Nüpode Huitoto
Encyclopedia
Nüpode Huitoto or Nɨpode is an indigenous American language spoken in western South America. It has occasionally been referred to as Muinane Witoto, not to be confused with the related Muinane language
.
language family. Along with Mɨnɨca and Murai it is one of the three Witoto Proper languages.
Muinane language
-Classification:Muinane belongs to the Witotoan language family. Along with Bora, it comprises the Boran sub-grouping.-Geographic distribution:Muinane is spoken by 150 people in Colombia along the Upper Cahuinarí river in the Department of Amazonas...
.
Classification
Nüpode Huitoto belongs to the WitotoanWitotoan languages
Bora–Witóto is a proposal to unite the Bora and Witotoan language families of northeastern Peru , southwestern Colombia , and western Brazil...
language family. Along with Mɨnɨca and Murai it is one of the three Witoto Proper languages.
Geographic distribution
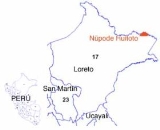
Nüpode Huitito is spokenby just one hundred people in the South American country of Perú's northeastern Loreto province, where it has official standing. Speakers also use the other two Huitoto languages (Murui and Minica). It is written using the roman alphabet and has had some bible portions translated into it in addition to a dictionary and grammar rules.Consonants
| Bilabial Bilabial consonant In phonetics, a bilabial consonant is a consonant articulated with both lips. The bilabial consonants identified by the International Phonetic Alphabet are:... |
Alveolar Alveolar consonant Alveolar consonants are articulated with the tongue against or close to the superior alveolar ridge, which is called that because it contains the alveoli of the superior teeth... |
Postalveolar Postalveolar consonant Postalveolar consonants are consonants articulated with the tongue near or touching the back of the alveolar ridge, further back in the mouth than the alveolar consonants, which are at the ridge itself, but not as far back as the hard palate... / Palatal Palatal consonant Palatal consonants are consonants articulated with the body of the tongue raised against the hard palate... |
Velar Velar consonant Velars are consonants articulated with the back part of the tongue against the soft palate, the back part of the roof of the mouth, known also as the velum).... |
Glottal Glottal consonant Glottal consonants, also called laryngeal consonants, are consonants articulated with the glottis. Many phoneticians consider them, or at least the so-called fricative, to be transitional states of the glottis without a point of articulation as other consonants have; in fact, some do not consider... |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal Nasal consonant A nasal consonant is a type of consonant produced with a lowered velum in the mouth, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. Examples of nasal consonants in English are and , in words such as nose and mouth.- Definition :... |
m | n | ɲ | ŋ | |
| Plosive | p b | t d | tʃ dʒ | k ɡ | ʔ |
| Implosive Implosive consonant Implosive consonants are stops with a mixed glottalic ingressive and pulmonic egressive airstream mechanism. That is, the airstream is controlled by moving the glottis downward in addition to expelling air from the lungs. Therefore, unlike the purely glottalic ejective consonants, implosives can... |
ɓ | ɗ | |||
| Fricative Fricative consonant Fricatives are consonants produced by forcing air through a narrow channel made by placing two articulators close together. These may be the lower lip against the upper teeth, in the case of ; the back of the tongue against the soft palate, in the case of German , the final consonant of Bach; or... |
β | h | |||
| Flap Flap consonant In phonetics, a flap or tap is a type of consonantal sound, which is produced with a single contraction of the muscles so that one articulator is thrown against another.-Contrast with stops and trills:... |
r |
Vowels
| Front Front vowel A front vowel is a type of vowel sound used in some spoken languages. The defining characteristic of a front vowel is that the tongue is positioned as far in front as possible in the mouth without creating a constriction that would be classified as a consonant. Front vowels are sometimes also... |
Central Central vowel A central vowel is a type of vowel sound used in some spoken languages. The defining characteristic of a central vowel is that the tongue is positioned halfway between a front vowel and a back vowel... |
Back Back vowel A back vowel is a type of vowel sound used in spoken languages. The defining characteristic of a back vowel is that the tongue is positioned as far back as possible in the mouth without creating a constriction that would be classified as a consonant. Back vowels are sometimes also called dark... |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| High | i | ɨ | u |
| Low | e | a | o |

