
Nut (hardware)
Encyclopedia

Hardware
Hardware is a general term for equipment such as keys, locks, hinges, latches, handles, wire, chains, plumbing supplies, tools, utensils, cutlery and machine parts. Household hardware is typically sold in hardware stores....
fastener
Fastener
A fastener is a hardware device that mechanically joins or affixes two or more objects together.Fasteners can also be used to close a container such as a bag, a box, or an envelope; or they may involve keeping together the sides of an opening of flexible material, attaching a lid to a container,...
with a threaded
Screw thread
A screw thread, often shortened to thread, is a helical structure used to convert between rotational and linear movement or force. A screw thread is a ridge wrapped around a cylinder or cone in the form of a helix, with the former being called a straight thread and the latter called a tapered thread...
hole. Nuts are almost always used opposite a mating bolt to fasten a stack of parts together. The two partners are kept together by a combination of their threads' friction, a slight stretch of the bolt, and compression of the parts. In applications where vibration or rotation may work a nut loose, various locking mechanisms may be employed: Adhesives, safety pins or lockwire, nylon inserts, or slightly oval-shaped threads. The most common shape is hexagonal, for similar reasons as the bolt head - 6 sides give a good granularity of angles for a tool to approach from (good in tight spots), but more (and smaller) corners would be vulnerable to being rounded off. Other specialized shapes exist for certain needs, such as wing nuts for finger adjustment and captive nuts for inaccessible areas.
Nuts are graded with strength ratings compatible with their respective bolts; for example, an ISO property class 10 nut will be able to support the bolt proof strength load of an ISO property class 10.9 bolt without stripping. Likewise, an SAE class 5 nut can support the proof load of an SAE class 5 bolt, and so on.

Types



- Acorn nutAcorn nutThe acorn nut is a type of fastener which gets its name from its shape. It is a nut that has a domed top to prevent contact with the external thread. It is usually made of brass, steel, stainless steel or nylon. It can also be chrome plated and given a mirror finish....
(cap nut) - Barrel nutBarrel nutA sex bolt, also known as a barrel nut, barrel bolt, Chicago screw or post and screw, is a type of fastener which has a barrel-shaped flange and protruding boss that is internally threaded. The boss sits within the components being fastened, and the flange provides the bearing surface...
- Cage nutCage nutA cage nut or caged nut consists of a square nut in a spring steel cage which wraps around the nut. The cage has two wings that when compressed allow the cage to be inserted into the square holes in equipment racks, and when released hold the nut in position behind the hole...
- Clip-on nutClip-on nutA clip-on nut, also known as a sheet metal nut or a speed nut , is a type of nut designed to be clipped to sheet metal. They come in many forms based upon: where they clip on, shape, and type of thread. Each clip-on nut is designed for only a small range of sheet metal gauges...
(J-nut or U-nut) - Coupling nutCoupling nutA coupling nut is a threaded fastener for joining two male threads, most commonly threaded rod. The outside of the fastener is usually a hex so a wrench can hold it...
- Cross dowel
- Flange nutFlange nutA flange nut has a wide flange at one end that acts as an integrated, non-spinning washer. This serves to distribute the pressure of the nut over the part being secured, reducing the chance of damage to the part and making it less likely to loosen as a result of an uneven fastening surface.MATERIAL...
(collar nut) - Insert nutInsert nutAn insert nut provides a threaded socket for a wooden workpiece, similar to a wall anchor. Insert nuts are inserted into a pre-drilled hole by one of two means: screw in and hammer in...
- Internal wrenching nutInternal wrenching nutAn internal wrenching nut, also known as an Allenut or Allen nut, is a cylindrical nut that is internally threaded on one side and has an Allen socket on the other side; the outside of the nut is smooth or has knurling on it. The Allen socket may be 6 point or 12 point . They are used where hex or...
(Allen nut) - KnurledKnurlingKnurling is a manufacturing process, typically conducted on a lathe, whereby a visually attractive diamond-shaped pattern is cut or rolled into metal.- Uses :...
nut (thumb nut) - Lug nutLug nutA lug nut is a fastener, specifically a nut, used to secure a wheel on a vehicle. Typically, lug nuts are found on automobiles, trucks , and other large vehicles utilizing rubber tires.-Design:...
- Nut-type MJTMulti-jackbolt tensionerMulti-jackbolt tensioners provide an alternative to traditional bolted joints Rather than needing to tighten one large bolt, MJTs use several smaller jackbolts to drastically reduce the torque required to attain a certain preload. MJTs range in thread sizes from 3/4” to 32” and can achieve up to...
