Nuclear power in Spain
Encyclopedia
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
has eight nuclear reactor
Nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device to initiate and control a sustained nuclear chain reaction. Most commonly they are used for generating electricity and for the propulsion of ships. Usually heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid , which runs through turbines that power either ship's...
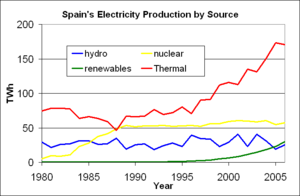
s producing 20% of the country’s electricity or 7,448 net megawatts (MWe). Spain imports approximately 2% of its energy from France but exports the same amount to Portugal
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
.
A nuclear power moratorium was enacted by the socialist government in 1983. For a time the country had a policy of phasing out nuclear power in favor of renewables
Renewable energy commercialization
Renewable energy commercialization involves the deployment of three generations of renewable energy technologies dating back more than 100 years. First-generation technologies, which are already mature and economically competitive, include biomass, hydroelectricity, geothermal power and heat...
. The oldest unit (at José Cabrera nuclear power plant) was shut down at the end of 2006, 40 years after its construction.
However, in 2009, the operating permit for the Garoña plant
Santa María de Garoña Nuclear Power Plant
Santa María de Garoña Nuclear Power Plant is a nuclear power station at Santa María de Garoña, Burgos . It consists of one boiling water reactor of 466 megawatts ....
was extended to 42 years.
In 2011, the government lifted the 40-year limit on all reactors, allowing owners to apply for license extensions in 10-year increments.
History
In early 1947, the Commission is created within the National Research Council in order to rule on issues of "Technical Physics of greatest interest to the country. " In the middle of that year, the Naval Attache of the United States Embassy in Spain, won the Laboratory and Workshop on Research Staff of the Navy an extensive collection of American journals specializing in nuclear fission and its civil and military applications. This was the first contact with the outside world, and led to international collaborations.To that end, establishing the Atomic Research Board in the form of study (Irani 1987). His work during the triennium (1948-1950) focuses on two aspects. On the one hand, begin to train abroad the first Spanish experts on nuclear issues. On the other hand, begins the search for uranium to serve as raw material for the development of the first investigations. Studies conducted by the Board, lead by Decree-Law on October 22, 1951 to the Nuclear Energy Board, which aims to provide new knowledge in the process of energy production.
In 1963, two significant events occur: the enactment of the Nuclear Energy Act and prior authorization from the Central will be the first Spanish (Almonacid de Zorita, Guadalajara) later known as Jose Cabrera. In June 1965 construction began three years after the plant was synchronized and provided power to the grid for the first time.
Three years later it opened in 1971, launched the Santa Maria de Garoña (Burgos), with a capacity of 460MW. In 1972, the network was connected to the Spanish-French central Vandellós (Tarragona) with a capacity of 500MW. The fire occurred in 1989 in this last plant, destroyed part of its facilities. After evaluating the technical and economic feasibility of repair made a year after the fire, led to the decision to withdraw this plant.
These three so-called first-generation plants represent a combined capacity of 1220 MW. Following the good results obtained in them, and the growing need for energy, we decided to build seven new groups (four plants) of much greater production capacity, resulting in an additional nuclear power of 6500 MW.
At the beginning of 1981 begin producing electricity the first group of Almaraz (Cáceres) with a capacity of 930 MW. In 1983 starts the reactor Asco (Tarragona) with a capacity of 930MW, is operated and the second group with the same power Almaraz.
In 1984 he inaugurated the central Cofrentes (Valencia) with a capacity of 975 MW, a year after the network is connected to the second reactor of 930 MW Asco group. In December 1987, enters the central testing period Vandellós II, and finally, in 1989 is put into operation the central TrilloI (Guadalajara) to 1066MW.
As shown, nuclear power plants in Spain are located in the northern half. This is because the area is less seismic impact of the peninsula and where the presence of large rivers Tajo and Ebro meet their needs for water used for cooling.
Current situation
Spain has a total of 10 nuclear installations within their mainland, among which are six stations, which are a total of eight nuclear units: Almaraz I and II, Asco I and II, Cofrentes, Santa Maria de Garoña, Trillo, Vandellós I and II.The José Cabrera, better known as Zorita, ceased operations on April 30, 2006. On the other hand, Vandellós I is currently being dismantled.
Spain also possesses a nuclear fuel factory in Salamanca (Juzbado) and a storage facility for radioactive waste, low and intermediate level in Córdoba (El Cabril).
Environmental impact
The atmosphere is essential for life on Earth for many reasons, including for its oxygen content. It also contains a large number of other gases and chemicals, some as a result of human activity. It is proven that emissions of certain gases in the atmosphere have a significant and negative impact on the environment.Called greenhouse gases to overheat the earth's surface by the growth of the amount of solar energy is trapped by the atmosphere, due to certain gases whose presence and proportion have been modified by human activity. Among the greenhouse gases most important are: CO2, CH4, NOx, CFC, SF6.
Nuclear plants unlike thermal plants do not emit this series of greenhouse gases, however, we can not exclude other contamination. In recent years, governments have become aware of climate change, example is the report by the Intergovernmental Panel (a body belonging to the United Nations): "This is unprecedented warming over the last 10000 years. Much has been observed over the last half century and is attributed to increased concentrations of greenhouse gases, mainly CO2, arising from the use of oil, gas and coal."
