Outline of Suriname
Encyclopedia
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
.
Suriname was formerly known as
Geographical renaming
Geographical renaming is the changing of the name of a geographical feature or area. This can range from the uncontroversial change of a street name to a highly disputed change to the name of a country. Some names are changed locally but the new names are not recognised by other countries,...
Nederlands Guyana, Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
Guiana or Dutch Guiana. Suriname is situated between French Guiana
French Guiana
French Guiana is an overseas region of France, consisting of a single overseas department located on the northern Atlantic coast of South America. It has borders with two nations, Brazil to the east and south, and Suriname to the west...
to the east and Guyana
Guyana
Guyana , officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, previously the colony of British Guiana, is a sovereign state on the northern coast of South America that is culturally part of the Anglophone Caribbean. Guyana was a former colony of the Dutch and of the British...
to the west. The southern border is shared with Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
and the northern border is the Atlantic
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
coast. The southernmost border with French Guiana is disputed along the Marowijne
Maroni River
The Maroni or Marowijne is a river in South America. It originates in the Tumuk Humak Mountains and forms the border between French Guiana and Suriname...
river; while the once-disputed boundary with Guyana was arbitrated by the United Nations Convention on Law of the Sea on September 20, 2007. The country is the smallest sovereign
Sovereignty
Sovereignty is the quality of having supreme, independent authority over a geographic area, such as a territory. It can be found in a power to rule and make law that rests on a political fact for which no purely legal explanation can be provided...
state in terms of area
Area
Area is a quantity that expresses the extent of a two-dimensional surface or shape in the plane. Area can be understood as the amount of material with a given thickness that would be necessary to fashion a model of the shape, or the amount of paint necessary to cover the surface with a single coat...
and population
Population
A population is all the organisms that both belong to the same group or species and live in the same geographical area. The area that is used to define a sexual population is such that inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with individuals...
in South America.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Suriname:
General reference
- PronunciationInternational Phonetic AlphabetThe International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic...
: - Common English country name: SurinameSurinameSuriname , officially the Republic of Suriname , is a country in northern South America. It borders French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west, Brazil to the south, and on the north by the Atlantic Ocean. Suriname was a former colony of the British and of the Dutch, and was previously known as...
- Official English country name: The Republic of Suriname
- Common endonym(s):
- Official endonym(s):
- Adjectival(s): Surinamese
- Demonym(s):
- EtymologyEtymologyEtymology is the study of the history of words, their origins, and how their form and meaning have changed over time.For languages with a long written history, etymologists make use of texts in these languages and texts about the languages to gather knowledge about how words were used during...
: Name of Suriname - ISO country codes: SR, SUR, 740
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:SRISO 3166-2:SRISO 3166-2:SR is the entry for Suriname in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization , which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1.Currently for Suriname, ISO 3166-2 codes are...
- InternetInternetThe Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
country code top-level domainCountry code top-level domainA country code top-level domain is an Internet top-level domain generally used or reserved for a country, a sovereign state, or a dependent territory....
: .sr.sr.sr is the Internet country code top-level domain for Suriname. This top-level domain is operated by Telesur, the local telecom company.-External links:* * *...
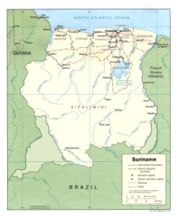
Geography of Suriname
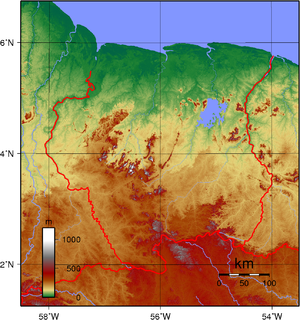
- Suriname is: a country
- Location:
- Northern HemisphereNorthern HemisphereThe Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
- Western HemisphereWestern HemisphereThe Western Hemisphere or western hemisphere is mainly used as a geographical term for the half of the Earth that lies west of the Prime Meridian and east of the Antimeridian , the other half being called the Eastern Hemisphere.In this sense, the western hemisphere consists of the western portions...