- Panel nutPanel nutA panel nut is very thin nut with a relatively large hole commonly used to mount threaded electrical switches.These are often used where light duty precision fasteners are needed. They have width close to the diameter of the fastener they secure. These usually have low thread count...
- PEM nutPEM nutA PEM nut is an internally threaded fastener, that when pressed into ductile metal, displaces the host material around the mounting hole, causing it to cold flow into a specially designed annular recess in the shank of the fastener. A serrated clinching ring prevents the fastener from rotating in...
(for metal) - Plate nutPlate nutA plate nut, also known as a nut plate, is a stamped sheet metal nut that is riveted to a workpiece. They have a long tube that is internally threaded and a plate with two clearance holes for rivets...
(nut plate) - Rivet nut or blind nut
- Self-aligning nutSelf-aligning nutA self-aligning nut, also known as a spherical nut or leveling nut, is a type of nut that is used in applications where the fastener is not perpendicular to the surface the nut anchors to. It achieves this action by using a flanged nut inside a specially shaped dished out washer. They are commonly...
- Sex bolt
- Slotted nutSlotted nutSlotted nut or slot nut can refer to:*Castellated nut also slotted nut*Split beam nut also slotted beam nut*T-slot nut...
- Split nutSplit nutA split nut is a nut that consists of two pieces which can be clamped together to engage the thread of the nut with the bolt, or released, to allow the nut to move along the bolt without turning the bolt. The two pieces have chamfered ends . The nut is split lengthwise so that it may be opened for...
- Sleeve nutSleeve nutA sleeve nut is a nut used instead of a turnbuckle, when high strength rods are required.It is used to couple rods and provide some degree of length adjustment. It is stronger than the corresponding connecting rod of the same materials. It is produced from hexagonal or round bars . It is given a...
- Square nutSquare nutA square nut is a four-sided nut. Compared to standard hex nuts, square nuts have a greater surface in contact with the part being fastened, and therefore provide greater resistance to loosening . They are also much less likely to become rounded-off after repeated loosening/tightening cycles...
- Staked/welded nut (for plastic)
- Swage nutSwage nutA swage nut is a type of nut is used on sheet metal. It permanently anchors itself to the sheet metal by swaging the surrounding material. The swaged material plastically deforms into an undercut in the nut, keeping it from pulling out or rotating....
- T-nutT-nutA T-nut, also known as a blind nut, is a type of nut used to fasten a wood, particle or composite materials workpiece, leaving a flush surface. It has a long, thin body and a flange at one end, resembling a T in profile...
- T-slot nutT-slot nutA T-slot nut is used with a threaded clamp to position and secure pieces being worked on in a woodshop. The T-slot nut slides along a T-slot track, which is set in workbench or table for a router, drill press, or bandsaw...
(T-groove) nut - Weld nutWeld nutA weld nut is a special type of nut specifically designed to be welded to another object. There are various types for different applications.-Types:Round base nutsThese nuts have a long threaded cylinder with a large circular base to make welding easy...
- Well nutWell nutA well nut is a type of fastener used to blindly fasten a piece and to seal the bolt hole. It consists of a flanged neoprene bushing with a nut embedded in the non-flanged end. The bolt is passed through one of the pieces to be fastened and threaded onto the nut from the flanged end. The...
- Wing nutWingnut (hardware)A wingnut or wing nut is a type of nut with two large metal "wings," one on each side, so it can be easily tightened and loosened by hand without tools. It is sometimes called a thumbscrew.-Bicycles:...
Locknuts
- Castellated nutCastellated nutA castellated nut, also called a castle nut or slotted nut, is a nut with slots cut into one end. The name comes from the nut’s resemblance to the crenellated parapet of a medieval castle....
- Distorted thread locknut
- Centerlock nut
- Elliptical offset locknut
- Toplock nut
- Interfering thread nutInterfering thread nutAn interfering thread nut is a type of locknut that has an over-sized root diameter. This creates an interference between the nut and the fastener, plastically deforming the threads on the fastener. Due to this deformation they are usually only used on permanent or semi-permanent installations.A...
- Tapered thread nut
- Jam nutJam nutA jam nut is a low profile type of nut, typically half as tall as a standard nut. It is commonly used as a type of locknut, where it is "jammed" up against a standard nut to lock the two in place...
- Jet nutJet nutA jet nut, also known as a K-nut, is a special type of hex locknut that is commonly used in the aerospace and automotive racing industries. It has a flange on one end of the nut, the hex is smaller than a standard sized hex nut, and it is shorter than a standard hex nut. It achieves its locking...