Nuclear power is characterized by producing, in addition to electric power, nuclear waste to be stored in insulated tanks and monitored for a long time. In exchange, does not produce air pollution from the combustion gases that produce the greenhouse effect, or require the use of fossil fuels for operation.
However, indirect emissions resulting from its own construction, manufacturing of fuel and the subsequent management of radioactive waste (called management at all treatment processes of waste, including storage) are not negligible.
In Spain nuclear plants generated 20% of the electricity needed in 2008.
Nuclear power plants
In 1964, Spain began construction on its first of three nuclear reactors and completed construction in 1968.This became the first commercial nuclear reactor. In the 1970s, Spain began construction on seven second generation reactors, but only completed five. A moratorium
Moratorium (law)
A moratorium is a delay or suspension of an activity or a law. In a legal context, it may refer to the temporary suspension of a law to allow a legal challenge to be carried out....
was enacted by the socialist government in 1983. Spain stopped the building of new nuclear power plants in 1984.
The first generation of nuclear plants in Spain were all turnkey
Turnkey
A turn-key or a turn-key project is a type of project that is constructed by a developer and sold or turned over to a buyer in a ready-to-use condition.-Common usage:...
projects, including the José Cabrera Nuclear Power Plant and the Vandellòs Nuclear Power Plant
Vandellòs Nuclear Power Plant
The Vandellòs Nuclear Power Plant is a nuclear power station in Vandellòs located close to the Coll de Balaguer pass in Catalonia, Spain....
.
The second generation of plants were domestically built by companies including Empresarios Agrupados, INITEC and ENSA
ENSA
ENSA may refer to:* ENSA, the Entertainments National Service Association* ENSA * École Nationale des Sciences Appliquées d'Oujda, an engineering school in Morocco* EC-Council Network Security Administrator...
. Five of these were built.
The third generation (not to be confused with Generation III
Generation III reactor
A generation III reactor is a development of any of the generation II nuclear reactor designs incorporating evolutionary improvements in design developed during the lifetime of the generation II reactor designs...
) includes the Trillo-1
Trillo Nuclear Power Plant
Trillo Nuclear Power Plant is a nuclear power station in Spain.It consists of one pressurized water reactor of 1066 MWe. Construction of unit one began in 1979, and first criticality was on 14 May 1988....
and Vandellos-2
Vandellòs Nuclear Power Plant
The Vandellòs Nuclear Power Plant is a nuclear power station in Vandellòs located close to the Coll de Balaguer pass in Catalonia, Spain....
. All of the other five units of this series were halted in the middle of construction after a moratorium stopping further construction passed in 1994. Capacity of the nuclear fleet has still increased since then due to power uprates.
There are currently no plans for either expansion or accelerated closure of nuclear plants. A leak of radioactive material from the Asco I nuclear power plant in November 2007 sparked protests. The country’s government has pledged to shut down its eight nuclear reactors once wind and solar energy become viable alternatives such as in neighouring country Portugal
Renewable energy in Portugal
Renewable energy in Portugal was the source for 52% of the country's electricity generation in 2010 - an increase of 28% in 5 years.In 2001, the Portuguese government launched a new energy policy instrument – the E4 Programme , consisting of a set of multiple, diversified measures aimed at...
.
Fuel cycle
ENUSA is a company in Spain with various holdings in Uranium mining. A Uranium mine in Saelices el ChicoSaelices el Chico
Saelices el Chico is a municipality located in the province of Salamanca, Castile and León, Spain. According to the 2004 census , the municipality has a population of 157 inhabitants....
was operated for some time, but is now decommissioned and Spain imports all of its Uranium fuel.
State owned Empresa Nacional de Residuos Radiactivos SA was established in 1984 and is the responsible outfit for radioactive waste disposal and decommissioning. There is a temporary dry storage facility at the Trillo Nuclear Power Plant
Trillo Nuclear Power Plant
Trillo Nuclear Power Plant is a nuclear power station in Spain.It consists of one pressurized water reactor of 1066 MWe. Construction of unit one began in 1979, and first criticality was on 14 May 1988....
, and research for a long term geological repository won't commence until 2010.
Nuclear waste
Spain currently stores nuclear waste at the reactor sites for ten years with no reprocessing. Plans for future storage include a temporary storage facility in Trillo, until the establishment of a longer-term storage facility. Funding for nuclear waste management is paid by a tax of 1% on all revenues from nuclear power.See also
- Nuclear powerNuclear powerNuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
- Nuclear energy policyNuclear energy policyNuclear energy policy is a national and international policy concerning some or all aspects of nuclear energy, such as mining for nuclear fuel, extraction and processing of nuclear fuel from the ore, generating electricity by nuclear power, enriching and storing spent nuclear fuel and nuclear fuel...
- Nuclear energy policy
- Economy of SpainEconomy of SpainThe economy of Spain is the twelfth-largest economy in the world, based on nominal GDP comparisons, and the fifth-largest in Europe. It is regarded as the world's 20th most developed country....
- Anti-nuclear movement in SpainAnti-nuclear movement in SpainThe late 1950s and early 1960s saw a strong push from the Spanish Government to establish a national nuclear power industry. In response to the surge in nuclear power plant plans, a strong anti-nuclear movement emerged in 1973, which ultimately impeded the realisation of most of the...