- South AmericaSouth AmericaSouth America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
- South America
- Time zoneTime zoneA time zone is a region on Earth that has a uniform standard time for legal, commercial, and social purposes. In order for the same clock time to always correspond to the same portion of the day as the Earth rotates , different places on the Earth need to have different clock times...
: UTC-03 - Extreme points of Suriname
- High: Juliana Top 1230 m (4,035 ft)
- Low: North Atlantic Ocean 0 m
- Land boundaries: 1,703 km
- Northern Hemisphere
-
 Guyana 600 km
Guyana 600 km Brazil 593 km
Brazil 593 km French Guiana 510 km
French Guiana 510 km
- Coastline: North Atlantic Ocean 386 km
- Population of Suriname: 458,000 - 168th most populous country
- Area of Suriname: 163,821 km2
- Atlas of Suriname
Environment of Suriname

- Climate of Suriname
- Environmental issues in Suriname
- Ecoregions in Suriname
- Renewable energy in Suriname
- Geology of Suriname
- Protected areas of Suriname
- Biosphere reserves in Suriname
- National parks of Suriname
- Wildlife of Suriname
- Flora of Suriname
- Fauna of Suriname
- Birds of Suriname
- Mammals of Suriname
Natural geographic features of Suriname
- Fjords of Suriname
- Glaciers of Suriname
- Islands of Suriname
- Lakes of Suriname
- Mountains of Suriname
- Volcanoes in Suriname
- Rivers of Suriname
- Waterfalls of Suriname
- Valleys of Suriname
- World Heritage Sites in Suriname
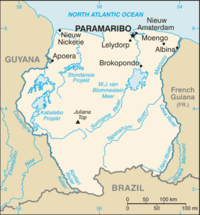
Administrative divisions of Suriname
- Districts of SurinameDistricts of Suriname-Overview:-History:The country was first divided up into subdivisions by the Dutch on October 8, 1834, when a Royal Decree declared that there were to be 8 divisions and 2 districts:*Upper Suriname and Torarica*Para*Upper Commewijne*Upper Cottica and Perica...
Districts of Suriname
- BrokopondoBrokopondo DistrictBrokopondo is a district of Suriname. Its capital city is Brokopondo; other towns include Brownsweg and Kwakoegron.The district has a population of 8,340, and an area of 7,364 square kilometres....
- CommewijneCommewijne DistrictCommewijne is a district of Suriname, located on the right bank of the Suriname River. Commewijne's capital city is Nieuw Amsterdam. Alliance is another major town.The district has a population of 25,200 and an area of 2,353 km²....
- CoronieCoronie DistrictCoronie is a district of Suriname, situated on the coast. Coronie's capital city is Totness, with other towns including Corneliskondre, Friendship, Jenny...
- MarowijneMarowijne DistrictMarowijne is a district of Suriname, located on the north-east coast. Marowijne's capital city is Albina, with other towns including Moengo and Wanhatti...
- NickerieNickerie DistrictNickerie is a district of Suriname, on the north-west coast. Nickerie's capital city is Nieuw-Nickerie, the second largest city in the country. Other towns include Washoda and Wageningen...
- ParaPara DistrictPara is a district of Suriname, in the north. Para's capital city is Onverwacht, with other towns including Paranam, Sabana and Zanderij.Para has a population of 15,120 and an area of 5,393 km²....
- ParamariboParamaribo DistrictParamaribo is a district of Suriname, encompassing the city of Paramaribo and the surrounding area.Paramaribo district has a population of 213,840 and an area 183 km²....
- SaramaccaSaramacca DistrictSaramacca is a district of Suriname, in the north. Saramacca's capital city is Groningen, with other towns and cities including Batavia and Boskamp.Saramacca has a population of 13,600 and an area of 3,636 km²....
- SipaliwiniSipaliwini DistrictSipaliwini is the largest district of Suriname, located in the south. Sipaliwini does not have a regional capital as it is directly administered by the national government in Paramaribo...
