Outline of North Carolina
Encyclopedia
North Carolina
North Carolina
North Carolina is a state located in the southeastern United States. The state borders South Carolina and Georgia to the south, Tennessee to the west and Virginia to the north. North Carolina contains 100 counties. Its capital is Raleigh, and its largest city is Charlotte...
– U.S. state
U.S. state
A U.S. state is any one of the 50 federated states of the United States of America that share sovereignty with the federal government. Because of this shared sovereignty, an American is a citizen both of the federal entity and of his or her state of domicile. Four states use the official title of...
on the Eastern Seaboard
East Coast of the United States
The East Coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, refers to the easternmost coastal states in the United States, which touch the Atlantic Ocean and stretch up to Canada. The term includes the U.S...
, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean in the Southeastern United States
Southeastern United States
The Southeastern United States, colloquially referred to as the Southeast, is the eastern portion of the Southern United States. It is one of the most populous regions in the United States of America....
. North Carolina was one of the original Thirteen Colonies
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were English and later British colonies established on the Atlantic coast of North America between 1607 and 1733. They declared their independence in the American Revolution and formed the United States of America...
and signed the United States Declaration of Independence
United States Declaration of Independence
The Declaration of Independence was a statement adopted by the Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, which announced that the thirteen American colonies then at war with Great Britain regarded themselves as independent states, and no longer a part of the British Empire. John Adams put forth a...
on July 4, 1776. North Carolina was the 12th of the original 13 states to approve the Constitution of the United States of America on January 2, 1788. North Carolina joined the Confederate States of America
Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America was a government set up from 1861 to 1865 by 11 Southern slave states of the United States of America that had declared their secession from the U.S...
during the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
from 1861 to 1865, but was readmitted to the Union in 1868.
General reference
- Names
- Common name: North CarolinaNorth CarolinaNorth Carolina is a state located in the southeastern United States. The state borders South Carolina and Georgia to the south, Tennessee to the west and Virginia to the north. North Carolina contains 100 counties. Its capital is Raleigh, and its largest city is Charlotte...
- Pronunciation: ˌnɔrθ kærəˈlaɪnə
- Official name: State of North Carolina
- Abbreviations and name codes
- Postal symbol: NC
- ISO 3166-2 code: US-NC
- InternetInternetThe Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
second-level domainSecond-level domainIn the Domain Name System hierarchy, a second-level domain is a domain that is directly below a top-level domain . For example, in example.com, example is the second-level domain of the .com TLD....
: .nc.us
- Nicknames
- Old North State
- Tar HeelTar HeelTar Heel is a nickname applied to the state and inhabitants of North Carolina as well as the nickname of the University of North Carolina athletic teams, students, alumni, and fans....
State - TurpentineTurpentineTurpentine is a fluid obtained by the distillation of resin obtained from trees, mainly pine trees. It is composed of terpenes, mainly the monoterpenes alpha-pinene and beta-pinene...
State - Variety Vacationland
- Rip Van WinkleRip Van Winkle"Rip Van Winkle" is a short story by the American author Washington Irving published in 1819, as well as the name of the story's fictional protagonist. Written while Irving was living in Birmingham, England, it was part of a collection entitled The Sketch Book of Geoffrey Crayon...
State - Land of the SkyLand of the SkyThe Land of the Sky, or, adventures in mountain by-ways is a novel by Mrs. Frances Tiernan, under the pseudonym Christian Reid. It was published in 1876.The name refers to the Blue Ridge Mountains and Great Smoky Mountains in western North Carolina...
- First in Flight State (currently used on license plates)
- Common name: North Carolina
- Adjectivals: North CarolinaNorth CarolinaNorth Carolina is a state located in the southeastern United States. The state borders South Carolina and Georgia to the south, Tennessee to the west and Virginia to the north. North Carolina contains 100 counties. Its capital is Raleigh, and its largest city is Charlotte...
, North Carolinian - Demonym: North Carolinian
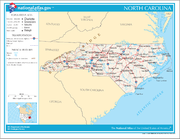
Geography of North Carolina
- Main article: Geography of North CarolinaGeography of North CarolinaThe Geography of North Carolina falls naturally into three divisions or sections—the Appalachian Mountains formed mostly by the Blue Ridge and Great Smoky Mountains, the Middle or Piedmont Plateau, and the Eastern or Tidewater section, also known as the Coastal Plain. North Carolina covers and is ...
