Outline of Virginia
Encyclopedia
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
Commonwealth of Virginia:
General reference
- Names
- Common name: VirginiaVirginiaThe Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there...
- Pronunciation: vərˈdʒɪnjə
- Official name: Commonwealth of Virginia
- Abbreviations and name codes
- Postal symbol: VA
- ISO 3166-2 code: US-VA
- InternetInternetThe Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
second-level domainSecond-level domainIn the Domain Name System hierarchy, a second-level domain is a domain that is directly below a top-level domain . For example, in example.com, example is the second-level domain of the .com TLD....
: .va.us
- Nicknames
- Mother of Presidents
- The Old Dominion
- The Commonwealth
- Common name: Virginia
- Adjectivals: VirginiaVirginiaThe Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there...
, VirginianVirginianVirginian is an adjective used to describe something as being of, from, or related to the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States.Virginian may also refer to:-Automobiles:... - Demonym: VirginianVirginianVirginian is an adjective used to describe something as being of, from, or related to the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States.Virginian may also refer to:-Automobiles:...
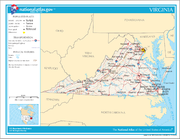
Geography of Virginia
- Main article: Geography of Virginia
- Virginia is: a U.S. stateU.S. stateA U.S. state is any one of the 50 federated states of the United States of America that share sovereignty with the federal government. Because of this shared sovereignty, an American is a citizen both of the federal entity and of his or her state of domicile. Four states use the official title of...
, a federal state of the United States of America - Location
- Northern hemisphereNorthern HemisphereThe Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
- Western hemisphereWestern HemisphereThe Western Hemisphere or western hemisphere is mainly used as a geographical term for the half of the Earth that lies west of the Prime Meridian and east of the Antimeridian , the other half being called the Eastern Hemisphere.In this sense, the western hemisphere consists of the western portions...
- AmericasAmericasThe Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
- North AmericaNorth AmericaNorth America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
- Anglo America
- Northern AmericaNorthern AmericaNorthern America is the northernmost region of the Americas, and is part of the North American continent. It lies directly north of the region of Middle America; the land border between the two regions coincides with the border between the United States and Mexico...
- United States of America
- Contiguous United StatesContiguous United StatesThe contiguous United States are the 48 U.S. states on the continent of North America that are south of Canada and north of Mexico, plus the District of Columbia....
- Eastern United StatesEastern United StatesThe Eastern United States, the American East, or simply the East is traditionally defined as the states east of the Mississippi River. The first two tiers of states west of the Mississippi have traditionally been considered part of the West, but can be included in the East today; usually in...
- East Coast of the United StatesEast Coast of the United StatesThe East Coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, refers to the easternmost coastal states in the United States, which touch the Atlantic Ocean and stretch up to Canada. The term includes the U.S...
- Mid-Atlantic statesMid-Atlantic StatesThe Mid-Atlantic states, also called middle Atlantic states or simply the mid Atlantic, form a region of the United States generally located between New England and the South...
- Southeastern United StatesSoutheastern United StatesThe Southeastern United States, colloquially referred to as the Southeast, is the eastern portion of the Southern United States. It is one of the most populous regions in the United States of America....
- East Coast of the United States
- Southern United StatesSouthern United StatesThe Southern United States—commonly referred to as the American South, Dixie, or simply the South—constitutes a large distinctive area in the southeastern and south-central United States...
- Eastern United States
- Contiguous United States
- United States of America
- North America
- Americas
- Northern hemisphere
- Population of Virginia: 8,001,024 (2010 U.S. Census)
- Area of Virginia:
- Atlas of Virginia
Places in Virginia
- Historic places in Virginia
- Abandoned communities in Virginia
- Ghost towns in Virginia
- National Historic Landmarks in Virginia
- National Register of Historic Places listings in VirginiaNational Register of Historic Places listings in VirginiaBuildings, sites, districts, and objects in Virginia listed on the National Register of Historic Places:As of November 25, 2011, there are 2,768 properties and districts listed on the National Register of Historic Places in all 95 Virginia counties and 36 of 39 independent cities, including 119...