- WanicaWanica DistrictWanica is a district of Suriname, in the northeast. Wanica's capital city is Lelydorp.Wanica has a population of near 76,320 and an area of 444 km²...
Government and politics of Suriname
- Main article: Government of Suriname and Politics of SurinamePolitics of SurinamePolitics of Suriname takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the President of Suriname is the head of government, and of a pluriform multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the...
- Form of governmentForm of governmentA form of government, or form of state governance, refers to the set of political institutions by which a government of a state is organized. Synonyms include "regime type" and "system of government".-Empirical and conceptual problems:...
: - Capital of Suriname: Paramaribo
- Elections in SurinameElections in SurinameElections in Suriname gives information on election and election results in Suriname.Suriname elects on national level a head of state - the president - and a legislature. The president is elected for a five year term by an electoral college based on the parliament...
- (specific elections)
- Political parties in Suriname
- Political scandals of Suriname
- Taxation in Suriname
Executive branch of the government of Suriname
- Head of stateHead of StateA head of state is the individual that serves as the chief public representative of a monarchy, republic, federation, commonwealth or other kind of state. His or her role generally includes legitimizing the state and exercising the political powers, functions, and duties granted to the head of...
: President of SurinamePresident of SurinameThe President of the Republic of Suriname is, in accordance with the Constitution of 1987, the head of state, head of government, and commander-in-chief of Suriname....
, - Head of governmentHead of governmentHead of government is the chief officer of the executive branch of a government, often presiding over a cabinet. In a parliamentary system, the head of government is often styled prime minister, chief minister, premier, etc...
: Prime Minister of Suriname, - Cabinet of Suriname
Legislative branch of the government of Suriname
- Parliament of Suriname (bicameral)
- Upper houseUpper houseAn upper house, often called a senate, is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house; a legislature composed of only one house is described as unicameral.- Possible specific characteristics :...
: Senate of Suriname - Lower houseLower houseA lower house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the upper house.Despite its official position "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide the lower house has come to wield more power...
: House of Commons of Suriname
- Upper house
Judicial branch of the government of Suriname
- Supreme Court of Suriname
Foreign relations of Suriname
- Diplomatic missions in Suriname
- Diplomatic missions of SurinameDiplomatic missions of SurinameThis is a list of diplomatic missions of Suriname, excluding honorary consulates.-Europe:** Brussels ** Cayenne, French Guiana ** The Hague ** Amsterdam...
International organization membership
The Republic of Suriname is a member of:- African, Caribbean, and Pacific Group of States (ACP)
- Agency for the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons in Latin America and the Caribbean (OPANAL)
- Caribbean Community and Common Market (Caricom)
- Food and Agriculture OrganizationFood and Agriculture OrganizationThe Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations is a specialised agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger. Serving both developed and developing countries, FAO acts as a neutral forum where all nations meet as equals to negotiate agreements and...
(FAO) - Group of 77Group of 77The Group of 77 at the United Nations is a loose coalition of developing nations, designed to promote its members' collective economic interests and create an enhanced joint negotiating capacity in the United Nations. There were 77 founding members of the organization, but the organization has...
(G77) - Inter-American Development BankInter-American Development BankThe Inter-American Development Bank is the largest source of development financing for Latin America and the Caribbean...
(IADB) - International Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentInternational Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentThe International Bank for Reconstruction and Development is one of five institutions that compose the World Bank Group. The IBRD is an international organization whose original mission was to finance the reconstruction of nations devastated by World War II. Now, its mission has expanded to fight...
(IBRD) - International Civil Aviation OrganizationInternational Civil Aviation OrganizationThe International Civil Aviation Organization , pronounced , , is a specialized agency of the United Nations. It codifies the principles and techniques of international air navigation and fosters the planning and development of international air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth...
(ICAO) - International Criminal CourtInternational Criminal CourtThe International Criminal Court is a permanent tribunal to prosecute individuals for genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes, and the crime of aggression .It came into being on 1 July 2002—the date its founding treaty, the Rome Statute of the...
