
Operating leverage
Encyclopedia
The operating leverage is a measure of how revenue growth translates into growth in operating income. It is a measure of leverage
, and of how risky (volatile) a company's operating income is.
which can be interpreted analogously to financial leverage.
One measure is fixed costs to total costs: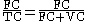
Compare to debt to value
, which is
Another measure is fixed costs to variable costs: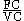
Compare to debt to equity ratio
: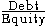
Both of these measures depend on sales: if the unit variable cost is constant, then as sales increase, operating leverage (as measured by fixed costs to total costs or variable costs) decreases.
is a measure of operating leverage: the higher the contribution margin is (the lower variable costs are as a percentage of total costs), the faster the profits increase with sales. Note that unlike other measures of operating leverage, in the linear Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
Model, contribution margin is a fixed quantity, and does not change with Sales.
Contribution = Sales - Variable Cost
The Degree of Operating Leverage (DOL) can be computed in a number of equivalent ways; one way it is defined as the ratio of the percentage change in Operating Income for a given percentage change in Sales :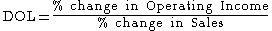
This can also be computed as Total Contribution Margin
over Operating Income: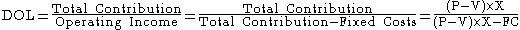
Alternatively, as Contribution Margin Ratio over Operating Margin
:
For instance, if a company has sales of 1,000,000 units, at price $50, unit variable cost of $10, and fixed costs of $10,000,000, then its unit contribution is $40, its Total Contribution is $40m, and its Operating Income is $30m, so its DOL is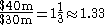
This could also be computed as 80%=$40m/$50m Contribution Margin Ratio divided by 60%=$30m/$50m Operating Margin.
It currently has Sales of $50m and Operating Income of $30m, so additional Unit Sales (say of 100,000 units) yield $5m more Sales and $4m more Operating Income: a 10% increase in Sales and a 10%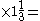 13 1/3% increase in Operating Income.
13 1/3% increase in Operating Income.
Assuming the model, for a given level of sales and profit, the DOL is higher the higher fixed costs are (an example): for a given level of sales and profit, a company with higher fixed costs has a higher contribution margin, and hence its Operating Income increases more rapidly with Sales than a company with lower fixed costs (and correspondingly lower contribution margin).
If a company has no fixed costs (and hence breaks even at zero), then its DOL equals 1: a 10% increase in Sales yields a 10% increase in Operating Income, and its operating margin
equals its contribution margin
: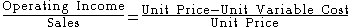
DOL is highest near the break-even point; in fact, at the break-even point, DOL is undefined, because it is infinite: an increase of 10% in sales, say, increases Operating Income for 0 to some positive number (say, $10), which is an infinite (or undefined) percentage change; in terms of margins, its Operating Margin is zero, so its DOL is undefined.
Similarly, for a very small positive Operating Income (say, $.1), a 10% increase in sales may increase Operating Income to $10, a 100x (or 9,900%) increase, for a DOL of 990; in terms of margins, its Operating Margin is very small, so its DOL is very large.
DOL is closely related to the rate of increase in the operating margin
: as sales increase past the break-even point, operating margin rapidly increases from 0% (reflected in a high DOL), and as sales increase, asymptotically approaches the contribution margin: thus the rate of change in operating margin decreases, as does the DOL, which asymptotically approaches 1.
perspective, the ratio of preproduction costs (e.g. design widgets) versus incremental production costs (e.g. produce a widget) is a useful measure of operating leverage.
a product or service is a method used to change the ratio of fixed costs to variable costs in a business. Outsourcing can be used to change the balance of this ratio by offering a move from fixed to variable cost and also by making variable costs more predictable.
Leverage (finance)
In finance, leverage is a general term for any technique to multiply gains and losses. Common ways to attain leverage are borrowing money, buying fixed assets and using derivatives. Important examples are:* A public corporation may leverage its equity by borrowing money...
, and of how risky (volatile) a company's operating income is.
Definition
There are various measures of operating leverage,which can be interpreted analogously to financial leverage.
Costs
One analogy is "fixed costs + variable costs = total costs ..similar to.. debt + equity = assets". This analogy is partly motivated because (for a given amount of debt) debt servicing is a fixed cost. This leads to two measures of operating leverage:One measure is fixed costs to total costs:
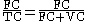
Compare to debt to value
Debt to equity ratio
The debt-to-equity ratio is a financial ratio indicating the relative proportion of shareholders' equity and debt used to finance a company's assets. Closely related to leveraging, the ratio is also known as Risk, Gearing or Leverage...
, which is

Another measure is fixed costs to variable costs:
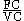
Compare to debt to equity ratio
Debt to equity ratio
The debt-to-equity ratio is a financial ratio indicating the relative proportion of shareholders' equity and debt used to finance a company's assets. Closely related to leveraging, the ratio is also known as Risk, Gearing or Leverage...
:
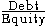
Both of these measures depend on sales: if the unit variable cost is constant, then as sales increase, operating leverage (as measured by fixed costs to total costs or variable costs) decreases.
Contribution
Contribution marginContribution margin
In cost-volume-profit analysis, a form of management accounting, contribution margin is the marginal profit per unit sale. It is a useful quantity in carrying out various calculations, and can be used as a measure of operating leverage...
is a measure of operating leverage: the higher the contribution margin is (the lower variable costs are as a percentage of total costs), the faster the profits increase with sales. Note that unlike other measures of operating leverage, in the linear Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
Coon-Volume-profit , in managerial economics is a form of cost accounting. It is a simplified model, useful for elementary instruction and for short-run decisions....
