Outline of Guam
Encyclopedia
Guam
Guam is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States located in the western Pacific Ocean. It is one of five U.S. territories with an established civilian government. Guam is listed as one of 16 Non-Self-Governing Territories by the Special Committee on Decolonization of the United...
is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States of America that comprises the Island of Guam in the western North Pacific Ocean. It is one of five U.S. territories with an established civilian government. The island's capital is Hagåtña
Hagåtña, Guam
Hagåtña , formerly English Agana and in Spanish Agaña, is the capital of the United States island territory of Guam. It is the island's second smallest village in both area and population. From the 18th through mid 20th century, it was Guam's population center...
(formerly Agana). Guam is the largest and southernmost of the Mariana Islands
Mariana Islands
The Mariana Islands are an arc-shaped archipelago made up by the summits of 15 volcanic mountains in the north-western Pacific Ocean between the 12th and 21st parallels north and along the 145th meridian east...
.
The Chamorros
Chamorros
The Chamorro people, or Chamoru people, are the indigenous peoples of the Mariana Islands, which include the American territory of Guam and the United States Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands in Micronesia. Today, significant Chamoru populations also exist in several U.S. states...
, Guam's indigenous inhabitants, first populated the island approximately 4,000 years ago. The island has a long history of European colonialism beginning in 1668 with the arrival of Spanish settlers including Padre San Vitores, a Catholic missionary
Missionary
A missionary is a member of a religious group sent into an area to do evangelism or ministries of service, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care and economic development. The word "mission" originates from 1598 when the Jesuits sent members abroad, derived from the Latin...
. The island was taken over from Spain
Spanish East Indies
Spanish East Indies was a term used to describe Spanish territories in Asia-Pacific which lasted for three centuries . With the seat of government in Manila, the territory encompassed the Philippine Islands, Guam and the Mariana Islands, the Caroline Islands, and for a period of time, parts of...
by the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
during the Spanish American War in 1898. As the largest island in Micronesia
Micronesia
Micronesia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising thousands of small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It is distinct from Melanesia to the south, and Polynesia to the east. The Philippines lie to the west, and Indonesia to the southwest....
and the only American-held island in the region before World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, Guam was occupied by the Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
ese between December 1941 and July 1944. Today, Guam's economy is mainly supported by tourism
Tourism
Tourism is travel for recreational, leisure or business purposes. The World Tourism Organization defines tourists as people "traveling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business and other purposes".Tourism has become a...
(primarily from Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
) and U.S. military
Military of the United States
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. They consist of the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, Air Force, and Coast Guard.The United States has a strong tradition of civilian control of the military...
bases.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Guam:
General reference
- Pronunciation: ˈɡwɑːm
- Common English country name: GuamGuamGuam is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States located in the western Pacific Ocean. It is one of five U.S. territories with an established civilian government. Guam is listed as one of 16 Non-Self-Governing Territories by the Special Committee on Decolonization of the United...
- Official English country name: The United StatesUnited StatesThe United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
Territory of Guam - Common endonym(s): List of countries and capitals in native languages
- Official endonym(s): List of official endonyms of present-day nations and states
- Adjectival(s): Guamanian
- Demonym(s):
- EtymologyEtymologyEtymology is the study of the history of words, their origins, and how their form and meaning have changed over time.For languages with a long written history, etymologists make use of texts in these languages and texts about the languages to gather knowledge about how words were used during...
: Name of Guam - ISO country codes: GU, GUM, 316
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:GUISO 3166-2:GUISO 3166-2:GU is the entry for Guam in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization , which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1.Currently no ISO 3166-2 codes are defined in the...
- InternetInternetThe Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
country code top-level domainCountry code top-level domainA country code top-level domain is an Internet top-level domain generally used or reserved for a country, a sovereign state, or a dependent territory....
: .gu.gu.gu is the Internet country code top-level domain for Guam.Registrations are free of charge but are limited to people or companies with a contact in Guam, and are limited to third-level registrations beneath second-level names such as .com.gu...