- North Carolina is: a U.S. stateU.S. stateA U.S. state is any one of the 50 federated states of the United States of America that share sovereignty with the federal government. Because of this shared sovereignty, an American is a citizen both of the federal entity and of his or her state of domicile. Four states use the official title of...
, a federal state of the United States of America - Location
- Northern hemisphereNorthern HemisphereThe Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
- Western hemisphereWestern HemisphereThe Western Hemisphere or western hemisphere is mainly used as a geographical term for the half of the Earth that lies west of the Prime Meridian and east of the Antimeridian , the other half being called the Eastern Hemisphere.In this sense, the western hemisphere consists of the western portions...
- AmericasAmericasThe Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
- North AmericaNorth AmericaNorth America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
- Anglo America
- Northern AmericaNorthern AmericaNorthern America is the northernmost region of the Americas, and is part of the North American continent. It lies directly north of the region of Middle America; the land border between the two regions coincides with the border between the United States and Mexico...
- United States of America
- Contiguous United StatesContiguous United StatesThe contiguous United States are the 48 U.S. states on the continent of North America that are south of Canada and north of Mexico, plus the District of Columbia....
- Eastern United StatesEastern United StatesThe Eastern United States, the American East, or simply the East is traditionally defined as the states east of the Mississippi River. The first two tiers of states west of the Mississippi have traditionally been considered part of the West, but can be included in the East today; usually in...
- East Coast of the United StatesEast Coast of the United StatesThe East Coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, refers to the easternmost coastal states in the United States, which touch the Atlantic Ocean and stretch up to Canada. The term includes the U.S...
- East Coast of the United States
- Southern United StatesSouthern United StatesThe Southern United States—commonly referred to as the American South, Dixie, or simply the South—constitutes a large distinctive area in the southeastern and south-central United States...
- Southeastern United StatesSoutheastern United StatesThe Southeastern United States, colloquially referred to as the Southeast, is the eastern portion of the Southern United States. It is one of the most populous regions in the United States of America....
- South Atlantic StatesSouth Atlantic StatesThe South Atlantic United States form one of the nine Census Bureau Divisions within the United States that are recognized by the United States Census Bureau....
- South Atlantic States
- Southeastern United States
- Eastern United States
- Contiguous United States
- United States of America
- North America
- Americas
- Northern hemisphere
- Population of North Carolina: 9,535,483 (2010 U.S. Census)
- Area of North Carolina:
- Atlas of North Carolina
Places in North Carolina
- Historic places in North Carolina
- National Historic Landmarks in North Carolina
- National Register of Historic Places listings in North Carolina
- National Natural Landmarks in North Carolina
- National parks in North Carolina
- State parks in North Carolina
Environment of North Carolina
- Climate of North CarolinaClimate of North CarolinaNorth Carolina's climate varies from the Atlantic coast in the east to the Appalachian Mountain range in the west. The mountains often act as a "shield", blocking cold temperatures and storms from the Midwest from entering the Piedmont of North Carolina...
- Protected areas in North Carolina
- Superfund sites in North Carolina
- Wildlife of North CarolinaWildlife of North CarolinaThis article seeks to serve as a field-guide, central repository, listing, and tour-guide for the flora and fauna of North Carolina and surrounding territories.-State ecology:...
- Fauna of North Carolina
- Birds of North Carolina
- Fauna of North Carolina
- Tidewater region of North CarolinaTidewater region of North Carolina- Tidewater Region of North Carolina :-Tidewater Research Station:...
Natural geographic features of North Carolina
- Rivers of North Carolina
Regions of North Carolina
- Central North Carolina
- Eastern North CarolinaEastern North CarolinaEastern North Carolina is the region encompassing the eastern tier of North Carolina. It is known geographically as the state's Coastal Plain region. Primary subregions of Eastern North Carolina include the Fayetteville Metropolitan Area, the Lower Cape Fear , the Sandhills, the Inner Banks and...
- Northern North Carolina
- Northeastern North Carolina
- Southern North Carolina
- Southeastern North Carolina
- Western North CarolinaWestern North CarolinaWestern North Carolina is the region of North Carolina which includes the Appalachian Mountains, thus it is often known geographically as the state's Mountain Region. It is sometimes included with upstate South Carolina as the "Western Carolinas", which is also counted as a single media market...
