclear fuel chain, is the progression of nuclear fuel through a series of differing stages. It consists of steps in the front end, which are the preparation of the fuel, steps in the service period in which the fuel is used during reactor operation, and steps in...
. Other measures include efficiency standards, safety regulations, emission standard
Emission standard
Emission standards are requirements that set specific limits to the amount of pollutants that can be released into the environment. Many emissions standards focus on regulating pollutants released by automobiles and other powered vehicles but they can also regulate emissions from industry, power...
s, fiscal policies
Fiscal policy
In economics and political science, fiscal policy is the use of government expenditure and revenue collection to influence the economy....
, and legislation
Legislation
Legislation is law which has been promulgated by a legislature or other governing body, or the process of making it...
on energy trading, transport of nuclear waste and contaminated
Contamination
Contamination is the presence of a minor and unwanted constituent in material, physical body, natural environment, at a workplace, etc.-Specifics:"Contamination" also has more specific meanings in science:...
materials, and their storage. Governments might subsidize nuclear energy and arrange international treaties and trade agreements about the import and export of nuclear technology
Nuclear technology
Nuclear technology is technology that involves the reactions of atomic nuclei. Among the notable nuclear technologies are nuclear power, nuclear medicine, and nuclear weapons...
, electricity
Electricity
Electricity is a general term encompassing a variety of phenomena resulting from the presence and flow of electric charge. These include many easily recognizable phenomena, such as lightning, static electricity, and the flow of electrical current in an electrical wire...
, nuclear waste, and uranium
Uranium
Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons...
.
Following the March 2011 Fukushima I nuclear accidents, China, Germany, Switzerland, Israel, Malaysia, Thailand, United Kingdom, and the Philippines are reviewing their nuclear power programs. Indonesia and Vietnam still plan to build nuclear power plants. Thirty-one countries operate nuclear power stations, and there are a considerable number of new reactors being built in China, South Korea, India, and Russia. As of June 2011, countries such as Australia
Anti-nuclear movement in Australia
Nuclear testing, uranium mining and export, and nuclear energy have often been the subject of public debate in Australia, and the anti-nuclear movement in Australia has a long history...
, Austria
Anti-nuclear movement in Austria
Construction of the first Austrian nuclear power plant in Zwentendorf on the Danube, about 20 miles upstream from the capital, Vienna, began in 1972. Zwentendorf Nuclear Power Plant was designed as a boiling water reactor with a capacity of 700 MW, that was expected to generate about 10% of the...
, Denmark
Nuclear energy in Denmark
Denmark does not produce nuclear energy, which is in accordance with a 1985 law passed by the Danish parliament that prohibits the production of nuclear energy in Denmark. Instead, the country has focused on renewable energy sources such as wind energy. In 2007, about 11.4 TWh of electricity...
, Greece
Nuclear energy in Greece
Although Greece has established the Greek Atomic Energy Commission , a decision has been made not to implement a nuclear power program to generate electricity....
, Ireland, Latvia, Lichtenstein, Luxembourg
Nuclear energy in Luxembourg
In 1978, Luxembourg proposed the construction of a 1,200 MW nuclear reactor but dropped the plans after threats of major protests....
, Malta
Nuclear energy in Malta
Malta has no nuclear energy facilities and when Silvio Berlusconi suggested that the island nation build such plants to supply Italy with electricity, the suggestion created an outcry in Malta where opinion is strongly anti-nuclear....
, Portugal
Nuclear energy in Portugal
Nuclear energy in Portugal is very limited and strictly non-commercial. Portugal has one research reactor located in the National Nuclear Research Centre. Nuclear energy activities are not planned in the near future...
, Israel, Malaysia
Nuclear energy in Malaysia
Although Malaysia has established Nuclear Agency and been actively involved in the periodic review of the nuclear option, currently there is no nuclear power generation plant neither is there a plan to embark on a nuclear power program in the foreseeable future....
, New Zealand
New Zealand's nuclear-free zone
In 1984, Prime Minister David Lange barred nuclear-powered or nuclear-armed ships from using New Zealand ports or entering New Zealand waters. Under the New Zealand Nuclear Free Zone, Disarmament, and Arms Control Act 1987, territorial sea, land and airspace of New Zealand became nuclear-free zones...