(K-nut) - Keps nutKeps nutA Keps nut, also called a K-nut or washer nut, is a nut with an attached, free-spinning washer. It is used to make assembly more convenient. Common washer types are star-type lock washers, conical, and flat washers....
(K-nut or washer nut) with a star-type lock washer - Nyloc plate nutPlate nutA plate nut, also known as a nut plate, is a stamped sheet metal nut that is riveted to a workpiece. They have a long tube that is internally threaded and a plate with two clearance holes for rivets...
- Polymer insert nut (Nyloc)
- Serrated face nutSerrated face nutA serrated face nut is a locknut with ridges on the face of the nut that bite into the surface it is tightened against. The serrations are angled such that they keep the nut from rotating in the direction that would loosen the nut. Because of the serrations they cannot be used with a washer or on...
- Serrated flange nutFlange nutA flange nut has a wide flange at one end that acts as an integrated, non-spinning washer. This serves to distribute the pressure of the nut over the part being secured, reducing the chance of damage to the part and making it less likely to loosen as a result of an uneven fastening surface.MATERIAL...
- Speed nutSpeed nutA speed nut, also known as a sheet metal nut, is a type of locknut with two sheet metal prongs that act as one thread. They are made from spring steel. The fastener serves the functions of both a lock washer and a nut. As the fastener is tightened in the nut the prongs are drawn inward until they...
(Sheet metal nut or Tinnerman nut) - Split beam nutSplit beam nutA split beam nut, also known as a split hex nut or slotted beam nut, is a locknut with slots cut in the top that separate the outside end into two or more sections that are bent slightly inward, making the thread diameter undersized in the slotted portion...
Standard metric hex nuts sizes
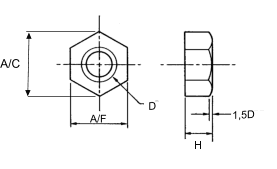
| Nominal diameter hole D (mm) |
Pitch P (mm) |
Flat size A/F (mm) |
External diameter A/C (mm) |
Height H (mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st choice |
2nd choice |
coarse | fine | ISO International Organization for Standardization The International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial... |
DIN Deutsches Institut für Normung is the German national organization for standardization and is that country's ISO member body. DIN is a Registered German Association headquartered in Berlin... |
JIS Japanese Industrial Standards Japanese Industrial Standards specifies the standards used for industrial activities in Japan.The standardization process is coordinated by Japanese Industrial Standards Committee and published through Japanese Standards Association.-History:... |
Hex Nut | Jam Nut | Nylon Nut | |
| 1 | 0.25 | 2.5 | ||||||||
| 1.2 | 0.25 | |||||||||
| 1.4 | 0.3 | |||||||||
| 1.6 | 0.35 | 3.2 | ||||||||
| 1.8 | 0.35 | |||||||||
| 2 | 0.4 | 4 | 1.6 | 1.2 | ||||||
| 2.5 | 0.45 | 5 | 2 | 1.6 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.5 | 5.5 | 6.4 | 2.4 | 1.8 | 4 | ||||
| 3.5 | 0.6 | 6 | ||||||||
| 4 | 0.7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 8.1 | 3.2 | 2.2 | 5 | ||
| 5 | 0.8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 9.2 | 4 | 2.7 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 1 | 0.75 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 11.5 | 5 | 3.2 | 6 | |
| 7 | 1 | 11 | 5.5 | 3.5 | ||||||
| 8 | 1.25 | 1 | 13 | 13 | 12 | 15 | 6.5 | 4 | 8 | |
| 10 | 1.5 | 1.25 or 1 | 16 | 17 | 14 | 19.6 | 8 | 5 | 10 | |
| 12 | 1.75 | 1.5 or 1.25 | 18 | 19 | 17 | 22.1 | 10 | 6 | 12 | |
| 14 | 2 | 1.5 | 21 | 22 | 19 | 11 | 7 | 14 | ||
| 16 | 2 | 1.5 | 24 | 24 | 22 | 27.7 | 13 | 8 | 16 | |
| 18 | 2.5 | 2 or 1.5 | 27 | 15 | 9 | 18.5 | ||||
| 20 | 2.5 | 2 or 1.5 | 30 | 30 | 34.6 | 16 | 10 | 20 | ||
| 22 | 2.5 | 2 or 1.5 | 32 | |||||||
| 24 | 3 | 2 | 36 | 41.6 | 19 | |||||
| 27 | 3 | 2 | 41 | |||||||
| 30 | 3.5 | 2 | 46 | 53.1 | 24 | |||||
| 33 | 3.5 | 2 | ||||||||
| 36 | 4 | 3 | 55 | 63.5 | 29 | |||||
| 39 | 4 | 3 | ||||||||
| 42 | 4.5 | 3 | ||||||||
| 45 | 4.5 | 3 | ||||||||
| 48 | 5 | 3 | ||||||||
| 52 | 5 | 4 | ||||||||
| 56 | 5.5 | 4 | ||||||||
| 60 | 5.5 | 4 | ||||||||
| 64 | 6 | 4 |
Classifications