Model, contribution margin is a fixed quantity, and does not change with Sales.
Contribution = Sales - Variable Cost
DOL and Operating income
Operating leverage can also be measured in terms of change in operating income for a given change in sales (revenue).The Degree of Operating Leverage (DOL) can be computed in a number of equivalent ways; one way it is defined as the ratio of the percentage change in Operating Income for a given percentage change in Sales :
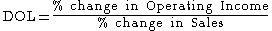
This can also be computed as Total Contribution Margin
Contribution margin
In cost-volume-profit analysis, a form of management accounting, contribution margin is the marginal profit per unit sale. It is a useful quantity in carrying out various calculations, and can be used as a measure of operating leverage...
over Operating Income:
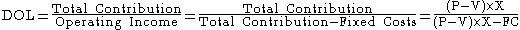
Alternatively, as Contribution Margin Ratio over Operating Margin
Operating margin
In business, operating margin — also known as operating income margin, operating profit margin and return on sales — is the ratio of operating income divided by net sales, usually presented in percent....
:

For instance, if a company has sales of 1,000,000 units, at price $50, unit variable cost of $10, and fixed costs of $10,000,000, then its unit contribution is $40, its Total Contribution is $40m, and its Operating Income is $30m, so its DOL is
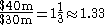
This could also be computed as 80%=$40m/$50m Contribution Margin Ratio divided by 60%=$30m/$50m Operating Margin.
It currently has Sales of $50m and Operating Income of $30m, so additional Unit Sales (say of 100,000 units) yield $5m more Sales and $4m more Operating Income: a 10% increase in Sales and a 10%
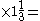 13 1/3% increase in Operating Income.
13 1/3% increase in Operating Income.Assuming the model, for a given level of sales and profit, the DOL is higher the higher fixed costs are (an example): for a given level of sales and profit, a company with higher fixed costs has a higher contribution margin, and hence its Operating Income increases more rapidly with Sales than a company with lower fixed costs (and correspondingly lower contribution margin).
If a company has no fixed costs (and hence breaks even at zero), then its DOL equals 1: a 10% increase in Sales yields a 10% increase in Operating Income, and its operating margin
Operating margin
In business, operating margin — also known as operating income margin, operating profit margin and return on sales — is the ratio of operating income divided by net sales, usually presented in percent....
equals its contribution margin
Contribution margin
In cost-volume-profit analysis, a form of management accounting, contribution margin is the marginal profit per unit sale. It is a useful quantity in carrying out various calculations, and can be used as a measure of operating leverage...
:
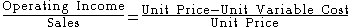
DOL is highest near the break-even point; in fact, at the break-even point, DOL is undefined, because it is infinite: an increase of 10% in sales, say, increases Operating Income for 0 to some positive number (say, $10), which is an infinite (or undefined) percentage change; in terms of margins, its Operating Margin is zero, so its DOL is undefined.
Similarly, for a very small positive Operating Income (say, $.1), a 10% increase in sales may increase Operating Income to $10, a 100x (or 9,900%) increase, for a DOL of 990; in terms of margins, its Operating Margin is very small, so its DOL is very large.
DOL is closely related to the rate of increase in the operating margin
Operating margin
In business, operating margin — also known as operating income margin, operating profit margin and return on sales — is the ratio of operating income divided by net sales, usually presented in percent....
: as sales increase past the break-even point, operating margin rapidly increases from 0% (reflected in a high DOL), and as sales increase, asymptotically approaches the contribution margin: thus the rate of change in operating margin decreases, as does the DOL, which asymptotically approaches 1.
Industry-specific
Examples of companies with high operating leverage include companies with high R&D costs, such as pharmaceuticals: it can cost billions to develop a drug, but then pennies to produce it. Hence from a life cycle cost analysisLife cycle cost analysis
Life cycle cost analysis may refer to:* Life cycle assessment, the investigation and valuation of the environmental impacts of a given product or service caused or necessitated by its existence...
perspective, the ratio of preproduction costs (e.g. design widgets) versus incremental production costs (e.g. produce a widget) is a useful measure of operating leverage.
Outsourcing
OutsourcingOutsourcing
Outsourcing is the process of contracting a business function to someone else.-Overview:The term outsourcing is used inconsistently but usually involves the contracting out of a business function - commonly one previously performed in-house - to an external provider...
a product or service is a method used to change the ratio of fixed costs to variable costs in a business. Outsourcing can be used to change the balance of this ratio by offering a move from fixed to variable cost and also by making variable costs more predictable.
See also
- Cost accountingCost accountingCost accounting information is designed for managers. Since managers are taking decisions only for their own organization, there is no need for the information to be comparable to similar information from other organizations...
- Efficiency ratioEfficiency ratioThe efficiency ratio, a ratio that is typically applied to banks, in simple terms is defined as expenses as a percentage of revenue , with a few variations. A lower percentage is better since that means expenses are low and earnings are high...
- Operating marginOperating marginIn business, operating margin — also known as operating income margin, operating profit margin and return on sales — is the ratio of operating income divided by net sales, usually presented in percent....
- Financial leverage
- Contribution marginContribution marginIn cost-volume-profit analysis, a form of management accounting, contribution margin is the marginal profit per unit sale. It is a useful quantity in carrying out various calculations, and can be used as a measure of operating leverage...