- Piedmont TriadPiedmont TriadThe Piedmont Triad, or Triad, is a north-central region of the U.S. state of North Carolina that consists of the area within and surrounding the three major cities of Greensboro, Winston-Salem, and High Point. This close group or "triad" of cities lies in the Piedmont geographical region of the...
Administrative divisions of North Carolina
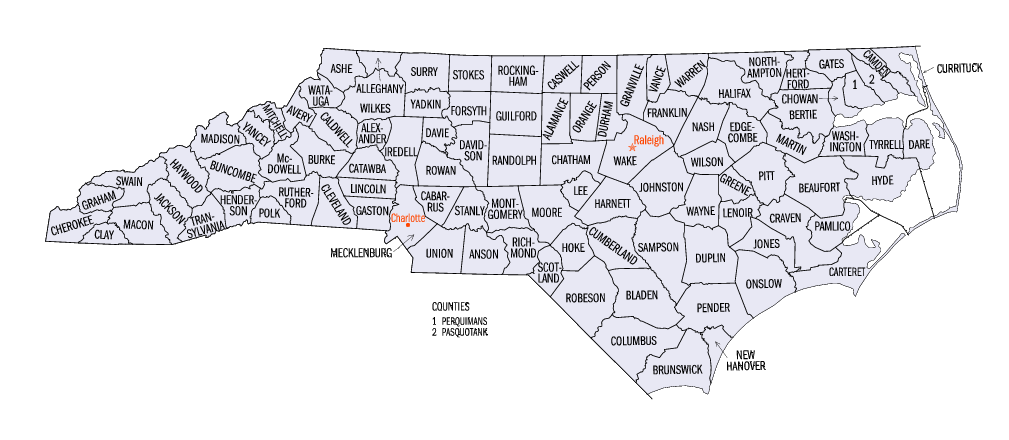
- The 100 Counties of the State of North Carolina
- Municipalities in North Carolina
- Cities in North Carolina
- State capital of North Carolina:
- City nicknames in North Carolina
- Sister cities in North Carolina
- Unincorporated communities in North Carolina
- Cities in North Carolina
- Municipalities in North Carolina
Politics and government of North Carolina
- Main article: Politics and government of North CarolinaPolitics and government of North CarolinaThe government of North Carolina, shaped by its political system, is divided into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial. These consist of the state governor's office, a bicameral state legislature known as the general assembly, and a state court system. The state constitution...
- Form of governmentForm of governmentA form of government, or form of state governance, refers to the set of political institutions by which a government of a state is organized. Synonyms include "regime type" and "system of government".-Empirical and conceptual problems:...
: U.S. state governmentState governments of the United StatesState governments in the United States are those republics formed by citizens in the jurisdiction thereof as provided by the United States Constitution; with the original 13 States forming the first Articles of Confederation, and later the aforementioned Constitution. Within the U.S... - United States congressional delegations from North CarolinaUnited States Congressional Delegations from North CarolinaThese are tables of congressional delegations from North Carolina to the United States Senate and United States House of Representatives.-United States Senate:-House of Representatives:-Key:...
- North Carolina State CapitolNorth Carolina State CapitolThe North Carolina State Capitol is the main house of government of the U.S. state of North Carolina. Housing the offices of the Governor of North Carolina, it is located in the state capital of Raleigh on Union Square at One East Edenton Street. The cornerstone of the Greek Revival building was...
- Elections in North Carolina
- Electoral reform in North CarolinaElectoral reform in North CarolinaElectoral reform in North Carolina refers to efforts to change the voting and election laws in the Tar Heel State.-Instant Runoff Voting:Cary, North Carolina was scheduled to hold its first instant runoff voting election on October 9, 2007, and Hendersonville, North Carolina was scheduled to use...
- Electoral reform in North Carolina
- Political party strength in North CarolinaPolitical party strength in North CarolinaThe following table indicates the party of elected officials in the U.S. state of North Carolina:*Governor*Lieutenant Governor*Secretary of State*Attorney General*State Auditor*State Treasurer*Superintendent of Public Instruction*Commissioner of Agriculture...
Executive branch of the government of North Carolina
- Governor of North CarolinaGovernor of North CarolinaThe Governor of North Carolina is the chief executive of the State of North Carolina, one of the U.S. states. The current governor is Bev Perdue, North Carolina's first female governor.-Powers:...
