Outline of Armenia
Encyclopedia
Mountain
Image:Himalaya_annotated.jpg|thumb|right|The Himalayan mountain range with Mount Everestrect 58 14 160 49 Chomo Lonzorect 200 28 335 52 Makalurect 378 24 566 45 Mount Everestrect 188 581 920 656 Tibetan Plateaurect 250 406 340 427 Rong River...
ous, sovereign country located in Eurasia
Eurasia
Eurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
between the Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
and the Caspian Sea
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. The sea has a surface area of and a volume of...
in the Southern Caucasus. Armenia borders Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
to the west, Georgia
Georgia (country)
Georgia is a sovereign state in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the southwest by Turkey, to the south by Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital of...
to the north, Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan , officially the Republic of Azerbaijan is the largest country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the east, Russia to the north, Georgia to the northwest, Armenia to the west, and Iran to...
to the east, and Iran
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
and the Nakhchivan exclave of Azerbaijan to the south. A transcontinental country
Transcontinental country
This is a list of countries spanning more than one continent, known as transcontinental states. While there are many countries with non-contiguous overseas territories fitting this definition, only a limited number of countries have territory spanning an overland continental...
at the juncture of Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
and Southwest Asia
Southwest Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, Southwest Asia or Southwestern Asia are terms that describe the westernmost portion of Asia. The terms are partly coterminous with the Middle East, which describes a geographical position in relation to Western Europe rather than its location within Asia...
, Armenia has had and continues to have extensive socio-political and cultural connections with Europe.
A former republic of the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
, Armenia is a unitary
Unitary state
A unitary state is a state governed as one single unit in which the central government is supreme and any administrative divisions exercise only powers that their central government chooses to delegate...
, multiparty
Multi-party system
A multi-party system is a system in which multiple political parties have the capacity to gain control of government separately or in coalition, e.g.The Conservative-Liberal Democrat coalition in the United Kingdom formed in 2010. The effective number of parties in a multi-party system is normally...
, democratic
Democracy
Democracy is generally defined as a form of government in which all adult citizens have an equal say in the decisions that affect their lives. Ideally, this includes equal participation in the proposal, development and passage of legislation into law...
nation-state
Nation-state
The nation state is a state that self-identifies as deriving its political legitimacy from serving as a sovereign entity for a nation as a sovereign territorial unit. The state is a political and geopolitical entity; the nation is a cultural and/or ethnic entity...
with an ancient and historic cultural heritage. The Kingdom of Armenia was the first state to adopt Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
as its religion in the early years of the 4th century (the traditional date is 301). The modern Republic of Armenia is constitutionally a secular state, although the Christian faith plays a major role in the history and identification of the Armenian people.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Armenia:
General reference
- Pronunciation: ɑrˈmiːniə
- Common English country name: ArmeniaArmeniaArmenia , officially the Republic of Armenia , is a landlocked mountainous country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia...
- Official English country name: Republic of Armenia
- Common endonym(s): Հայաստան (Hayastan)
- Official endonym(s): Հայաստանի Հանրապետություն (Hayastani Hanrapetut’yun)
- Adjectival(s): Armenian
- Demonym(s): Armenian
- EtymologyEtymologyEtymology is the study of the history of words, their origins, and how their form and meaning have changed over time.For languages with a long written history, etymologists make use of texts in these languages and texts about the languages to gather knowledge about how words were used during...
: Name of Armenia - International rankings of ArmeniaInternational rankings of ArmeniaThe following are international rankings of Armenia.-Demographics:*United Nations: Population, ranked X out of 223 countries*CIA World Factbook: Urbanization ranked X out of 193 countries-Economy:...
- ISO country codes: AM, ARM, 051
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:AMISO 3166-2:AMISO 3166-2:AM is the entry for Armenia in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization , which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1.Currently for Armenia, ISO 3166-2 codes are...
- InternetInternetThe Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
country code top-level domainCountry code top-level domainA country code top-level domain is an Internet top-level domain generally used or reserved for a country, a sovereign state, or a dependent territory....
: .am.am.am is the Internet country code top-level domain for Armenia.- Regulation :The registry for .am is operated by , the local chapter of the Internet Society.Regulatory notes:...