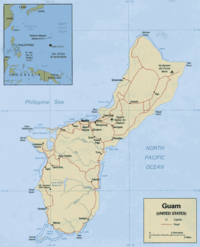
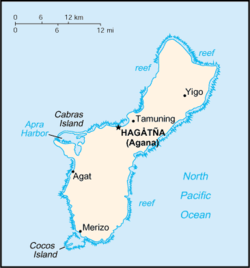
Geography of Guam
- Guam is: a United States territory
- Location:
- Northern HemisphereNorthern HemisphereThe Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
and Eastern HemisphereEastern HemisphereThe Eastern Hemisphere, also Eastern hemisphere or eastern hemisphere, is a geographical term for the half of the Earth that is east of the Prime Meridian and west of 180° longitude. It is also used to refer to Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australasia, vis-à-vis the Western Hemisphere, which includes... - Pacific OceanPacific OceanThe Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
- North Pacific
- OceaniaOceaniaOceania is a region centered on the islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Conceptions of what constitutes Oceania range from the coral atolls and volcanic islands of the South Pacific to the entire insular region between Asia and the Americas, including Australasia and the Malay Archipelago...
- MicronesiaMicronesiaMicronesia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising thousands of small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It is distinct from Melanesia to the south, and Polynesia to the east. The Philippines lie to the west, and Indonesia to the southwest....
- Micronesia
- Oceania
- North Pacific
- Time zoneTime zoneA time zone is a region on Earth that has a uniform standard time for legal, commercial, and social purposes. In order for the same clock time to always correspond to the same portion of the day as the Earth rotates , different places on the Earth need to have different clock times...
: Chamorro Standard Time (UTC+10UTC+10UTC+10 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +10. This time is used in:-As standard time :*Australia **Queensland*Federated States of Micronesia**Chuuk, Yap and surrounding area...
) - Extreme points of Guam
- High: Mount LamlamMount LamlamMount Lamlam is a peak on the island of Guam. It is located in the village of Agat, in the southwest of the island. At 1,332 feet , it is the highest peak in Guam. The distance from the peak to the bottom of the nearby Mariana Trench is perhaps the greatest change in elevation on Earth over such a...
406 m (1,332 ft) – 11,377 meters above Challenger DeepChallenger DeepThe Challenger Deep is the deepest known point in the oceans, with a depth of to by direct measurement from submersibles, and slightly more by sonar bathymetry . It is located at the southern end of the Mariana Trench near the Mariana Islands group... - Low: North Pacific Ocean 0 m
- High: Mount Lamlam
- Land boundaries: none
- Coastline: 125.5 km
- Northern Hemisphere
- Population of Guam: 173,000 - 179th most populous country
- Area of Guam: 541 km2
- Atlas of Guam
Environment of Guam
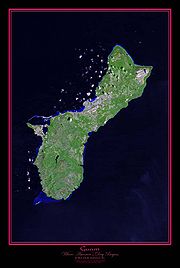
- Climate of Guam
- Environmental issues in Guam
- Ecoregions in Guam
- Renewable energy in Guam
- Geology of Guam
- Protected areas of Guam
- Biosphere reserves in Guam
- National parks of Guam
- Superfund sites in Guam
- Wildlife of Guam
- Flora of Guam
- Fauna of Guam
- Birds of Guam
- Mammals of Guam
Natural geographic features of Guam
- Fjords of Guam
- Glaciers of Guam
- Islands of Guam
- Lakes of Guam
- Mountains of Guam
- Volcanoes in Guam
- Rivers of Guam
- Waterfalls of Guam
- Valleys of Guam
- World Heritage Sites in Guam: None
Municipalities of Guam
- Capital of Guam: Hagåtña
- Cities of Guam
Government and politics of Guam
- Main article: Government of GuamGovernment of GuamThe Government of Guam is a presidential representative democratic system, whereby the Governor is head of government, and of a multi-party system...
and Politics of GuamPolitics of GuamPolitics of Guam takes place in a framework of a presidential representative democratic system, whereby the Governor is head of government, and of a multi-party system...
- Form of governmentForm of governmentA form of government, or form of state governance, refers to the set of political institutions by which a government of a state is organized. Synonyms include "regime type" and "system of government".-Empirical and conceptual problems:...
: presidentialPresidential systemA presidential system is a system of government where an executive branch exists and presides separately from the legislature, to which it is not responsible and which cannot, in normal circumstances, dismiss it....
representative democracyRepresentative democracyRepresentative democracy is a form of government founded on the principle of elected individuals representing the people, as opposed to autocracy and direct democracy... - Capital of Guam: Hagåtña
- Elections in GuamElections in GuamElections in Guam gives information on election and election results in Guam.Guam elects on territorial level a governor and a legislature with the governor elected for a four year term by the people...
- (specific elections)
- Political parties in Guam
- Political scandals of Guam
- Taxation in Guam
Executive branch of the government of Guam
- Head of stateHead of StateA head of state is the individual that serves as the chief public representative of a monarchy, republic, federation, commonwealth or other kind of state. His or her role generally includes legitimizing the state and exercising the political powers, functions, and duties granted to the head of...