- Lieutenant Governor of North CarolinaLieutenant Governor of North CarolinaThe Lieutenant Governor of North Carolina is the second highest elected official in the U.S. state of North Carolina and is the only elected official to have powers in both the legislative and executive branches of state government...
- Secretary of State of North Carolina
- State Treasurer of North Carolina
- Lieutenant Governor of North Carolina
- State departments
- North Carolina Department of TransportationNorth Carolina Department of TransportationThe North Carolina Department of Transportation is responsible for building, repairing, and operating highways, bridges, and other modes of transportation, including ferries in the U.S. state of North Carolina.-History:...
- North Carolina Department of Transportation
Legislative branch of the government of North Carolina
- North Carolina General AssemblyNorth Carolina General AssemblyThe North Carolina General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of North Carolina. The General Assembly drafts and legislates the state laws of North Carolina, also known as the General Statutes...
(bicameral)- Upper houseUpper houseAn upper house, often called a senate, is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house; a legislature composed of only one house is described as unicameral.- Possible specific characteristics :...
: North Carolina SenateNorth Carolina SenateThe North Carolina Senate is one of the two houses of the North Carolina General Assembly.Its prerogatives and powers are similar to those of the other house, the House of Representatives. Its members do, however, represent districts that are larger than those of their colleagues in the House. The... - Lower houseLower houseA lower house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the upper house.Despite its official position "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide the lower house has come to wield more power...
: North Carolina House of RepresentativesNorth Carolina House of RepresentativesThe North Carolina House of Representatives is one of the two houses of the North Carolina General Assembly. The House is a 120-member body led by a Speaker of the House, who holds powers similar to those of the President pro-tem in the state senate....
- Upper house
Judicial branch of the government of North Carolina
- Supreme Court of North CarolinaNorth Carolina Supreme CourtThe Supreme Court of North Carolina is the state's highest appellate court. Until the creation of the North Carolina Court of Appeals in the 1960s, it was the state's only appellate court. The Supreme Court consists of six associate justices and one chief justice, although the number of justices...
Law and order in North Carolina
Law of North Carolina- Capital punishment in North Carolina
- Constitution of North Carolina
- Crime in North CarolinaCrime in North Carolina-Statistics:In 2008 there were 416,060 crimes reported in North Carolina including 604 murders a full list can be found -Capital punishment laws:Capital punishment is legal in this state...
- Gun laws in North Carolina
- Law enforcement in North Carolina
- Same-sex marriage in North CarolinaSame-sex marriage in North CarolinaNorth Carolina recognizes neither same-sex marriages nor any other form of legal recognition of same sex-unions. The state bans same-sex marriage by state statute, though there is currently no constitutional amendment banning same-sex unions implanted at this time...
Military in North Carolina
- North Carolina Air National GuardNorth Carolina Air National GuardThe North Carolina Air National Guard is the air force militia of the U.S. state of North Carolina. It is, along with the North Carolina Army National Guard, an element of the North Carolina National Guard...
- North Carolina Army National GuardNorth Carolina Army National GuardThe North Carolina Army National Guard is a component of the United States Army, the United States National Guard, and the North Carolina National Guard. Nationwide, the Army National Guard comprises approximately one half of the US Army's available combat forces and approximately one third of its...
History of North Carolina, by period
- Indigenous peoples
- Mississippian cultureMississippian cultureThe Mississippian culture was a mound-building Native American culture that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 CE to 1500 CE, varying regionally....
- JoaraJoaraJoara was a large Native American settlement, a regional chiefdom of the Mississippian culture, located in what is now Burke County, North Carolina. Joara is notable as a significant archaeological and historic site. It was a place of encounter in 1540 between the Mississippian people and the...
- Joara
- Mississippian culture
- SpanishSpainSpain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
colony of FloridaSpanish FloridaSpanish Florida refers to the Spanish territory of Florida, which formed part of the Captaincy General of Cuba, the Viceroyalty of New Spain, and the Spanish Empire. Originally extending over what is now the southeastern United States, but with no defined boundaries, la Florida was a component of...
, 1565–1763- Fort San Juan at JoaraJoaraJoara was a large Native American settlement, a regional chiefdom of the Mississippian culture, located in what is now Burke County, North Carolina. Joara is notable as a significant archaeological and historic site. It was a place of encounter in 1540 between the Mississippian people and the...