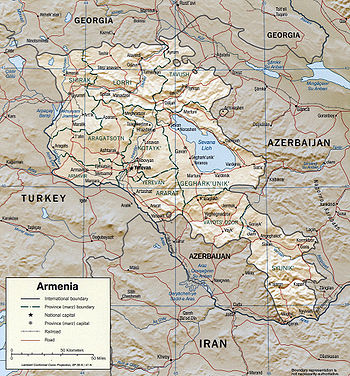
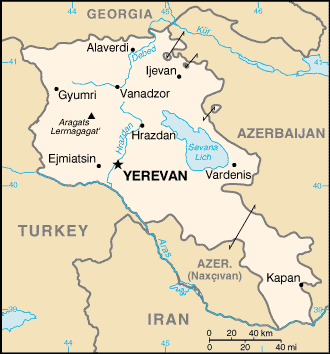
Geography of Armenia
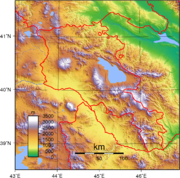
- Armenia is: a landlocked country
- Location:
- Northern HemisphereNorthern HemisphereThe Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
and Eastern HemisphereEastern HemisphereThe Eastern Hemisphere, also Eastern hemisphere or eastern hemisphere, is a geographical term for the half of the Earth that is east of the Prime Meridian and west of 180° longitude. It is also used to refer to Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australasia, vis-à-vis the Western Hemisphere, which includes...
- EurasiaEurasiaEurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
- AsiaAsiaAsia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
- Southwest AsiaSouthwest AsiaWestern Asia, West Asia, Southwest Asia or Southwestern Asia are terms that describe the westernmost portion of Asia. The terms are partly coterminous with the Middle East, which describes a geographical position in relation to Western Europe rather than its location within Asia...
- CaucasusCaucasusThe Caucasus, also Caucas or Caucasia , is a geopolitical region at the border of Europe and Asia, and situated between the Black and the Caspian sea...
- South CaucasusSouth CaucasusThe South Caucasus is a geopolitical region located on the border of Eastern Europe and Southwest Asia also referred to as Transcaucasia, or The Trans-Caucasus...
- South Caucasus
- Caucasus
- Southwest Asia
- EuropeEuropeEurope is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
- Eastern EuropeEastern EuropeEastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
- CaucasusCaucasusThe Caucasus, also Caucas or Caucasia , is a geopolitical region at the border of Europe and Asia, and situated between the Black and the Caspian sea...
- South CaucasusSouth CaucasusThe South Caucasus is a geopolitical region located on the border of Eastern Europe and Southwest Asia also referred to as Transcaucasia, or The Trans-Caucasus...
- South Caucasus
- Caucasus
- Eastern Europe
- Asia
- Eurasia
- Time zoneTime zoneA time zone is a region on Earth that has a uniform standard time for legal, commercial, and social purposes. In order for the same clock time to always correspond to the same portion of the day as the Earth rotates , different places on the Earth need to have different clock times...
: Armenia TimeArmenia TimeArmenia Time is a time zone used in Armenia. The standard time zone is four hours ahead of UTC at UTC+4 and the summer time one hour ahead of the standard AMT at UTC+5.-External links:...
UTC+04, Armenia Summer Time UTC+05 - Extreme points of Armenia
- High: Mount AragatsMount AragatsMount Aragats , Alagoz - is a large andesitic-to-dacitic stratovolcano in NW Armenia about 40 km NW of the capital city of Yerevan. It is the highest point in Armenia, located in the province of Aragatsotn, northwest from Yerevan. Located on its slopes are the Byurakan Observatory and the...
4090 m (13,419 ft) - Low: DebedDebedThe Debed or Debeda is a river in Armenia and Georgia. It also serves as a natural boundary between Armenia and Georgia at the village Sadakhlo, Georgia....
400 m (1,312 ft)
- High: Mount Aragats
- Land boundaries: 1,254 km
- Northern Hemisphere
-
 Azerbaijan 787 km
Azerbaijan 787 km Turkey 268 km
Turkey 268 km Georgia (country) 164 km
Georgia (country) 164 km Iran 35 km
Iran 35 km
- Coastline: none
- Population of Armenia: 3,231,900 – 135th most populous country
- Area of Armenia: 29800 square kilometres (11,505.8 sq mi) – 142nd largest country
- Atlas of Armenia
Environment of Armenia

- Climate of Armenia
- Environmental issues in Armenia
- Ecoregions in Armenia
- Renewable energy in Armenia
- Geology of Armenia
- Protected areas of Armenia
- Biosphere reserves in Armenia
- National parks of Armenia
- Wildlife of ArmeniaWildlife of ArmeniaWildlife of Armenia includes its flora and fauna and their natural habitats.Wildlife in Armenia includes wild boar, porcupines, various lizards, snakes and numerous species of birds...