- Abandoned communities in Virginia
- National Natural Landmarks in Virginia
- National parks in Virginia
- State parks in Virginia
Environment of Virginia
- Climate of VirginiaClimate of VirginiaThe climate of Virginia, a state on the east coast of the United States, is considered mild compared to other areas of the United States. Most of Virginia east of the Blue Ridge Mountains,the southern part of the Shenandoah Valley, and the Roanoke Valley, has a humid subtropical climate...
- Protected areas in Virginia
- Superfund sites in Virginia
Natural geographic features of Virginia
- Lakes of Virginia
- Mountains of Virginia
- Gaps of Virginia
- Rivers of Virginia
Administrative divisions of Virginia

- The 95 Counties and 39 Cities of the Commonwealth of Virginia
- Municipalities in Virginia
- Cities in Virginia
- State capital of Virginia:
- City nicknames in Virginia
- Towns in Virginia
- Unincorporated communities in Virginia
- Cities in Virginia
- Municipalities in Virginia
Government and politics of Virginia
- Main article: Government of VirginiaGovernment of VirginiaThe government of Virginia combines the three branches of authority in the Commonwealth of Virginia. The current Governor of Virginia is Bob McDonnell. The State Capitol building in Richmond was designed by Thomas Jefferson, and the cornerstone was laid by Governor Patrick Henry in 1785. Virginia...
and Politics of VirginiaPolitics of VirginiaThe politics of Virginia reflect a state that is beginning to experience a conflict between its increasingly liberal northern region and its traditionally conservative southern region...
- Form of governmentForm of governmentA form of government, or form of state governance, refers to the set of political institutions by which a government of a state is organized. Synonyms include "regime type" and "system of government".-Empirical and conceptual problems:...
: U.S. state governmentState governments of the United StatesState governments in the United States are those republics formed by citizens in the jurisdiction thereof as provided by the United States Constitution; with the original 13 States forming the first Articles of Confederation, and later the aforementioned Constitution. Within the U.S... - United States congressional delegations from VirginiaUnited States Congressional Delegations from VirginiaThese are tables of congressional delegations from Virginia to the United States Senate and United States House of Representatives.Virginia has undergone so many demographic changes that in some cases, a district often is not a direct continuation of the same numbered district before reapportionment...
- Virginia State CapitolVirginia State CapitolThe Virginia State Capitol is the seat of state government in the Commonwealth of Virginia, located in Richmond, the third capital of Virginia. It houses the oldest legislative body in the United States, the Virginia General Assembly...
- Elections in Virginia
- Electoral reform in VirginiaElectoral reform in VirginiaElectoral reform in Virginia refers to efforts to change the electoral system in the Commonwealth of Virginia. Virginia has undergone much electoral change since its settling in 1607, many of which were required by federal legislation...
- Electoral reform in Virginia
- Political party strength in VirginiaPolitical party strength in VirginiaThe following table indicates the party of elected officials in the U.S. state of Virginia:*Governor*Lieutenant Governor*Attorney GeneralThe table also indicates the historical party composition in the:*State Senate*State House of Delegates...
Executive branch of the government of Virginia
- Governor of VirginiaGovernor of VirginiaThe governor of Virginia serves as the chief executive of the Commonwealth of Virginia for a four-year term. The position is currently held by Republican Bob McDonnell, who was inaugurated on January 16, 2010, as the 71st governor of Virginia....
- Lieutenant Governor of VirginiaLieutenant Governor of VirginiaThe Lieutenant Governor is a constitutional officer of the Commonwealth of Virginia. The Lieutenant Governor is elected every four years along with the Governor and Attorney General. The office is currently held by Republican William T. Bolling. The governor and lieutenant governor are elected...
- Secretary of State of Virginia
- Lieutenant Governor of Virginia
- State departments
- Virginia Department of TransportationVirginia Department of TransportationThe Virginia Department of Transportation is the agency of state government responsible for transportation in the state of Virginia in the United States. Headquartered in Downtown Richmond, VDOT is responsible for building, maintaining, and operating the roads, bridges and tunnels in the...