: President of United States - Head of governmentHead of governmentHead of government is the chief officer of the executive branch of a government, often presiding over a cabinet. In a parliamentary system, the head of government is often styled prime minister, chief minister, premier, etc...
: Governor of Guam - Cabinet of Guam
Legislative branch of the government of Guam
- Parliament of Guam (bicameral)
- Upper houseUpper houseAn upper house, often called a senate, is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house; a legislature composed of only one house is described as unicameral.- Possible specific characteristics :...
: Senate of Guam - Lower houseLower houseA lower house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the upper house.Despite its official position "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide the lower house has come to wield more power...
: House of Commons of Guam
- Upper house
Judicial branch of the government of Guam
- Supreme Court of Guam
Foreign relations of Guam
- Diplomatic missions in Guam
- Diplomatic missions of Guam
International organization membership
The United States Territory of Guam is a member of:- International Olympic CommitteeInternational Olympic CommitteeThe International Olympic Committee is an international corporation based in Lausanne, Switzerland, created by Pierre de Coubertin on 23 June 1894 with Demetrios Vikelas as its first president...
(IOC) - Secretariat of the Pacific CommunitySecretariat of the Pacific CommunityThe Secretariat of the Pacific Community, or SPC , is a regional intergovernmental organisation whose membership includes both nations and territories...
(SPC) - Universal Postal UnionUniversal Postal UnionThe Universal Postal Union is an international organization that coordinates postal policies among member nations, in addition to the worldwide postal system. The UPU contains four bodies consisting of the Congress, the Council of Administration , the Postal Operations Council and the...
(UPU)
Law and order in Guam
- Main article: Law of Guam
- Capital punishment in Guam
- Constitution of Guam
- Crime in Guam
- Human rights in Guam
- LGBT rights in GuamLGBT rights in GuamPrivate, adult, consensual and non-commerical homosexual acts have been legal in Guam since a reform of the criminal code in 1979. No, laws explicitly address harassment or discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation or gender identity and same-sex marriage is not legally recognized...
- Freedom of religion in Guam
- LGBT rights in Guam
- Law enforcement in Guam
Military of Guam
- Main article: Military of Guam
- Command
- Commander-in-chiefCommander-in-ChiefA commander-in-chief is the commander of a nation's military forces or significant element of those forces. In the latter case, the force element may be defined as those forces within a particular region or those forces which are associated by function. As a practical term it refers to the military...
:- Ministry of Defence of Guam
- Commander-in-chief
- Forces
- Army of Guam
- Navy of Guam
- Air Force of Guam
- Special forces of Guam
- Military history of Guam
- Military ranks of Guam
History of Guam
- Main article: History of GuamHistory of GuamThe history of Guam involves phases including the early arrival of people known today as the ancient Chamorros, the development of "pre-contact" society, Spanish colonization, and the present American rule of the island...
, Timeline of the history of Guam, and Current events of Guam
History of Guam, by period
- Indigenous peoples
- Chamorro people
- First European contact, 1521–1668
-
- On March 6, 1521, three Spanish shipsSpanish NavyThe Spanish Navy is the maritime branch of the Spanish Armed Forces, one of the oldest active naval forces in the world. The Armada is responsible for notable achievements in world history such as the discovery of Americas, the first world circumnavigation, and the discovery of a maritime path...
under the command of Fernão de Magalhães (Ferdinand Magellan) land on the Island of Guam after a seemingly endless eleven week voyage across the Pacific OceanPacific OceanThe Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
. Magalhães names the archipelago Las Isles de las Velas LatinasMariana IslandsThe Mariana Islands are an arc-shaped archipelago made up by the summits of 15 volcanic mountains in the north-western Pacific Ocean between the 12th and 21st parallels north and along the 145th meridian east...
(The Islands of the Latine Sails). When the Spaniards refuse to pay for supplies, natives take iron from the ships. Magalhães renames the archipelago Las Islas de los LadronesMariana IslandsThe Mariana Islands are an arc-shaped archipelago made up by the summits of 15 volcanic mountains in the north-western Pacific Ocean between the 12th and 21st parallels north and along the 145th meridian east...
(The Islands of the Thieves).
- On March 6, 1521, three Spanish ships
-
- Spanish East IndiesSpanish East IndiesSpanish East Indies was a term used to describe Spanish territories in Asia-Pacific which lasted for three centuries . With the seat of government in Manila, the territory encompassed the Philippine Islands, Guam and the Mariana Islands, the Caroline Islands, and for a period of time, parts of...