- Flora of Armenia
- Fauna of ArmeniaFauna of ArmeniaFauna in Armenia is diverse given the country's relatively small geographic size, owing to the varied habitats created by the area's mountainess terrain. Armenia is an important area for migratory animals, about 350 different bird species were recorded in the country...
Natural geographic features of Armenia
- Glaciers of Armenia
- Islands of Armenia
- Lakes of Armenia
- Mountains of ArmeniaMountains of Armeniathumb|right|A view of [[Mount Aragats]].Armenia a land of rugged mountains and extinct volcanoes, its highest point is Mount Aragats, 13,435 ft .-Mountain ranges:# Javakheti mountain range# Armeno-Georgian mountain range...
- Rivers of Armenia
- Waterfalls of Armenia
- Valleys of Armenia
- World Heritage Sites in Armenia
Administrative divisions of Armenia
- Provinces of Armenia
Provinces of Armenia
Armenia
Armenia
Armenia , officially the Republic of Armenia , is a landlocked mountainous country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia...
is divided into ten provinces and a special administrative division for the capital, Yerevan:
- YerevanYerevanYerevan is the capital and largest city of Armenia and one of the world's oldest continuously-inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerevan is the administrative, cultural, and industrial center of the country...
- Shirak
- ArmavirArmavir (province)Armavir is a province of Armenia with the capital in Armavir. It is in the west of the country, located in the Ararat valley, between Mount Ararat and Mount Aragats, and shares a 45-mile border with Turkey to the south and west...
- Lori
- AraratArarat (province)Ararat is a province of Armenia with capital in Artashat. Named after Mount Ararat, the province borders Turkey to the west and Azerbaijan's Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic to the south...
- Kotayk
- Gegharkunik
- SyunikSyunikSyunik is the southernmost province of Armenia. It borders the Vayots Dzor marz to the north, Azerbaijan's Nakhchivan exclave to the west, Karabakh to the east, and Iran to the south. Its capital is Kapan. Other important cities and towns include Goris, Sisian, Meghri, Agarak, and Dastakert...
- AragatsotnAragatsotnAragatsotn is a province of Armenia. It is in the west of the country, and its capital is Ashtarak. The name means "a foot of Aragats" . During the Arsacid Dynasty of the Kingdom of Armenia, the region was part of the Ayrarat province...
- TavushTavushTavush is a province of Armenia. The marz of Tavush is located in the north of Armenia and borders on Georgia and Azerbaijan.It is well known for its mountains. The most part of its territory is situated 800-1,000 m above sea level...
- Vayots DzorVayots DzorVayots Dzor is a province of Armenia. It lies in the south-east of the country, bordering the Nakhichevan exclave of Azerbaijan in the west and the Azerbaijan in the east. It covers an area of 2,308 km². With a population of only 53,230 , it is the most sparsely populated province in the country...
Cities of Armenia
- Capital of Armenia: Yerevan
- Cities of Armenia
- YerevanYerevanYerevan is the capital and largest city of Armenia and one of the world's oldest continuously-inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerevan is the administrative, cultural, and industrial center of the country...
Government and politics of Armenia
- Form of governmentForm of governmentA form of government, or form of state governance, refers to the set of political institutions by which a government of a state is organized. Synonyms include "regime type" and "system of government".-Empirical and conceptual problems:...
: presidentialPresidential systemA presidential system is a system of government where an executive branch exists and presides separately from the legislature, to which it is not responsible and which cannot, in normal circumstances, dismiss it....
representative democraticRepresentative democracyRepresentative democracy is a form of government founded on the principle of elected individuals representing the people, as opposed to autocracy and direct democracy...
republicRepublicA republic is a form of government in which the people, or some significant portion of them, have supreme control over the government and where offices of state are elected or chosen by elected people. In modern times, a common simplified definition of a republic is a government where the head of... - Capital of Armenia: Yerevan
- Elections in ArmeniaElections in ArmeniaElections in Armenia gives information on election and election results in Armenia.Armenia elects on national level a head of state - the president - and a legislature. The president is elected for a five-year term by the people...