, and Norway
Nuclear energy in Norway
No nuclear power plant has ever been established in Norway; however, the country has a legal framework for licensing the construction and operation of nuclear installations. Also, four research reactors have been built in Norway, the first was JEEP I which was operative from 1951 to 1966. Two...
remain opposed to nuclear power.
Since nuclear energy and nuclear weapon
Nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission or a combination of fission and fusion. Both reactions release vast quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first fission bomb test released the same amount...
s technologies are closely related, military
Military
A military is an organization authorized by its greater society to use lethal force, usually including use of weapons, in defending its country by combating actual or perceived threats. The military may have additional functions of use to its greater society, such as advancing a political agenda e.g...
aspirations can act as a factor in energy policy decisions. The fear of nuclear proliferation
Nuclear proliferation
Nuclear proliferation is a term now used to describe the spread of nuclear weapons, fissile material, and weapons-applicable nuclear technology and information, to nations which are not recognized as "Nuclear Weapon States" by the Treaty on the Nonproliferation of Nuclear Weapons, also known as the...
influences some international nuclear energy policies.
The global picture

After 1986's Chernobyl disaster
Chernobyl disaster
The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Ukraine , which was under the direct jurisdiction of the central authorities in Moscow...
, public fear of nuclear power led to a virtual halt in reactor construction, and several countries decided to phase out nuclear power altogether. However, increasing energy demand
World energy resources and consumption
]World energy consumption in 2010: over 5% growthEnergy markets have combined crisis recovery and strong industry dynamism. Energy consumption in the G20 soared by more than 5% in 2010, after the slight decrease of 2009. This strong increase is the result of two converging trends...
is beginning to require new sources of electric power, and rising fossil fuel prices
Price of petroleum
The price of petroleum as quoted in news generally refers to the spot price per barrel of either WTI/light crude as traded on the New York Mercantile Exchange for delivery at Cushing, Oklahoma, or of Brent as traded on the Intercontinental Exchange for delivery at Sullom Voe.The price...
coupled with new concerns about reducing greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone...
emissions (see Climate change mitigation) have sparked heightened interest in nuclear power and predictions of a nuclear renaissance
Nuclear renaissance
Since about 2001 the term nuclear renaissance has been used to refer to a possible nuclear power industry revival, driven by rising fossil fuel prices and new concerns about meeting greenhouse gas emission limits. At the same time, various barriers to a nuclear renaissance have been identified...
(made possible in part by major improvements in nuclear reactor safety
Nuclear safety
Nuclear safety covers the actions taken to prevent nuclear and radiation accidents or to limit their consequences. This covers nuclear power plants as well as all other nuclear facilities, the transportation of nuclear materials, and the use and storage of nuclear materials for medical, power,...
).
As of 2007, 31 countries operated nuclear power plants. Nuclear power tends to be found in nations connected to the largest electrical grids, and so the largest nations (or groups of them) such as China, India, the US, Russia and the European nations all utilize it (see graphic to right). The largest producer of nuclear capacity is the USA with 28% of worldwide capacity, followed by France (18%) and Japan (12%). In 2007, there were 439 operating nuclear generating units throughout the world, with a total capacity of about 351 gigawatts.
According to the IAEA, as of September, 2008, nuclear power is projected to remain at a 12.4% to 14.4% share of the world's electricity production through 2030.
Nuclear concerns
Nuclear accidents and radioactive waste disposal are major concerns. Other concerns include nuclear proliferationNuclear proliferation
Nuclear proliferation is a term now used to describe the spread of nuclear weapons, fissile material, and weapons-applicable nuclear technology and information, to nations which are not recognized as "Nuclear Weapon States" by the Treaty on the Nonproliferation of Nuclear Weapons, also known as the...
, the high cost of nuclear power plants
Economics of new nuclear power plants
The economics of new nuclear power plants is a controversial subject, since there are diverging views on this topic, and multi-billion dollar investments ride on the choice of an energy source...
, and nuclear terrorism
Nuclear terrorism
Nuclear terrorism denotes the use, or threat of the use, of nuclear weapons or radiological weapons in acts of terrorism, includingattacks against facilities where radioactive materials are present...
.
Energy security
For some countries, nuclear power affords energy independence. In the words of the French, "We have no coalCoal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
, we have no oil
Petroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
, we have no gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
, we have no choice." Therefore, the discussion of a future for nuclear energy is intertwined with a discussion of energy security
Energy security
Energy security is a term for an association between national security and the availability of natural resources for energy consumption. Access to cheap energy has become essential to the functioning of modern economies. However, the uneven distribution of energy supplies among countries has led...
and the use of energy mix, including renewable energy development.