, 1565-(1668–1898)-1899- Diego Luis de San VitoresDiego Luis de San VitoresBlessed Diego Luis de San Vitores was a Spanish Jesuit missionary who founded the first Catholic church on the island of Guam. He is responsible for establishing the Spanish presence in the Mariana Islands.-Early life:...
renames the Chamorro archipelago Islas MarianasMariana IslandsThe Mariana Islands are an arc-shaped archipelago made up by the summits of 15 volcanic mountains in the north-western Pacific Ocean between the 12th and 21st parallels north and along the 145th meridian east...
in honor of his patroness, Queen Mariana of AustriaMariana of AustriaMariana of Austria was Queen consort of Spain as the second wife of King Philip IV, who was also her maternal uncle...
, 1668
- Diego Luis de San Vitores
- Spanish-American WarSpanish-American WarThe Spanish–American War was a conflict in 1898 between Spain and the United States, effectively the result of American intervention in the ongoing Cuban War of Independence...
, April 23 – August 12, 1898- Spanish EmpireSpanish EmpireThe Spanish Empire comprised territories and colonies administered directly by Spain in Europe, in America, Africa, Asia and Oceania. It originated during the Age of Exploration and was therefore one of the first global empires. At the time of Habsburgs, Spain reached the peak of its world power....
declares war on the United StatesUnited StatesThe United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, April 23, 1898 - United StatesUnited StatesThe United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
capture of GuamCapture of GuamThe Capture of Guam was a bloodless event between the United States and the Kingdom of Spain during the Spanish-American War. The U.S. Navy sent a single cruiser, the , to capture the island of Guam, then under Spanish control. However, the Spanish garrison on the island had no knowledge of the war...
, June 20–21, 1898 - Treaty of ParisTreaty of Paris (1898)The Treaty of Paris of 1898 was signed on December 10, 1898, at the end of the Spanish-American War, and came into effect on April 11, 1899, when the ratifications were exchanged....
, December 10, 1898
- Spanish Empire
- United StatesUnited StatesThe United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
Territory of Guam, since December 10, 1898- World War IWorld War IWorld War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, June 28, 1914 – November 11, 1918- United StatesUnited StatesThe United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
enters Great War on April 6, 1917
- United States
- World War IIWorld War IIWorld War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, September 1, 1939 – September 2, 1945- United StatesUnited StatesThe United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
enters Second World War on December 8, 1941 - Battle of Guam of 1941Battle of Guam (1941)The First Battle of Guam, was an engagement during the Pacific War in World War II, and took place on 8 December 1941 on Guam in the Mariana Islands between the Empire of Japan and the United States...
- Battle of Guam of 1944
- United States
- Cold WarCold WarThe Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
, March 5, 1946 – December 25, 1991 - Korean WarKorean WarThe Korean War was a conventional war between South Korea, supported by the United Nations, and North Korea, supported by the People's Republic of China , with military material aid from the Soviet Union...
, June 25, 1950 – July 27, 1953 - Guam Organic ActGuam Organic Act of 1950The Guam Organic Act of 1950, is a United States federal law that redesignated the island of Guam as an unincorporated territory of the United States, established executive, legislative, and judicial branches, and transferred Federal jurisdiction from the United States Navy to the Department of...
, August 1, 1950
- World War I
Culture of Guam
- Main article: Culture of Guam
- Architecture of Guam
- Cuisine of Guam
- Ethnic minorities in Guam
- Festivals in Guam
- Humor in Guam
- Languages of Guam
- Media in Guam
- National symbols of Guam
- Coat of arms of Guam
- Flag of GuamFlag of GuamThe flag of the Territory of Guam was adopted on February 9, 1948. The territorial flag is dark blue with a narrow red border on all sides . In the center of the flag is the coat of arms; an almond shaped emblem, which depicts a proa sailing in Agana Bay near Hagåtña, and GUAM colored in red letters...
- National anthem of Guam
- People of Guam
- Prostitution in Guam
- Public holidays in Guam
- Records of Guam
- Religion in Guam
- Buddhism in Guam
- Christianity in Guam
- Hinduism in Guam
- Islam in GuamIslam in GuamThe presence of Islam in Guam is quite small, centered on the island's only mosque, the Masjid Al-noor in Mangilao. Muslims in Guam are from a wide variety of backgrounds, both originating in traditionally Muslim countries, as well as Chamorros and mainland Americans.-External links:* at Guampedia...