, 1567–1568
- Fort San Juan at Joara
- EnglishEnglandEngland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
Colony of Roanoke, 1585–1587 - EnglishEnglandEngland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
Province of CarolinaProvince of CarolinaThe Province of Carolina, originally chartered in 1629, was an English and later British colony of North America. Because the original Heath charter was unrealized and was ruled invalid, a new charter was issued to a group of eight English noblemen, the Lords Proprietors, in 1663...
, 1663–1707 - FrenchFranceThe French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
colony of LouisianeLouisiana (New France)Louisiana or French Louisiana was an administrative district of New France. Under French control from 1682–1763 and 1800–03, the area was named in honor of Louis XIV, by French explorer René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de la Salle...
, 1699–1763 - BritishUnited KingdomThe United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
Province of CarolinaProvince of CarolinaThe Province of Carolina, originally chartered in 1629, was an English and later British colony of North America. Because the original Heath charter was unrealized and was ruled invalid, a new charter was issued to a group of eight English noblemen, the Lords Proprietors, in 1663...
, 1707–1712 - BritishUnited KingdomThe United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
Province of North CarolinaProvince of North CarolinaThe Province of North Carolina was originally part of the Province of Carolina in British America, which was chartered by eight Lords Proprietor. The province later became the U.S. states of North Carolina and Tennessee....
, 1712–1776 - French and Indian WarFrench and Indian WarThe French and Indian War is the common American name for the war between Great Britain and France in North America from 1754 to 1763. In 1756, the war erupted into the world-wide conflict known as the Seven Years' War and thus came to be regarded as the North American theater of that war...
, 1754–1763- Treaty of Fontainebleau of 1762Treaty of Fontainebleau (1762)The Treaty of Fontainebleau was a secret agreement in which France ceded Louisiana to Spain. The treaty followed the last battle in the French and Indian War, the Battle of Signal Hill in September 1762, which confirmed British control of Canada. However, the associated Seven Years War continued...
- Treaty of Paris of 1763Treaty of Paris (1763)The Treaty of Paris, often called the Peace of Paris, or the Treaty of 1763, was signed on 10 February 1763, by the kingdoms of Great Britain, France and Spain, with Portugal in agreement. It ended the French and Indian War/Seven Years' War...
- Treaty of Fontainebleau of 1762
- BritishUnited KingdomThe United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
Indian ReserveIndian Reserve (1763)The Indian Reserve was a territory under British rule in North America set aside in the Royal Proclamation of 1763 for use by American Indians between 1763 and 1783....
, 1763–1783- Royal Proclamation of 1763Royal Proclamation of 1763The Royal Proclamation of 1763 was issued October 7, 1763, by King George III following Great Britain's acquisition of French territory in North America after the end of the French and Indian War/Seven Years' War...
- Royal Proclamation of 1763
- American Revolutionary WarAmerican Revolutionary WarThe American Revolutionary War , the American War of Independence, or simply the Revolutionary War, began as a war between the Kingdom of Great Britain and thirteen British colonies in North America, and ended in a global war between several European great powers.The war was the result of the...
, April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783- United States Declaration of IndependenceUnited States Declaration of IndependenceThe Declaration of Independence was a statement adopted by the Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, which announced that the thirteen American colonies then at war with Great Britain regarded themselves as independent states, and no longer a part of the British Empire. John Adams put forth a...
, July 4, 1776 - Treaty of ParisTreaty of Paris (1783)The Treaty of Paris, signed on September 3, 1783, ended the American Revolutionary War between Great Britain on the one hand and the United States of America and its allies on the other. The other combatant nations, France, Spain and the Dutch Republic had separate agreements; for details of...
, September 3, 1783
- United States Declaration of Independence
- State of North Carolina since 1776
- Chickamauga WarsChickamauga warsThe Chickamauga Wars were a series of raids, campaigns, ambushes, minor skirmishes, and several full-scale frontier battles which were a continuation of the Cherokee struggle against encroachment by American frontiersmen from the former British colonies...
, 1776–1794- Tenth state to ratify the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, signed July 21, 1778
- Western territorial claimsState cessionsThe state cessions are those areas of the United States that the separate states ceded to the federal government in the late 18th and early 19th century...
ceded 1784 - Twelfth State to ratify the Constitution of the United States of America on November 21, 1789
- War of 1812War of 1812The War of 1812 was a military conflict fought between the forces of the United States of America and those of the British Empire. The Americans declared war in 1812 for several reasons, including trade restrictions because of Britain's ongoing war with France, impressment of American merchant...