- (specific elections)
- Political parties in Armenia
- Political scandals of Armenia
- Taxation in ArmeniaTaxation in ArmeniaArmenia's complex tax system was revised in 1997 and again in 2001. The top corporate profit tax rate was lowered from 30% to 20%. As of July 1, 2001 a single rate was applied to all taxable profits, defined as the difference between revenues and the sum of wages, amortization payments, raw and...
Executive branch of the government of Armenia
- Head of stateHead of StateA head of state is the individual that serves as the chief public representative of a monarchy, republic, federation, commonwealth or other kind of state. His or her role generally includes legitimizing the state and exercising the political powers, functions, and duties granted to the head of...
: President of ArmeniaPresident of ArmeniaPresident of Armenia is the title of the head of state of Armenia since its independence from the Soviet Union in 1991.-Democratic Republic of Armenia :*Avetis Aharonyan *Avetik Sahakyan *Avetis Aharonyan -Transcaucasian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and Armenian...
, Serzh Sargsyan - Head of governmentHead of governmentHead of government is the chief officer of the executive branch of a government, often presiding over a cabinet. In a parliamentary system, the head of government is often styled prime minister, chief minister, premier, etc...
: Prime Minister of ArmeniaPrime Minister of ArmeniaThe Prime Minister of Armenia is the most senior minister within the Armenian government, and is required by the constitution to "oversee the Government's regular activities and coordinate the work of the Ministers." The Prime Minister is appointed by the President of Armenia, but can be removed by...
, Tigran SargsyanTigran SargsyanTigran Sargsyan has been the Prime Minister of Armenia since 9 April 2008.Tigran Sargsyan was born in Kirovakan, Armenian SSR . From 1980 to 1983, he attended Leningrad's Voznesenski Financial and Economic Institute. From 1983 to 1987 his postgraduate education ended in obtaining PhD degree... - Cabinet of Armenia
Legislative branch of the government of Armenia
- Parliament of Armenia (unicameral)
- Azgayin Zhoghov
Judicial branch of the government of Armenia
- Supreme Court of Armenia
Foreign relations of Armenia
- Diplomatic missions in Armenia
- Diplomatic missions of ArmeniaDiplomatic missions of ArmeniaThis is a list of diplomatic missions of Armenia. Armenia is a landlocked country located in the Southern Caucasus. Over 5 million Armenians reside abroad, with large communities located in Russia, France, Iran, United States, Georgia, Syria, Lebanon, Argentina, and Ukraine...
International organization membership
The Republic of Armenia is a member of:- Arab Bank for Economic Development in AfricaArab Bank for Economic Development in AfricaThe Arab Bank for Economic Development in Africa is a financial institution funded by the Governments of the Member States of the League of Arab States on 18 February 1974 . It is an independent international institution enjoying international legal status and autonomy in administrative and...
(ABEDA) (observer) - Asian Development BankAsian Development BankThe Asian Development Bank is a regional development bank established on 22 August 1966 to facilitate economic development of countries in Asia...
(ADB) - Black Sea Economic Cooperation Zone (BSEC)
- Collective Security Treaty OrganizationCollective Security Treaty OrganizationThe Collective Security Treaty Organization is an intergovernmental military alliance which was signed on 15 May 1992. On 7 October 2002, the Presidents of Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia and Tajikistan signed a charter in Tashkent founding the CSTO.Nikolai Bordyuzha was appointed...
(CSTO) - Commonwealth of Independent StatesCommonwealth of Independent StatesThe Commonwealth of Independent States is a regional organization whose participating countries are former Soviet Republics, formed during the breakup of the Soviet Union....
(CIS) - Council of EuropeCouncil of EuropeThe Council of Europe is an international organisation promoting co-operation between all countries of Europe in the areas of legal standards, human rights, democratic development, the rule of law and cultural co-operation...
(CE) - Eurasian Economic CommunityEurasian Economic CommunityThe Eurasian Economic Community originated from the Commonwealth of Independent States customs union between Belarus, Russia and Kazakhstan on 29 March 1996...