- Virginia Department of Transportation
Legislative branch of the government of Virginia
- Virginia General AssemblyVirginia General AssemblyThe Virginia General Assembly is the legislative body of the Commonwealth of Virginia, and the oldest legislative body in the Western Hemisphere, established on July 30, 1619. The General Assembly is a bicameral body consisting of a lower house, the Virginia House of Delegates, with 100 members,...
(bicameral)- Upper houseUpper houseAn upper house, often called a senate, is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house; a legislature composed of only one house is described as unicameral.- Possible specific characteristics :...
: Virginia Senate - Lower houseLower houseA lower house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the upper house.Despite its official position "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide the lower house has come to wield more power...
: Virginia House of DelegatesVirginia House of DelegatesThe Virginia House of Delegates is the lower house of the Virginia General Assembly. It has 100 members elected for terms of two years; unlike most states, these elections take place during odd-numbered years. The House is presided over by the Speaker of the House, who is elected from among the...
- Upper house
Judicial branch of the government of Virginia
- Supreme Court of Virginia
Law and order in Virginia
Law of Virginia- Capital punishment in VirginiaCapital punishment in VirginiaCapital punishment is legal in the U.S. State of Virginia. In what is now the Commonwealth of Virginia, the first execution in the future United States was carried out in 1608. It was the first of 1,384 executions, the highest total of any state in the Union...
- Constitution of VirginiaConstitution of VirginiaThe Constitution of the Commonwealth of Virginia is the document that defines and limits the powers of the state government and the basic rights of the citizens of the U.S. Commonwealth of Virginia. Like all other state constitutions, it is supreme over Virginia's laws and acts of government,...
- Crime in VirginiaCrime in VirginiaIn 2008 there were 452,941 crimes reported in Virginia, including 21,811 violent crimes and 369 murders and homicides.-Crime in Richmond:Crime in Richmond, Virginia has been a major problem but is progressively getting better...
- Gun laws in Virginia
- Law enforcement in Virginia
- Law enforcement agencies in Virginia
- Virginia State PoliceVirginia State PoliceVirginia State Police is a state agency, conceived in 1919 and established in 1932, that acts as the state police force for the Commonwealth of Virginia. The agency originated out of the Virginia Department of Motor Vehicles as an inspector and enforcer of highway laws...
- Virginia State Police
- Law enforcement agencies in Virginia
History of Virginia, by period
- Prehistory of Virginia
- Native American tribes in VirginiaNative American tribes in VirginiaThis page details the history and current status of Indian tribes in the Commonwealth of Virginia.All of the Commonwealth of Virginia used to be Virginia Indian territory, an area estimated to have been occupied by indigenous peoples for more than 12,000 years. Their population has been estimated...
- PowhatanPowhatanThe Powhatan is the name of a Virginia Indian confederation of tribes. It is estimated that there were about 14,000–21,000 of these native Powhatan people in eastern Virginia when the English settled Jamestown in 1607...
- Powhatan
- Native American tribes in Virginia
- EnglishEnglandEngland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
Colony of Virginia, 1584–1707- Roanoke ColonyRoanoke ColonyThe Roanoke Colony on Roanoke Island in Dare County, present-day North Carolina, United States was a late 16th-century attempt to establish a permanent English settlement in what later became the Virginia Colony. The enterprise was financed and organized by Sir Walter Raleigh and carried out by...
, 1585–1587 - Jamestown, VirginiaJamestown, VirginiaJamestown was a settlement in the Colony of Virginia. Established by the Virginia Company of London as "James Fort" on May 14, 1607 , it was the first permanent English settlement in what is now the United States, following several earlier failed attempts, including the Lost Colony of Roanoke...
, 1607–1760 - History of slavery in VirginiaHistory of slavery in VirginiaThe History of slavery in Virginia can be traced back to the very founding of Virginia as an English colony by the London Virginia Company. The headright system tried to solve the labor shortage by providing colonists with land for each indentured servant they transported to Virginia...
