
Oregon Treaty
Encyclopedia
Treaty
A treaty is an express agreement under international law entered into by actors in international law, namely sovereign states and international organizations. A treaty may also be known as an agreement, protocol, covenant, convention or exchange of letters, among other terms...
between the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
and the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
that was signed on June 15, 1846, in Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution....
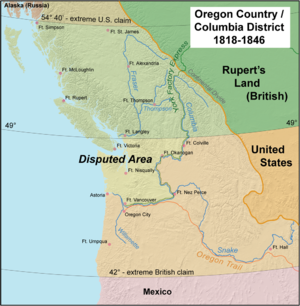
The treaty brought an end to the Oregon boundary dispute
Oregon boundary dispute
The Oregon boundary dispute, or the Oregon Question, arose as a result of competing British and American claims to the Pacific Northwest of North America in the first half of the 19th century. Both the United Kingdom and the United States had territorial and commercial aspirations in the region...
by settling competing American and British claims to the Oregon Country
Oregon Country
The Oregon Country was a predominantly American term referring to a disputed ownership region of the Pacific Northwest of North America. The region was occupied by British and French Canadian fur traders from before 1810, and American settlers from the mid-1830s, with its coastal areas north from...
, which had been jointly occupied by both Britain and the U.S. since the Treaty of 1818
Treaty of 1818
The Convention respecting fisheries, boundary and the restoration of slaves between the United States of America and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, also known as the London Convention, Anglo-American Convention of 1818, Convention of 1818, or simply the Treaty of 1818, was a...
.
Background
The Treaty of 1818 set the boundary between the United States and British North AmericaBritish North America
British North America is a historical term. It consisted of the colonies and territories of the British Empire in continental North America after the end of the American Revolutionary War and the recognition of American independence in 1783.At the start of the Revolutionary War in 1775 the British...
along the 49th parallel
49th parallel north
The 49th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 49 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean....
of north latitude from Minnesota
Minnesota
Minnesota is a U.S. state located in the Midwestern United States. The twelfth largest state of the U.S., it is the twenty-first most populous, with 5.3 million residents. Minnesota was carved out of the eastern half of the Minnesota Territory and admitted to the Union as the thirty-second state...
to the "Stony Mountains" (now known as the Rocky Mountains
Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains are a major mountain range in western North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch more than from the northernmost part of British Columbia, in western Canada, to New Mexico, in the southwestern United States...
). West of those mountains was known to the Americans as the Oregon Country
Oregon Country
The Oregon Country was a predominantly American term referring to a disputed ownership region of the Pacific Northwest of North America. The region was occupied by British and French Canadian fur traders from before 1810, and American settlers from the mid-1830s, with its coastal areas north from...
and to the British as the Columbia Department or Columbia District of the Hudson's Bay Company
Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company , abbreviated HBC, or "The Bay" is the oldest commercial corporation in North America and one of the oldest in the world. A fur trading business for much of its existence, today Hudson's Bay Company owns and operates retail stores throughout Canada...
. (Also included in the region was the southern portion of another fur district, New Caledonia
New Caledonia (Canada)
New Caledonia was the name given to a district of the Hudson's Bay Company that comprised the territory largely coterminous with the present-day province of British Columbia, Canada. Though not a British colony, New Caledonia was part of the British claim to North America. Its administrative...
.) The treaty provided for joint control of that land for ten years. Both countries could claim land and both were guaranteed free navigation throughout.
Joint control steadily grew less tolerable for both sides. After a British minister rejected U.S. President
President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
James K. Polk
James K. Polk
James Knox Polk was the 11th President of the United States . Polk was born in Mecklenburg County, North Carolina. He later lived in and represented Tennessee. A Democrat, Polk served as the 17th Speaker of the House of Representatives and the 12th Governor of Tennessee...
's offer to settle the boundary at the 49th parallel north
49th parallel north
The 49th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 49 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean....
, Democratic
Democratic Party (United States)
The Democratic Party is one of two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Republican Party. The party's socially liberal and progressive platform is largely considered center-left in the U.S. political spectrum. The party has the lengthiest record of continuous...
expansionists militantly called for the annexation
Annexation
Annexation is the de jure incorporation of some territory into another geo-political entity . Usually, it is implied that the territory and population being annexed is the smaller, more peripheral, and weaker of the two merging entities, barring physical size...
of the entire region up to Parallel 54°40′ north, the southern limit of Russian America as established by parallel treaties between the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
and the US (1824) and Britain (1825). However, after the outbreak of the Mexican-American War in April of 1846 diverted U.S. attention and military resources, a compromise was reached in the ongoing negotiations in Washington, D.C. and the matter was settled by the Polk administration (to the dismay of its own party's militant hardliners) to avoid a two war situation and the third war with the formidable military strength of Great Britain in less than 70 years.
Negotiations
The treaty was negotiated by U.S. Secretary of StateUnited States Secretary of State
The United States Secretary of State is the head of the United States Department of State, concerned with foreign affairs. The Secretary is a member of the Cabinet and the highest-ranking cabinet secretary both in line of succession and order of precedence...
James Buchanan
James Buchanan
James Buchanan, Jr. was the 15th President of the United States . He is the only president from Pennsylvania, the only president who remained a lifelong bachelor and the last to be born in the 18th century....
, who later became president, and Richard Pakenham, British envoy to the United States and member of the Privy Council of the United Kingdom
Privy Council of the United Kingdom
Her Majesty's Most Honourable Privy Council, usually known simply as the Privy Council, is a formal body of advisers to the Sovereign in the United Kingdom...
for Queen Victoria. The treaty was signed on June 15, 1846.