(EAEC) (observer) - Euro-Atlantic Partnership CouncilEuro-Atlantic Partnership CouncilThe Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council , a NATO institution, is a multilateral forum created to improve relations between NATO and non-NATO countries in Europe and those parts of Asia on the European periphery. The member states meet to cooperate and consult on a range of political and security issues...
(EAPC) - European Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentEuropean Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentFounded in 1991, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development uses the tools of investment to help build market economies and democracies in 30 countries from central Europe to central Asia. Its mission was to support the formerly communist countries in the process of establishing their...
(EBRD) - Food and Agriculture OrganizationFood and Agriculture OrganizationThe Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations is a specialised agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger. Serving both developed and developing countries, FAO acts as a neutral forum where all nations meet as equals to negotiate agreements and...
(FAO) - General Confederation of Trade UnionsGeneral Confederation of Trade UnionsThe General Confederation of Trade Unions or GCTU is an international trade union confederation. It was founded April 16, 1992 and incorporates members from the Commonwealth of Independent States....
(GCTU) - International Atomic Energy AgencyInternational Atomic Energy AgencyThe International Atomic Energy Agency is an international organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy, and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. The IAEA was established as an autonomous organization on 29 July 1957...
(IAEA) - International Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentInternational Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentThe International Bank for Reconstruction and Development is one of five institutions that compose the World Bank Group. The IBRD is an international organization whose original mission was to finance the reconstruction of nations devastated by World War II. Now, its mission has expanded to fight...
(IBRD) - International Civil Aviation OrganizationInternational Civil Aviation OrganizationThe International Civil Aviation Organization , pronounced , , is a specialized agency of the United Nations. It codifies the principles and techniques of international air navigation and fosters the planning and development of international air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth...
(ICAO) - International Criminal CourtInternational Criminal CourtThe International Criminal Court is a permanent tribunal to prosecute individuals for genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes, and the crime of aggression .It came into being on 1 July 2002—the date its founding treaty, the Rome Statute of the...
(ICCt) (signatory) - International Criminal Police Organization (Interpol)
- International Development AssociationInternational Development AssociationThe International Development Association , is the part of the World Bank that helps the world’s poorest countries. It complements the World Bank's other lending arm — the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development — which serves middle-income countries with capital investment and...
(IDA) - International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesInternational Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesThe International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies is a humanitarian institution that is part of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement along with the ICRC and 186 distinct National Societies...
(IFRCS) - International Finance CorporationInternational Finance CorporationThe International Finance Corporation promotes sustainable private sector investment in developing countries.IFC is a member of the World Bank Group and is headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States....
(IFC) - International Fund for Agricultural DevelopmentInternational Fund for Agricultural DevelopmentThe International Fund for Agricultural Development , a specialized agency of the United Nations, was established as an international financial institution in 1977 as one of the major outcomes of the 1974 World Food Conference. IFAD is dedicated to eradicating rural poverty in developing countries...
(IFAD) - International Labour OrganizationInternational Labour OrganizationThe International Labour Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that deals with labour issues pertaining to international labour standards. Its headquarters are in Geneva, Switzerland. Its secretariat — the people who are employed by it throughout the world — is known as the...
(ILO) - International Monetary FundInternational Monetary FundThe International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
(IMF) - International Olympic CommitteeInternational Olympic CommitteeThe International Olympic Committee is an international corporation based in Lausanne, Switzerland, created by Pierre de Coubertin on 23 June 1894 with Demetrios Vikelas as its first president...
(IOC) - International Organization for MigrationInternational Organization for MigrationThe International Organization for Migration is an intergovernmental organization. It was initially established in 1951 as the Intergovernmental Committee for European Migration to help resettle people displaced by World War II....
(IOM) - International Organization for StandardizationInternational Organization for StandardizationThe International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
(ISO) - International Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementInternational Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementThe International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is an international humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide which was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and to prevent and alleviate human...
(ICRM) - International Telecommunication UnionInternational Telecommunication UnionThe International Telecommunication Union is the specialized agency of the United Nations which is responsible for information and communication technologies...
(ITU) - International Telecommunications Satellite OrganizationInternational Telecommunications Satellite OrganizationThe International Telecommunications Satellite Organization is an intergovernmental organisation charged with overseeing the public service obligations of Intelsat.-External links:*...