, June 18, 1812 – March 23, 1815- Treaty of GhentTreaty of GhentThe Treaty of Ghent , signed on 24 December 1814, in Ghent , was the peace treaty that ended the War of 1812 between the United States of America and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland...
, December 24, 1814
- Treaty of Ghent
- Trail of TearsTrail of TearsThe Trail of Tears is a name given to the forced relocation and movement of Native American nations from southeastern parts of the United States following the Indian Removal Act of 1830...
, 1830–1838 - James K. PolkJames K. PolkJames Knox Polk was the 11th President of the United States . Polk was born in Mecklenburg County, North Carolina. He later lived in and represented Tennessee. A Democrat, Polk served as the 17th Speaker of the House of Representatives and the 12th Governor of Tennessee...
becomes 11th President of the United StatesPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
on March 4, 1845 - American Civil WarAmerican Civil WarThe American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
, April 12, 1861 – May 13, 1865- North Carolina in the American Civil War
-
- Tenth state to declare secession from the United States on May 20, 1861
- Tenth state admitted to the Confederate States of AmericaConfederate States of AmericaThe Confederate States of America was a government set up from 1861 to 1865 by 11 Southern slave states of the United States of America that had declared their secession from the U.S...
on May 21, 1861
- Carolinas CampaignCarolinas CampaignThe Carolinas Campaign was the final campaign in the Western Theater of the American Civil War. In January 1865, Union Maj. Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman advanced north from Savannah, Georgia, through the Carolinas, with the intention of linking up with Union forces in Virginia. The defeat of ...
, January 5 – April 26, 1865
-
- North Carolina in the American Civil War
- Andrew JohnsonAndrew JohnsonAndrew Johnson was the 17th President of the United States . As Vice-President of the United States in 1865, he succeeded Abraham Lincoln following the latter's assassination. Johnson then presided over the initial and contentious Reconstruction era of the United States following the American...
becomes 17th President of the United StatesPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
on April 15, 1865 - North Carolina in Reconstruction, 1865–1868
-
- Fourth former Confederate state readmitted to the United States on July 4, 1868
-
- Great Smoky Mountains National ParkGreat Smoky Mountains National ParkGreat Smoky Mountains National Park is a United States National Park and UNESCO World Heritage Site that straddles the ridgeline of the Great Smoky Mountains, part of the Blue Ridge Mountains, which are a division of the larger Appalachian Mountain chain. The border between Tennessee and North...
established on June 15, 1934
- Chickamauga Wars
History of North Carolina, by region
- By city
-
- History of Charlotte
- History of Raleigh (capital)
- History of Greensboro
- History of Winston-Salem
- History of Durham
- History of Fayetteville
- History of Cary
- History of High Point
- History of Wilmington
- History of Greenville
- History of Asheville
- History of Jacksonville
-
- History of Concord
- History of Rocky Mount
- History of Chapel Hill
- History of Wilson
- By county
-
- History of Alamance County
-
- History of Alleghany County
- History of Anson County
- History of Ashe County
- History of Avery County
-
- History of Bertie County
- History of Bladen County
- History of Brunswick County
- History of Buncombe County
- History of Burke County
- History of Cabarrus County
- History of Caldwell County
- History of Camden County
- History of Carteret County
- History of Caswell County
- History of Catawba County
- History of Chatham County
- History of Cherokee County
- History of Chowan County
- History of Clay County
- History of Cleveland County
- History of Columbus County
- History of Craven County
- History of Cumberland County
-
- History of Davidson County
- History of Davie County
- History of Duplin County
- History of Durham County
- History of Edgecombe County
- History of Forsyth County
- History of Franklin County
- History of Gaston County
- History of Gates County
- History of Graham County
- History of Granville County
- History of Greene County
- History of Guilford County
- History of Halifax County
- History of Harnett County
- History of Haywood County
- History of Henderson County
- History of Hertford County
- History of Hoke County
- History of Hyde County
-
- History of Jackson County
- History of Johnston County
- History of Jones County
- History of Lee County
- History of Lenoir County
- History of Lincoln County
- History of Macon County
- History of Madison County
- History of Martin County
- History of McDowell County
- History of Mecklenburg County
- History of Mitchell County
- History of Montgomery County
- History of Moore County
- History of Nash County
- History of New Hanover County
- History of Northampton County
- History of Onslow County
- History of Orange County
- History of Pamlico County
-
- History of Pender County
-
- History of Person County
- History of Pitt County
- History of Polk County
- History of Randolph County
- History of Richmond County
- History of Robeson County
- History of Rockingham County
- History of Rowan County
- History of Rutherford County
- History of Sampson County
- History of Scotland County
- History of Stanly County
- History of Stokes County
- History of Surry County
- History of Swain County
- History of Transylvania County
- History of Tyrrell County
- History of Union County
- History of Vance County
- History of Wake County
- History of Warren County
- History of Washington County
- History of Watauga County
- History of Wayne County
- History of Wilkes County
- History of Wilson County
- History of Wilson County
- History of Yadkin County
- History of Yancey County
History of North Carolina, by subject
- Effects of Hurricane Charley in North CarolinaEffects of Hurricane Charley in North CarolinaThe effects of Hurricane Charley in North Carolina were minor to moderate and included $25 million in damage. Hurricane Charley lasted from August 9 to August 15, 2004, and at peak intensity it attained 150 miles per hour winds, making it a strong Category 4 hurricane on the...