The Oregon Treaty set the U.S. and British North America
British North America
British North America is a historical term. It consisted of the colonies and territories of the British Empire in continental North America after the end of the American Revolutionary War and the recognition of American independence in 1783.At the start of the Revolutionary War in 1775 the British...
n border at the 49th parallel
49th parallel north
The 49th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 49 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean....
with the exception of Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is a large island in British Columbia, Canada. It is one of several North American locations named after George Vancouver, the British Royal Navy officer who explored the Pacific Northwest coast of North America between 1791 and 1794...
, which was retained in its entirety by the British. Vancouver Island, with all coastal islands, was constituted as the Colony of Vancouver Island
Colony of Vancouver Island
The Colony of Vancouver Island , was a crown colony of British North America from 1849 to 1866, after which it was united with British Columbia. The united colony joined the Dominion of Canada through Confederation in 1871...
in 1849. The U.S. portion of the region was organized as Oregon Territory
Oregon Territory
The Territory of Oregon was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from August 14, 1848, until February 14, 1859, when the southwestern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Oregon. Originally claimed by several countries , the region was...
on August 14, 1848, with Washington Territory
Washington Territory
The Territory of Washington was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from February 8, 1853, until November 11, 1889, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Washington....
being formed from it in 1853. The British portion remained unorganized until 1858 when the Colony of British Columbia
Colony of British Columbia
The Colony of British Columbia was a crown colony in British North America from 1858 until 1866. At its creation, it physically constituted approximately half the present day Canadian province of British Columbia, since it did not include the Colony of Vancouver Island, the vast and still largely...
was declared as a result of the Fraser Canyon Gold Rush
Fraser Canyon Gold Rush
The Fraser Canyon Gold Rush, began in 1858 after gold was discovered on the Thompson River in British Columbia at its confluence with the Nicoamen River. This was a few miles upstream from the Thompson's confluence with the Fraser River at present-day Lytton...
and fears of re-asserted American expansionist intentions. The two British colonies were amalgamated in 1866 as the United Colonies of Vancouver Island and British Columbia
United Colonies of Vancouver Island and British Columbia
The Colony of British Columbia is a crown colony that resulted from the amalgamation of the two former colonies, the Colony of Vancouver Island and the mainland Colony of British Columbia...
. When the Colony of British Columbia joined Canada in 1871, the 49th Parallel and marine boundaries established by the Oregon Treaty became the U.S.-Canadian border.
Treaty definitions
The treaty defined the border in the Strait of Juan de FucaStrait of Juan de Fuca
The Strait of Juan de Fuca is a large body of water about long that is the Salish Sea outlet to the Pacific Ocean...
through the major channel. The "major channel" was not defined, giving rise to further disputes
Pig War
The Pig War was a confrontation in 1859 between the United States and the British Empire over the boundary between the US and British North America. The territory in dispute was the San Juan Islands, which lie between Vancouver Island and the North American mainland...
in the San Juan Islands
San Juan Islands
The San Juan Islands are an archipelago in the northwest corner of the contiguous United States between the US mainland and Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. The San Juan Islands are part of the U.S...
in 1859. Other provisions included:
- Navigation of "channel[s] and straits, south of the forty-ninth parallel of north latitude, remain free and open to both parties."
- The "Puget's Sound Agricultural CompanyPugets Sound Agricultural CompanyThe Puget Sound Agricultural Company , commonly referred to with variations of the name using Puget Sound or Puget's Sound, was a joint stock company formed around 1840 as a subsidiary of the Hudson's Bay Company . The purpose of the company was ostensibly to promote settlement by British subjects...
" (a subsidiary of the Hudson's Bay Company) retains the right to their property north of the Columbia RiverColumbia RiverThe Columbia River is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, Canada, flows northwest and then south into the U.S. state of Washington, then turns west to form most of the border between Washington and the state...
, and shall be compensated for properties surrendered if required by the United States. - The property rights of the Hudson's Bay CompanyHudson's Bay CompanyThe Hudson's Bay Company , abbreviated HBC, or "The Bay" is the oldest commercial corporation in North America and one of the oldest in the world. A fur trading business for much of its existence, today Hudson's Bay Company owns and operates retail stores throughout Canada...
and all British subjectBritish subjectIn British nationality law, the term British subject has at different times had different meanings. The current definition of the term British subject is contained in the British Nationality Act 1981.- Prior to 1949 :...
s south of the new boundary will be respected.
See also
- James K. PolkJames K. PolkJames Knox Polk was the 11th President of the United States . Polk was born in Mecklenburg County, North Carolina. He later lived in and represented Tennessee. A Democrat, Polk served as the 17th Speaker of the House of Representatives and the 12th Governor of Tennessee...
- Oregon MissionOregon MissionThe Oregon Mission began as an effort by the Methodist Episcopal Church to convert the native Indians of the far west to Christianity. This mission, under the leadership of Jason Lee, largely failed in its initial goal, but played a significant role in the westward expansion of the United States...
- Joseph Smith HarrisJoseph Smith HarrisJoseph Smith Harris was an American surveyor, civil engineer, and railroad executive. Largely self-taught, he worked on several projects for the U.S. government, including the Coast Survey of the Mississippi Sound in 1854–56 and the Northwest Boundary Survey of 1857–61...
' account of surveying the border