(ITSO) - Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU)
- Multilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyMultilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyThe Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency is a member organization of the World Bank Group that offers political risk insurance. It was established to promote foreign direct investment into developing countries. MIGA was founded in 1988 with a capital base of $1 billion and is headquartered in...
(MIGA) - Nonaligned Movement (NAM) (observer)
- Organisation internationale de la Francophonie (OIF) (associate member)
- Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)
- Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW)
- Organization of American StatesOrganization of American StatesThe Organization of American States is a regional international organization, headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States...
(OAS) (observer) - Partnership for PeacePartnership for PeacePartnership for Peace is a North Atlantic Treaty Organisation program aimed at creating trust between NATO and other states in Europe and the former Soviet Union; 22 States are members...
(PFP) - United NationsUnited NationsThe United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
(UN) - United Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentUnited Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentThe United Nations Conference on Trade and Development was established in 1964 as a permanent intergovernmental body. It is the principal organ of the United Nations General Assembly dealing with trade, investment, and development issues....
(UNCTAD) - United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- United Nations Industrial Development OrganizationUnited Nations Industrial Development OrganizationThe United Nations Industrial Development Organization , French/Spanish acronym ONUDI, is a specialized agency in the United Nations system, headquartered in Vienna, Austria...
(UNIDO) - Universal Postal UnionUniversal Postal UnionThe Universal Postal Union is an international organization that coordinates postal policies among member nations, in addition to the worldwide postal system. The UPU contains four bodies consisting of the Congress, the Council of Administration , the Postal Operations Council and the...
(UPU) - World Customs OrganizationWorld Customs OrganizationThe World Customs Organization is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. With its worldwide membership, the WCO is recognized as the voice of the global customs community...
(WCO) - World Federation of Trade UnionsWorld Federation of Trade UnionsThe World Federation of Trade Unions was established in 1945 to replace the International Federation of Trade Unions. Its mission was to bring together trade unions across the world in a single international organization, much like the United Nations...
(WFTU) - World Health OrganizationWorld Health OrganizationThe World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
(WHO) - World Intellectual Property OrganizationWorld Intellectual Property OrganizationThe World Intellectual Property Organization is one of the 17 specialized agencies of the United Nations. WIPO was created in 1967 "to encourage creative activity, to promote the protection of intellectual property throughout the world"....
(WIPO) - World Meteorological OrganizationWorld Meteorological OrganizationThe World Meteorological Organization is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 189 Member States and Territories. It originated from the International Meteorological Organization , which was founded in 1873...
(WMO) - World Tourism OrganizationWorld Tourism OrganizationThe World Tourism Organization , based in Madrid, Spain, is a United Nations agency dealing with questions relating to tourism. It compiles the World Tourism rankings. The World Tourism Organization is a significant global body, concerned with the collection and collation of statistical information...
(UNWTO) - World Trade OrganizationWorld Trade OrganizationThe World Trade Organization is an organization that intends to supervise and liberalize international trade. The organization officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade , which commenced in 1948...
(WTO)
Law and order in Armenia
- Capital punishment in ArmeniaCapital punishment in ArmeniaThe last execution in Armenia took place on the 30 August 1991; it was carried out by a single bullet. Death penalty remained a legal punishment for murder, treason, and serious crimes of a military nature, until its abolition in 2003....
- Constitution of ArmeniaConstitution of ArmeniaThe Constitution of Armenia was adopted by a nationwide referendum on July 5, 1995. This constitution established Armenia as a democratic, sovereign, social, and constitutional state. Yerevan is defined as the state's capital. Power is vested in its citizens, who exercise it directly through the...
- Corruption in ArmeniaCorruption in ArmeniaPolitical corruption in Armenia is a widespread and growing problem in Armenian society. The United Nations Development Programme in Armenia views corruption in Armenia as "a serious challenge to its development."- Corruption levels :...
- Crime in ArmeniaCrime in ArmeniaCrime in Armenia is multi-dimensional. It includes human trafficking, domestic violence, murder, political murder, contract killing, tax evasion, corruption, extortion, money laundering, police brutality, organized crime, and clan or gang violence....
- Human rights in ArmeniaHuman rights in ArmeniaHuman rights in Armenia are better than those in most former Soviet republics and have drawn closer to acceptable standards, especially economically. Still, there are several considerable problems. Overall, Armenia's human rights record is similar to that of Georgia's...