Nuclear power has been relatively unaffected by embargo
Embargo
An embargo is the partial or complete prohibition of commerce and trade with a particular country, in order to isolate it. Embargoes are considered strong diplomatic measures imposed in an effort, by the imposing country, to elicit a given national-interest result from the country on which it is...
es, and uranium is mined in "reliable" countries, including Australia and Canada.
Nuclear energy renaissance
Since about 2001 the term "nuclear renaissance" has been used to refer to a possible nuclear powerNuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
industry revival, driven by rising fossil fuel prices
Price of petroleum
The price of petroleum as quoted in news generally refers to the spot price per barrel of either WTI/light crude as traded on the New York Mercantile Exchange for delivery at Cushing, Oklahoma, or of Brent as traded on the Intercontinental Exchange for delivery at Sullom Voe.The price...
and new concerns about meeting greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone...
emission limits. At the same time, various barriers to a nuclear renaissance have been identified. These include: unfavourable economics compared to other sources of energy, slowness in addressing climate change
Climate change
Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions or the distribution of events around that average...
, industrial bottlenecks and personnel shortages in nuclear sector, and the unresolved nuclear waste
High-level radioactive waste management
High-level radioactive waste management concerns management and disposal of highly radioactive materials created during production of nuclear power and nuclear warheads. The technical issues in accomplishing this are daunting, due to the extremely long periods radioactive wastes remain deadly to...
issue. There are also concerns about more nuclear accidents, security, and nuclear weapons proliferation
Nuclear proliferation
Nuclear proliferation is a term now used to describe the spread of nuclear weapons, fissile material, and weapons-applicable nuclear technology and information, to nations which are not recognized as "Nuclear Weapon States" by the Treaty on the Nonproliferation of Nuclear Weapons, also known as the...
.
New reactors under construction in Finland and France, which were meant to lead a nuclear renaissance, have been delayed and are running over-budget. China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
has 27 new reactors under construction, and there are also a considerable number of new reactors being built in South Korea, India, and Russia. At least 100 older and smaller reactors will "most probably be closed over the next 10-15 years".
In March 2011 the nuclear emergencies
Timeline of the Fukushima nuclear accidents
For the timelines of the nuclear accidents at Fukushima Daiichi and Fukushima Daini after the 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami, see:* Timeline of the Fukushima I nuclear accidents* Timeline of the Fukushima II nuclear accidents...
at Japan's Fukushima I Nuclear Power Plant
Fukushima I Nuclear Power Plant
The , also known as Fukushima Dai-ichi , is a disabled nuclear power plant located on a site in the towns of Okuma and Futaba in the Futaba District of Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. First commissioned in 1971, the plant consists of six boiling water reactors...
and other nuclear facilities raised questions among some commentators over the future of the renaissance. Following the Fukushima I accidents, the International Energy Agency
International Energy Agency
The International Energy Agency is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organization established in the framework of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development in 1974 in the wake of the 1973 oil crisis...
halved its estimate of additional nuclear generating capacity to be built by 2035.
Platts
Platts
Platts is a provider of energy and metals information and a source of benchmark price assessments in the physical energy markets. Platts was founded in Cleveland, Ohio in 1909 by Warren C...
has reported that "the crisis at Japan's Fukushima nuclear plants has prompted leading energy-consuming countries to review the safety of their existing reactors and cast doubt on the speed and scale of planned expansions around the world".
A study by UBS, reported on April 12, predicts that around 30 nuclear plants may be closed world-wide, with those located in seismic zones or close to national boundaries being the most likely to shut. The analysts believe that 'even pro-nuclear counties such as France
Nuclear power in France
Nuclear power is the primary source of electric power in France. In 2004, 425.8 TWh out of the country's total production of 540.6 TWh of electricity was from nuclear power , the highest percentage in the world....
will be forced to close at least two reactors to demonstrate political action and restore the public acceptability of nuclear power', noting that the events at Fukushima 'cast doubt on the idea that even an advanced economy can master nuclear safety
Nuclear safety
Nuclear safety covers the actions taken to prevent nuclear and radiation accidents or to limit their consequences. This covers nuclear power plants as well as all other nuclear facilities, the transportation of nuclear materials, and the use and storage of nuclear materials for medical, power,...