(ICCt) - International Criminal Police Organization (Interpol)
- International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesInternational Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesThe International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies is a humanitarian institution that is part of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement along with the ICRC and 186 distinct National Societies...
(IFRCS) - International Fund for Agricultural DevelopmentInternational Fund for Agricultural DevelopmentThe International Fund for Agricultural Development , a specialized agency of the United Nations, was established as an international financial institution in 1977 as one of the major outcomes of the 1974 World Food Conference. IFAD is dedicated to eradicating rural poverty in developing countries...
(IFAD) - International Hydrographic OrganizationInternational Hydrographic OrganizationThe International Hydrographic Organization is the inter-governmental organisation representing the hydrographic community. It enjoys observer status at the UN and is the recognised competent authority on hydrographic surveying and nautical charting...
(IHO) (suspended) - International Labour OrganizationInternational Labour OrganizationThe International Labour Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that deals with labour issues pertaining to international labour standards. Its headquarters are in Geneva, Switzerland. Its secretariat — the people who are employed by it throughout the world — is known as the...
(ILO) - International Maritime OrganizationInternational Maritime OrganizationThe International Maritime Organization , formerly known as the Inter-Governmental Maritime Consultative Organization , was established in Geneva in 1948, and came into force ten years later, meeting for the first time in 1959...
(IMO) - International Monetary FundInternational Monetary FundThe International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
(IMF) - International Olympic CommitteeInternational Olympic CommitteeThe International Olympic Committee is an international corporation based in Lausanne, Switzerland, created by Pierre de Coubertin on 23 June 1894 with Demetrios Vikelas as its first president...
(IOC) - International Organization for StandardizationInternational Organization for StandardizationThe International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
(ISO) (subscriber) - International Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementInternational Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementThe International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is an international humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide which was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and to prevent and alleviate human...
(ICRM) - International Telecommunication UnionInternational Telecommunication UnionThe International Telecommunication Union is the specialized agency of the United Nations which is responsible for information and communication technologies...
(ITU) - International Trade Union ConfederationInternational Trade Union ConfederationThe International Trade Union Confederation is the world's largest trade union federation. It was formed on November 1, 2006 out of the merger of the International Confederation of Free Trade Unions and the World Confederation of Labour...
(ITUC)
- Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU)
- Islamic Development BankIslamic Development BankThe Islamic Development Bank is a multilateral development financing institution located in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. It was founded by the first conference of Finance Ministers of the Organisation of the Islamic Conference , convened 23 Dhu'l Qa'dah 1393 AH.The bank officially began its activities on...
(IDB) - Latin American Economic SystemLatin American Economic SystemThe Latin American and the Caribbean Economic System, officially known as Sistema Económico Latinoamericano y del Caribe , is an organization founded in 1975 to promote economic cooperation and social development between Latin American and the Caribbean countries...
(LAES) - Multilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyMultilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyThe Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency is a member organization of the World Bank Group that offers political risk insurance. It was established to promote foreign direct investment into developing countries. MIGA was founded in 1988 with a capital base of $1 billion and is headquartered in...
(MIGA) - Nonaligned Movement (NAM)
- Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC)
- Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW)
- Organization of American StatesOrganization of American StatesThe Organization of American States is a regional international organization, headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States...
(OAS) - Permanent Court of ArbitrationPermanent Court of ArbitrationThe Permanent Court of Arbitration , is an international organization based in The Hague in the Netherlands.-History:The court was established in 1899 as one of the acts of the first Hague Peace Conference, which makes it the oldest institution for international dispute resolution.The creation of...
(PCA) - Union of South American Nations (UNASUR)
- United NationsUnited NationsThe United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
(UN) - United Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentUnited Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentThe United Nations Conference on Trade and Development was established in 1964 as a permanent intergovernmental body. It is the principal organ of the United Nations General Assembly dealing with trade, investment, and development issues....