- LGBT rights in Armenia
- Freedom of religion in ArmeniaFreedom of religion in ArmeniaThe Constitution as amended in December 2005 provides for freedom of religion; however, the law places some restrictions on the religious freedom of adherents of minority religious groups, and there were some restrictions in practice. The Armenian Church, which has formal legal status as the...
- Law enforcement in ArmeniaLaw enforcement in ArmeniaThe Police of the Republic of Armenia is the national police of Armenia. The head is Alik Sargsyan, in office since 29 May 2008.-Leadership:The activities of the Police are directed by the Chief of the Police, who is appointed by the President of Armenia at the nomination of the Prime Minister of...
Military of Armenia
- Command
- Commander-in-chiefCommander-in-ChiefA commander-in-chief is the commander of a nation's military forces or significant element of those forces. In the latter case, the force element may be defined as those forces within a particular region or those forces which are associated by function. As a practical term it refers to the military...
:- Ministry of Defence of Armenia
- Commander-in-chief
- Forces
- Army of Armenia
- NavyNavyA navy is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake- or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions...
of Armenia: None - Air Force of Armenia
- Special forces of Armenia
- Military history of ArmeniaMilitary history of ArmeniaThe military history of Armenia is defined by the situation of the Armenian Highland between the Hellenistic states, and later the Byzantine Empire, in the west and the Persian Empire to the east...
- Military ranks of Armenia
History of Armenia
- Economic history of Armenia
- Military history of ArmeniaMilitary history of ArmeniaThe military history of Armenia is defined by the situation of the Armenian Highland between the Hellenistic states, and later the Byzantine Empire, in the west and the Persian Empire to the east...
Culture of Armenia
- Architecture of Armenia
- Cuisine of Armenia
- Ethnic minorities in Armenia
- Festivals in Armenia
- Humor in Armenia
- Languages of ArmeniaLanguages of ArmeniaArmenian is the official language of Armenia, and is spoken as a first language by 97.7% of its population. Armenian belongs to an independent branch of the Indo-European language family. It is a highly inflective language, with a complicated system of declensions. Modern Armenian is agglutinative,...
- Media in Armenia
- National symbols of Armenia
- Coat of arms of ArmeniaCoat of arms of ArmeniaThe national coat of arms of Armenia consists of an eagle and a lion supporting a shield. The coat of arms combines new and old symbols...
- Flag of ArmeniaFlag of ArmeniaThe national flag of Armenia, the Armenian Tricolour , consists of three horizontal bands of equal width, red on the top, blue in the middle, and orange on the bottom. The Armenian Supreme Soviet adopted the current flag on 24 August 1990...
- National anthem of Armenia
- Coat of arms of Armenia
- People of Armenia
- Prostitution in Armenia
- Public holidays in ArmeniaPublic holidays in ArmeniaHolidays in Armenia:HolidaysDateEnglish NameLocal NameTransliterationRemarks1 JanuaryNew Year DayԱմանորAmanorTradition6 JanuaryChristmas DayՍուրբ ԾնունդSurb TsnundReligious...
- Records of Armenia
- Religion in ArmeniaReligion in Armenia97% of Armenians follow Christianity, which has existed in Armenia for over 1,700 years. Armenia has its own church, the Armenian Apostolic Church, which most Armenians follow...
- Buddhism in Armenia
- Christianity in Armenia
- Hinduism in ArmeniaHinduism in ArmeniaHinduism in Armenia remains a minor feature in Armenian religious life, generally represented through The International Society for Krishna Consciousness and a minority of Indian students, with backgrounds in Hinduism.-Indian population in Armenia:...
- Islam in ArmeniaIslam in ArmeniaIslam in Armenia consists mostly of temporary residents from Iran and other countries. There is no native population reported as Muslim.In 2009, the Pew Research Center estimated that less than 0.1% of the population, or about 1,000 people, were Muslims....
- Judaism in Armenia
- Sikhism in Armenia
- World Heritage Sites in Armenia
Art in Armenia
- Art in Armenia
- Cinema of ArmeniaCinema of ArmeniaThe cinema of Armenia was born on April 16, 1923, when the Armenian State Committee on Cinema was established by the government decree.In March 1924, the first Armenian film studio: Armenfilm was established in Yerevan, starting with Soviet Armenia the first Armenian documentary film.Namus was...