| Material | Proof strength | Tensile yield strength (min.) | Tensile ultimate strength (min.) | Nut marking | Nut class | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 898 (Metric) | |||||||
| Low or medium carbon steel | 380 MPa Pascal (unit) The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre... (55 ksi) |
420 MPa (61 ksi) | 520 MPa (75 ksi) |  |
5 | ||
| Medium carbon steel Q Quench In materials science, quenching is the rapid cooling of a workpiece to obtain certain material properties. It prevents low-temperature processes, such as phase transformations, from occurring by only providing a narrow window of time in which the reaction is both thermodynamically favorable and... &T Tempering Tempering is a heat treatment technique for metals, alloys and glass. In steels, tempering is done to "toughen" the metal by transforming brittle martensite or bainite into a combination of ferrite and cementite or sometimes Tempered martensite... |
580 MPa (84 ksi) | 640 MPa (93 ksi) | 800 MPa (116 ksi) |  |
8 | ||
| Alloy steel Q&T | 830 MPa (120 ksi) | 940 MPa (136 ksi) | 1040 MPa (151 ksi) |  |
10 | ||
| SAE J995 (English) | |||||||
| Low or medium carbon steel | 55 ksi (379 MPa) | 57 ksi (393 MPa) | 74 ksi (510 MPa) |  |
2 | ||
| Medium carbon steel Q&T | 85 ksi (586 MPa) | 92 ksi (634 MPa) | 120 ksi (827 MPa) |  |
5 | ||
| Alloy steel Q&T | 120 ksi (827 MPa) | 130 ksi (896 MPa) | 150 ksi (1034 MPa) |  |
8 | ||
Use of two nuts to prevent self-loosening
In normal use, a nut-and-bolt joint holds together because the bolt is under a constant tensile stress called the preload. The preload pulls the nut threads against the bolt threads, and the nut face against the bearing surface, with a constant forceForce
In physics, a force is any influence that causes an object to undergo a change in speed, a change in direction, or a change in shape. In other words, a force is that which can cause an object with mass to change its velocity , i.e., to accelerate, or which can cause a flexible object to deform...
, so that the nut cannot rotate without overcoming the friction
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and/or material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:...
between these surfaces. If the joint is subjected to vibration
Vibration
Vibration refers to mechanical oscillations about an equilibrium point. The oscillations may be periodic such as the motion of a pendulum or random such as the movement of a tire on a gravel road.Vibration is occasionally "desirable"...
, however, the preload increases and decreases with each cycle of movement. If the minimum preload during the vibration cycle is not enough to hold the nut firmly in contact with the bolt and the bearing surface, then the nut is likely to become loose.
Specialist locking nuts exist to prevent this problem, but sometimes it is sufficient to add a second nut. For this technique to be reliable, each nut must be tightened to the correct torque
Torque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
. The inner nut is tightened to about a quarter to a half of the torque of the outer nut. It is then held in place by a wrench
Wrench
A wrench or spanner is a tool used to provide grip and mechanical advantage in applying torque to turn objects—usually rotary fasteners, such as nuts and bolts—or keep them from turning....
while the outer nut is tightened on top using the full torque. This arrangement causes the two nuts to push on each other, creating a tensile stress in the short section of the bolt that lies between them. Even when the main joint is vibrated, the stress between the two nuts remains constant, thus holding the nut threads in constant contact with the bolt threads and preventing self-loosening. When the joint is assembled correctly, the outer nut bears the full tension of the joint. The inner nut functions merely to add a small additional force to the outer nut and does not need to be as strong, so a thin nut (also called a jam nut) can be used.
See also
- Bolted joint
- Pipe cap
- Tap
- Tapped hole
- Threaded insert
- WasherWasher (mechanical)A washer is a thin plate with a hole that is normally used to distribute the load of a threaded fastener, such as a screw or nut. Other uses are as a spacer, spring , wear pad, preload indicating device, locking device, and to reduce vibration...

