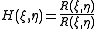Optical correlator
Encyclopedia
An optical correlator is a device for comparing two signals by utilising the Fourier transforming
properties of a lens
. It is commonly used in optics
for target tracking and identification.
which uses the cross correlation of the two signals.
The cross correlation or correlation plane,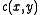 of a 2D signal
of a 2D signal 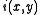 with
with 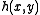 is
is
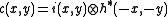
This can be re-expressed in Fourier space as
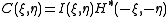
where the capital letters denote the Fourier transform of the lower case letter. So the correlation can then be calculated by inverse Fourier transforming the result.
theory a convex lens of focal length
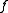 will produce the exact Fourier transform at a distance
will produce the exact Fourier transform at a distance  behind the lens of an object placed
behind the lens of an object placed 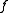 distance in front of the lens. So that complex amplitudes are multiplied the light source must be coherent
distance in front of the lens. So that complex amplitudes are multiplied the light source must be coherent
and is typically from a laser
. The input signal and filter are typically written onto a spatial light modulator
or SLM.
A typical arrangement is the 4f correlator. The input signal is written to an SLM which is illuminated with a laser. This is Fourier transformed with a lens and this is then modulated with a second SLM containing the filter. The resultant is again Fourier transformed with a second lens and the correlation result is captured on a camera.
 .
.
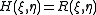
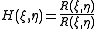
Fourier transform
In mathematics, Fourier analysis is a subject area which grew from the study of Fourier series. The subject began with the study of the way general functions may be represented by sums of simpler trigonometric functions...
properties of a lens
Lens (optics)
A lens is an optical device with perfect or approximate axial symmetry which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam. A simple lens consists of a single optical element...
. It is commonly used in optics
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
for target tracking and identification.
Introduction
The correlator has an input signal which is multiplied by some filter in the Fourier domain. An example filter is the matched filterMatched filter
In telecommunications, a matched filter is obtained by correlating a known signal, or template, with an unknown signal to detect the presence of the template in the unknown signal. This is equivalent to convolving the unknown signal with a conjugated time-reversed version of the template...
which uses the cross correlation of the two signals.
The cross correlation or correlation plane,
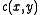 of a 2D signal
of a 2D signal 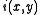 with
with 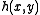 is
is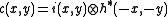
This can be re-expressed in Fourier space as
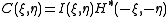
where the capital letters denote the Fourier transform of the lower case letter. So the correlation can then be calculated by inverse Fourier transforming the result.
Implementation
According to Fresnel DiffractionFresnel diffraction
In optics, the Fresnel diffraction equation for near-field diffraction, is an approximation of Kirchhoff-Fresnel diffraction that can be applied to the propagation of waves in the near field....
theory a convex lens of focal length
Focal length
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light. For an optical system in air, it is the distance over which initially collimated rays are brought to a focus...
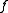 will produce the exact Fourier transform at a distance
will produce the exact Fourier transform at a distance  behind the lens of an object placed
behind the lens of an object placed 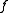 distance in front of the lens. So that complex amplitudes are multiplied the light source must be coherent
distance in front of the lens. So that complex amplitudes are multiplied the light source must be coherentCoherence (physics)
In physics, coherence is a property of waves that enables stationary interference. More generally, coherence describes all properties of the correlation between physical quantities of a wave....
and is typically from a laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
. The input signal and filter are typically written onto a spatial light modulator
Spatial light modulator
A spatial light modulator is an object that imposes some form of spatially-varying modulation on a beam of light. A simple example is an overhead projector transparency. Usually when the phrase SLM is used, it means that the transparency can be controlled by a computer. In the 1980s, large SLMs...
or SLM.
A typical arrangement is the 4f correlator. The input signal is written to an SLM which is illuminated with a laser. This is Fourier transformed with a lens and this is then modulated with a second SLM containing the filter. The resultant is again Fourier transformed with a second lens and the correlation result is captured on a camera.
Filter design
Many filters have been designed to be used with an optical correlator. Some have been proposed to address hardware limitations, others were developed to optimize a merit function or to be invariant under a certain transformation.Matched filter
The matched filter maximizes the signal-to-noise ratio and is simply obtained by using as a filter the Fourier transform of the reference signal .
.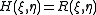
Phase-only filter
The phase-only filter is easier to implement due to limitation of many SLMs and has been shown to be more discriminant than the matched filter.