- Literature of Armenia
- Music of ArmeniaMusic of ArmeniaArmenia is situated close to the Caucasus Mountains, and its music is a mix of indigenous folk music, perhaps best-represented by Djivan Gasparyan's well-known duduk music, as well as light pop, and extensive Christian music, due to Armenia's status as the oldest Christian nation in the...
- Television in Armenia
- Theatre in Armenia
Sports in Armenia
- Football in ArmeniaFootball in ArmeniaFootball in Armenia is the country's most popular sport. Armenia is currently ranked 59 and has had much success since its independence. Since gaining independence in 1991, Armenia has had its own national association that takes part in all FIFA competitions...
- Armenia at the OlympicsArmenia at the OlympicsArmenia first participated at the Olympic Games as an independent nation in 1994, and has sent athletes to compete in every Summer Olympic Games and Winter Olympic Games since then....
Economy and infrastructure of Armenia
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 121st (one hundred and twenty first)
- Agriculture in ArmeniaAgriculture in ArmeniaArmenia has 2.1 million hectares of agricultural land, 72% of the country's land area. Most of this, however, is mountain pastures, and cultivable land is 480,000 hectares , or 16% of the country's area...
- Banking in ArmeniaBanking in ArmeniaThe Central Bank of Armenia is charged with regulating the money supply, circulating currency, and regulating the commercial banks of the country. Commercial banks in Armenia include HSBC Bank Armenia, Ameria-Cascade, Ardshinbank, Armagrobank, Armeconombank, Armimplexbank, Arminvestbank,...
- National Bank of Armenia
- Communications in ArmeniaCommunications in ArmeniaThis article is about telecommunications systems in Armenia.-Telephone:There are three telephone companies in Armenia: Beeline, which holds all fixed-line and 30% of cellular networks, and VivaCell-MTS, which holds 70% of cellular networks, and Orange...
- Internet in Armenia
- Companies of Armenia
- CurrencyCurrencyIn economics, currency refers to a generally accepted medium of exchange. These are usually the coins and banknotes of a particular government, which comprise the physical aspects of a nation's money supply...
of Armenia: DramArmenian dramThe dram is the monetary unit of Armenia and the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic. It is subdivided into 100 luma . The word "dram" translates into English as "money" and is cognate with the Greek drachma...
- ISO 4217ISO 4217ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Standards Organization, which delineates currency designators, country codes , and references to minor units in three tables:* Table A.1 – Current currency & funds code list...
: AMD
- ISO 4217
- Economic history of Armenia
- Energy in ArmeniaEnergy in ArmeniaEnergy in Armenia describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Armenia.The Armenian electrical energy sector has had a surplus capacity ever since emerging from a severe post-Soviet crisis in the mid-1990s thanks to the reopening of the nuclear power station at...
- Energy in ArmeniaEnergy in ArmeniaEnergy in Armenia describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Armenia.The Armenian electrical energy sector has had a surplus capacity ever since emerging from a severe post-Soviet crisis in the mid-1990s thanks to the reopening of the nuclear power station at...
- Energy policy of Armenia
- Oil industry in Armenia
- Energy in Armenia
- Health care in Armenia
- Mining in Armenia
- Armenia Stock Exchange
- Tourism in ArmeniaTourism in ArmeniaTourism in Armenia has been a key sector to the Armenian economy since the 1990s as half a million people visit the country ever year, mostly ethnic Armenians from the Diaspora...
- Transport in ArmeniaTransport in ArmeniaThis article considers transport in Armenia. For Soviet transportation, see Transport in the Soviet Union.-Total: in common carrier service; does not include industrial lines-Broad gauge:825 km of gauge...
- Airports in Armenia
- Rail transport in Armenia
- Roads in Armenia
- Water supply and sanitation in Armenia
See also
- Index of Armenia-related articles
- List of Armenia-related topics
- List of international rankings
- Member state of the United Nations
- Outline of AsiaOutline of AsiaThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Asia:Asia – world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
- Outline of geographyOutline of geographyThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geography:Geography – science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth.- Geography is :...
- Outline of Nagorno-KarabakhOutline of Nagorno-KarabakhNagorno-Karabakh is a disputed region in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia. It encompasses the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic, a de facto independent republic, and is officially part of the Republic of Azerbaijan, about west of the Azerbaijani capital of Baku and close to the border with...