'.
Reactions to Fukushima
Following the Fukushima nuclear disaster, Germany has permanently shut down eight of its reactors and pledged to close the rest by 2022. The Italians have voted overwhelmingly to keep their country non-nuclear. Switzerland and Spain have banned the construction of new reactors. Japan’s prime minster has called for a dramatic reduction in Japan’s reliance on nuclear power. Taiwan’s president did the same. Mexico has sidelined construction of 10 reactors in favor of developing natural-gas-fired plants. Belgium is considering phasing out its nuclear plants, perhaps as early as 2015.China—nuclear power’s largest prospective market—suspended approvals of new reactor construction while conducting a lengthy nuclear-safety review. Neighboring India, another potential nuclear boom market, has encountered effective local opposition, growing national wariness about foreign nuclear reactors, and a nuclear liability controversy that threatens to prevent new reactor imports. There have been mass protests against the French-backed 9900 MW Jaitapur Nuclear Power Project
Jaitapur nuclear power project
Jaitapur Nuclear Power Project is a proposed 9900 MW power project of Nuclear Power Corporation of India at Madban village of Ratnagiri district in Maharashtra...
in Maharashtra and the 2000 MW Koodankulam Nuclear Power Plant
Koodankulam Nuclear Power Plant
Koodankulam Nuclear Power Plant is a nuclear power station currently under construction in Koodankulam in the Tirunelveli district of the southern Indian state of Tamil Nadu...
in Tamil Nadu. The state government of West Bengal state has also refused permission to a proposed 6000 MW facility near the town of Haripur that intended to host six Russian reactors.
In the United States, new-reactor construction has also suffered—not because of public opposition but because of economics and tougher, yet-to-be-determined, safety regulations. In 2007, U.S. utilities applied to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission to build 28 nuclear-power plants before 2020; now, if more than three come online before the end of the decade, it will be a major accomplishment.
France is, per capita, the world’s most nuclear-powered state. Frequently heralded as a nuclear commercial model for the world, today it’s locked in a national debate over a partial nuclear phaseout. President Nicolas Sarkozy is still backing nuclear power, but his Socialist opponent, François Hollande, now well ahead in the polls, has proposed cutting nuclear power’s electricity contribution by more than a third by 2025.
Policies by territory
Following the March 2011 Fukushima I nuclear accidents, China, Germany, Switzerland, Israel, Malaysia, Thailand, United Kingdom, and the Philippines are reviewing their nuclear power programs. Indonesia and Vietnam still plan to build nuclear power plants. Countries such as Australia, Austria, Denmark, Greece, Ireland, Luxembourg, Portugal, New Zealand, and Norway remain opposed to nuclear power.See also
|
Nuclear power by country Thirty countries operate nuclear power stations, and there are a considerable number of new reactors being built in China, South Korea, India, Pakistan, and Russia... Nuclear power phase-out A nuclear power phase-out is the discontinuation of usage of nuclear power for energy production. Often initiated because of concerns about nuclear power, phase-outs usually include shutting down nuclear power plants and looking towards renewable energy and other fuels.Austria was the first country... Renewable energy commercialization Renewable energy commercialization involves the deployment of three generations of renewable energy technologies dating back more than 100 years. First-generation technologies, which are already mature and economically competitive, include biomass, hydroelectricity, geothermal power and heat... World Nuclear Industry Status Report The World Nuclear Industry Status Report is a yearly report that explores the global challenges facing the nuclear power industry. The reports show that the share of nuclear-generated electricity in the overall global energy production has decreased in the 2000s... |
Further reading
- Ferguson, Charles D., "Nuclear Energy: Balancing Benefits and Risks", Council on Foreign RelationsCouncil on Foreign RelationsThe Council on Foreign Relations is an American nonprofit nonpartisan membership organization, publisher, and think tank specializing in U.S. foreign policy and international affairs...
, 2007
External links
- NEI Public Policy Information
- Robert J. Duffy. Nuclear Politics in America: A History and Theory of Government Regulation (Studies in Government and Public Policy). Paperback. 1997. ISBN 0-7006-0853-2.
- Carlton Stoiber, Alec Baer, Norbert Pelzer, Wolfram Tonhauser, Handbook on Nuclear Law, IAEA (International Atomic Energy Agency), 2003.
- Annotated bibliography for nuclear power from the Alsos Digital Library for Nuclear Issues