- History of North Carolina State UniversityHistory of North Carolina State UniversityNorth Carolina State University was founded by the North Carolina General Assembly in 1887 as a land-grant college under the name North Carolina College of Agriculture and Mechanic Arts. As a land-grant college, NC State would provide a “liberal and practical education” while focusing on military...
Culture of North Carolina
- Main article: Culture of North CarolinaCulture of North CarolinaThe Culture of North Carolina is a subculture in the United States. As a coastal state, North Carolina culture has been greatly influenced by the southeastern united states and early settlers from England.- Food :...
- Museums in North Carolina
- Religion in North Carolina
- The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in North CarolinaThe Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in North CarolinaAs of year-end 2007, The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints reported reported 71,737 members in 15 stakes, 144 Congregations , 2 missions, and 1 temple in North Carolina.-History:...
- Episcopal Diocese of North CarolinaEpiscopal Diocese of North CarolinaThe Episcopal Diocese of North Carolina, founded in 1817, roughly corresponds to the segment of the U.S. state of North Carolina between I-77 in the west and I-95 in the east, including the most populous area of the state. Charlotte, Winston-Salem, Greensboro, Raleigh, Cary, and Durham are the...
- The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in North Carolina
- Scouting in North CarolinaScouting in North CarolinaScouting in North Carolina has a long history, from the 1910s to the present day, serving thousands of youth in programs that suit the environment in which they live.-Early history :...
- State symbols of North Carolina
- Flag of the State of North Carolina
- Great Seal of the State of North Carolina
Sports in North Carolina
- Main article: Sports in North CarolinaSports in North CarolinaAthletes and sports teams from North Carolina compete at every level of competition in the United States including NASCAR the NBA, the NFL, and the NHL along with several colleges and universities in various conferences across an array of divisions.-Baseball:...
Economy and infrastructure of North Carolina
- Main article: Economy of North CarolinaEconomy of North CarolinaNorth Carolina's 2010 total gross state product was $424.9 billion. In 2011 the civilian labor force was at around 4.5 million with employment near 4.1 million. The working population is employed across the major employment sectors...
- Communications in North Carolina
- Health care in North Carolina
- Transportation in North CarolinaTransportation in North CarolinaTransportation systems of North Carolina discusses the air, rail, road, and waterway systems of this state. The transportaion system has expanded as the state has become more populated and this expansion is linked to an overall increase in prosperity....
Education in North Carolina
- Main article: Education in North Carolina
- Schools in North Carolina
- School districts in North Carolina
- Colleges and universities in North Carolina
- University of North Carolina systemUniversity of North CarolinaChartered in 1789, the University of North Carolina was one of the first public universities in the United States and the only one to graduate students in the eighteenth century...
- North Carolina Community College SystemNorth Carolina Community College SystemThe North Carolina Community College System is a statewide network of fifty-eight public community colleges. Each college has a distinct governance system and policies. In total, the system enrolls over 800,000 students, and is the third largest community college system in the nation...
- University of North Carolina system
See also
- Outline of geographyOutline of geographyThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geography:Geography – science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth.- Geography is :...
- Outline of North America
- Outline of the United States
- Outline of North America
- Index of North Carolina-related articles