(UNCTAD) - United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- United Nations Industrial Development OrganizationUnited Nations Industrial Development OrganizationThe United Nations Industrial Development Organization , French/Spanish acronym ONUDI, is a specialized agency in the United Nations system, headquartered in Vienna, Austria...
(UNIDO) - Universal Postal UnionUniversal Postal UnionThe Universal Postal Union is an international organization that coordinates postal policies among member nations, in addition to the worldwide postal system. The UPU contains four bodies consisting of the Congress, the Council of Administration , the Postal Operations Council and the...
(UPU) - World Confederation of LabourWorld Confederation of LabourThe World Confederation of Labour was an international labour organization founded in 1920 and based in Europe. Totalitarian governments of the 1930s repressed the federation and imprisoned many of its leaders, limiting operations until the end of World War II...
(WCL) - World Federation of Trade UnionsWorld Federation of Trade UnionsThe World Federation of Trade Unions was established in 1945 to replace the International Federation of Trade Unions. Its mission was to bring together trade unions across the world in a single international organization, much like the United Nations...
(WFTU) - World Health OrganizationWorld Health OrganizationThe World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
(WHO) - World Intellectual Property OrganizationWorld Intellectual Property OrganizationThe World Intellectual Property Organization is one of the 17 specialized agencies of the United Nations. WIPO was created in 1967 "to encourage creative activity, to promote the protection of intellectual property throughout the world"....
(WIPO) - World Meteorological OrganizationWorld Meteorological OrganizationThe World Meteorological Organization is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 189 Member States and Territories. It originated from the International Meteorological Organization , which was founded in 1873...
(WMO) - World Trade OrganizationWorld Trade OrganizationThe World Trade Organization is an organization that intends to supervise and liberalize international trade. The organization officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade , which commenced in 1948...
(WTO)
Law and order in Suriname
- Capital punishment in SurinameCapital punishment in Suriname-History:Since Suriname was a Dutch colony until 1975, it followed Dutch law which abolished the death penalty in 1870. From 1975 to 1980, capital punishment was still on the books, but no crimes were committed heavy enough to warrant prosecution for it...
- Constitution of SurinameConstitution of SurinameThe current Constitution of Suriname was adopted on 30 September 1987, following a referendum. It marked the return to democracy after the Bouterse military dictatorship of the 1980s. The first constitution of independent Suriname was adopted in 1975, and was modeled after the Constitution of the...
- Crime in Suriname
- Human rights in Suriname
- LGBT rights in Suriname
- Freedom of religion in Suriname
- Law enforcement in Suriname
Military of Suriname
- Command
- Commander-in-chiefCommander-in-ChiefA commander-in-chief is the commander of a nation's military forces or significant element of those forces. In the latter case, the force element may be defined as those forces within a particular region or those forces which are associated by function. As a practical term it refers to the military...
:- Ministry of Defence of Suriname
- Commander-in-chief
- Forces
- Army of Suriname
- Navy of Suriname
- Air Force of Suriname
- Special forces of Suriname
- Military history of Suriname
- Military ranks of Suriname
History of Suriname
- Main article: History of SurinameHistory of Suriname-Native American period:The history of Suriname dates from 3000 BC when Native Americans first inhabited the area. Present-day Suriname was the home to many distinct indigenous cultures. The largest tribes were the Arawaks, a nomadic coastal tribe that lived from hunting and fishing, and the Caribs...
, Timeline of the history of Suriname, and Current events of Suriname
- Economic history of Suriname
- Military history of Suriname
Culture of Suriname
- Architecture of Suriname
- Cuisine of Suriname
- Ethnic minorities in Suriname
- Festivals in Suriname
- Humor in Suriname
- Languages of Suriname
- Media in Suriname
- National symbols of Suriname
- Coat of arms of SurinameCoat of arms of SurinameOn 25 November 1975 the independent Republic of Suriname adopted an official coat of arms. The motto reads Justitia - Pietas - Fides . It further consists of two natives who carry a shield. The left half of the shield symbolizes the past, as slaves were abducted via ship out of Africa...