- Judaism in Guam
- Sikhism in Guam
- World Heritage Sites in Guam: None
Art in Guam
- Art in Guam
- Cinema of Guam
- Literature of Guam
- Music of GuamMusic of GuamThe music of Guam encompasses the works of many Chamorro popular musicians, including KACY, Flora Baza Quan, Daniel De Leon Guerrero, singer-songwriter J. D. Crutch, who is on the local Napu Records and who released a best-selling local album with Guinaifen Manglo. The state song of Guam is "Guam...
- Television in Guam
- Theatre in Guam
Sports in Guam
- Main article: Sports in Guam
- Football in GuamFootball in GuamThe sport of football in the country of Guam is run by the Guam Football Association. The association administers the national football team as well as the Guam League....
- Guam at the OlympicsGuam at the OlympicsGuam has competed in six Summer Games. They have competed in the Winter Games once in 1988.-External links:*. Olympics at Sports-Reference.com...
Economy and infrastructure of Guam
- Main article: Economy of GuamEconomy of GuamEconomy - overview:The economy depends mainly on US military spending and on tourist revenue. Over the past 20 years, the tourist industry grew rapidly, creating a construction boom for new hotels, golf courses and other tourist amenities. More than 1.1 million tourists visit Guam each year...
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 150th (one hundred and fiftieth)
- Agriculture in Guam
- Banking in Guam
- National Bank of Guam
- Communications in GuamCommunications in GuamThough Guam is part of the United States, some U.S. long distance plans and courier services list Guam as an international location. As a result of Guam's being added to the North American Numbering Plan in 1997, calls made to the U.S., Canada, or other participating countries from Guam only...
- Internet in Guam
- Companies of Guam
- Currency of GuamCurrencyIn economics, currency refers to a generally accepted medium of exchange. These are usually the coins and banknotes of a particular government, which comprise the physical aspects of a nation's money supply...
: Dollar- ISO 4217ISO 4217ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Standards Organization, which delineates currency designators, country codes , and references to minor units in three tables:* Table A.1 – Current currency & funds code list...
: USD
- ISO 4217
- Economic history of Guam
- Energy in Guam
- Energy policy of Guam
- Oil industry in Guam
- Mining in Guam
- Tourism in Guam
- Transport in GuamTransport in GuamGuam has no railways, nor does it have a merchant marine. The largest port is Apra Harbor , which serves almost all commercial traffic including cruise, cargo and fishing vessels. There are smaller harbors located on the island which serve recreational boaters. Roads are primarily paved out of a...
- Guam Stock Exchange
Infrastructure of Guam
- Health care in Guam
- Transportation in Guam
- Airports in Guam
- Rail transport in Guam
- Roads in Guam
- Water supply and sanitation in Guam
See also
- Index of Guam-related articles
- List of Guam-related topics
- List of international rankings
- Outline of geographyOutline of geographyThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geography:Geography – science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth.- Geography is :...
- Outline of OceaniaOutline of OceaniaOceania is a geographical, and often geopolitical, region consisting of numerous lands—mostly islands in the Pacific Ocean and vicinity. The term is also sometimes used to denote a continent comprising Australia and proximate Pacific islands,....
- Outline of the United States
External links
Government- Official Portal for the Island of Guam
- Office of the Governor
- Congresswoman Madeleine Z. Bordallo, Delegate, U.S. Congress
- Guam Customs and Quarantine Agency
- Guam Election Commission
- Guam Code Annotated
- Guam Department of Revenue and Taxation
- Guam's Original Webpage
Invasive species
- (Potentially) Invasive plant species on Guam (info from the Pacific Island Ecosystems at Risk project (PIER))
- Brown tree snake (Boiga irregularis) information from the Hawaiian Ecosystems at Risk project (HEAR)
News
- Marianas Variety "Guam's only true independent news source"
- Pacific Daily News, A Gannett Newspaper
- KUAM, Guam's Primary News Channel
- "Pacific News Center - News You Can Trust
Overviews
- allthingsguam A Guam History resource—virtual textbook, virtual workbook and more
- Guampedia, Guam's Online Encyclopedia
- U.S. Library of Congress - Portals to the World: Guam
- The World Factbook on Guam
- Guam Connection - Guam directory and internet portal.
Military
- Commander, Naval Forces Marianas (COMNAVMAR) Guam
- Andersen Air Force Base (AAFB) Guam
- War in the Pacific - Liberation of Guam
- Congressional Testimony - Guam War Claims
Tourism
Others