- Flag of SurinameFlag of SurinameThe flag of Suriname is formed by five horizontal bands of green , white, red , white, and green . There is a large, yellow, five-pointed star centered in the red band....
- National anthem of Suriname
- Coat of arms of Suriname
- People of Suriname
- Prostitution in SurinameProstitution in Suriname-External links:****...
- Public holidays in Suriname
- Records of Suriname
- Religion in SurinameReligion in SurinameSuriname is home to a many diverse religious and ethnic groups. According to recent census data, 40.7 percent of the population of Suriname is Christian, including Roman Catholics and Protestant groups—among them Moravian, Lutheran, Dutch Reformed, Evangelical, Baptist, and Methodist...
- Buddhism in Suriname
- Christianity in Suriname
- Hinduism in Suriname
- Islam in SurinameIslam in SurinameAccording to the most recent census , the Muslim population of Suriname is 66,307, representing about 13.5 percent of the country's total population, giving the country the highest percentages of Muslims on the American continent....
- Judaism in Suriname
- Sikhism in Suriname
- World Heritage Sites in Suriname
Art in Suriname
- Art in Suriname
- Cinema of Suriname
- Literature of Suriname
- Music of SurinameMusic of SurinameThe music of Suriname is well known for kaseko music, and for having an Indo-Caribbean tradition.-Kaseko:Kaseko is probably derived from the French expression casser le corps , which was used during slavery to indicate a very swift dance. Kaseko is a fusion of numerous popular and folk styles...
- Television in Suriname
- Theatre in Suriname
Sports in Suriname
- Football in SurinameFootball in SurinameThe sport of football in the country of Suriname is run by the Surinamese Football Association. The association administers the national football team, as well as the national football league....
- Suriname at the OlympicsSuriname at the OlympicsSuriname first participated at the Olympic Games in 1960, and has sent athletes to compete in most Summer Olympic Games since then. The nation missed the 1964 Games, and also participated in the American-led boycott of the 1980 Summer Olympics...
Economy and infrastructure of Suriname
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 154th (one hundred and fifty fourth)
- Agriculture in SurinameAgriculture in SurinameAgriculture in Suriname plays a secondary role in the economy, employing around 12 percent of the workforce. Only 0.4 percent of Suriname's total land area is cultivable, with half of this devoted to rice production, which makes up around 10 percent of Suriname's total exports, with 180,000 tons...
- Banking in Suriname
- National Bank of Suriname
- Communications in SurinameCommunications in SurinameThere are a number of systems of communication in Suriname, including a system of telephony, and radio telecommunications. The country code and top-level domain for Suriname is "SR".-Telephony:...
- Internet in Suriname
- Companies of Suriname
- Currency of SurinameCurrencyIn economics, currency refers to a generally accepted medium of exchange. These are usually the coins and banknotes of a particular government, which comprise the physical aspects of a nation's money supply...
: Dollar- ISO 4217ISO 4217ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Standards Organization, which delineates currency designators, country codes , and references to minor units in three tables:* Table A.1 – Current currency & funds code list...
: SRD
- ISO 4217
- Economic history of Suriname
- Energy in Suriname
- Energy policy of Suriname
- Oil industry in Suriname
- Health care in Suriname
- Mining in Suriname
- Suriname Stock Exchange
- Tourism in Suriname
- Transport in SurinameTransport in SurinameThe South American country of Suriname has a number of forms of transport.-Railways:*Railways, total: 166 km single track.**standard gauge: 80 km gauge in West-Suriname, but not in use...
- Airports in Suriname
- Rail transport in Suriname
- Roads in Suriname
- Water supply and sanitation in Suriname
See also
- Index of Suriname-related articles
- List of Suriname-related topics
- List of international rankings
- Member state of the United Nations
- Outline of geographyOutline of geographyThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geography:Geography – science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth.- Geography is :...
- Outline of South America
- List of place names of Dutch origin