- Middle Plantation, VirginiaWilliamsburg, VirginiaWilliamsburg is an independent city located on the Virginia Peninsula in the Hampton Roads metropolitan area of Virginia, USA. As of the 2010 Census, the city had an estimated population of 14,068. It is bordered by James City County and York County, and is an independent city...
, since 1632 (WilliamsburgWilliamsburg, VirginiaWilliamsburg is an independent city located on the Virginia Peninsula in the Hampton Roads metropolitan area of Virginia, USA. As of the 2010 Census, the city had an estimated population of 14,068. It is bordered by James City County and York County, and is an independent city...
since 1698)
- Roanoke Colony
- FrenchFranceThe French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
colony of LouisianeLouisiana (New France)Louisiana or French Louisiana was an administrative district of New France. Under French control from 1682–1763 and 1800–03, the area was named in honor of Louis XIV, by French explorer René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de la Salle...
, 1699–1764 - BritishUnited KingdomThe United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
Colony of Virginia, 1707–1776 - French and Indian WarFrench and Indian WarThe French and Indian War is the common American name for the war between Great Britain and France in North America from 1754 to 1763. In 1756, the war erupted into the world-wide conflict known as the Seven Years' War and thus came to be regarded as the North American theater of that war...
, 1754–1763- Treaty of Fontainebleau of 1762Treaty of Fontainebleau (1762)The Treaty of Fontainebleau was a secret agreement in which France ceded Louisiana to Spain. The treaty followed the last battle in the French and Indian War, the Battle of Signal Hill in September 1762, which confirmed British control of Canada. However, the associated Seven Years War continued...
- Treaty of Paris of 1763Treaty of Paris (1763)The Treaty of Paris, often called the Peace of Paris, or the Treaty of 1763, was signed on 10 February 1763, by the kingdoms of Great Britain, France and Spain, with Portugal in agreement. It ended the French and Indian War/Seven Years' War...
- Treaty of Fontainebleau of 1762
- BritishUnited KingdomThe United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
Indian ReserveIndian Reserve (1763)The Indian Reserve was a territory under British rule in North America set aside in the Royal Proclamation of 1763 for use by American Indians between 1763 and 1783....
, 1763–1783- Royal Proclamation of 1763Royal Proclamation of 1763The Royal Proclamation of 1763 was issued October 7, 1763, by King George III following Great Britain's acquisition of French territory in North America after the end of the French and Indian War/Seven Years' War...
- Dunmore's WarDunmore's WarDunmore's War was a war in 1774 between the Colony of Virginia and the Shawnee and Mingo American Indian nations....
1774
- Royal Proclamation of 1763
- American Revolutionary WarAmerican Revolutionary WarThe American Revolutionary War , the American War of Independence, or simply the Revolutionary War, began as a war between the Kingdom of Great Britain and thirteen British colonies in North America, and ended in a global war between several European great powers.The war was the result of the...
, 1775–1783- United States Declaration of IndependenceUnited States Declaration of IndependenceThe Declaration of Independence was a statement adopted by the Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, which announced that the thirteen American colonies then at war with Great Britain regarded themselves as independent states, and no longer a part of the British Empire. John Adams put forth a...
of 1776 - Treaty of Paris of 1783Treaty of Paris (1783)The Treaty of Paris, signed on September 3, 1783, ended the American Revolutionary War between Great Britain on the one hand and the United States of America and its allies on the other. The other combatant nations, France, Spain and the Dutch Republic had separate agreements; for details of...
- United States Declaration of Independence
- Commonwealth of Virginia since 1776
- Chickamauga WarsChickamauga warsThe Chickamauga Wars were a series of raids, campaigns, ambushes, minor skirmishes, and several full-scale frontier battles which were a continuation of the Cherokee struggle against encroachment by American frontiersmen from the former British colonies...
, 1776–1794 - First state to ratify the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, signed July 9, 1778
- Northwestern territorial claimsState cessionsThe state cessions are those areas of the United States that the separate states ceded to the federal government in the late 18th and early 19th century...
ceded 1784 - Tenth state to ratify the Constitution of the United States of America on June 25, 1788
- George WashingtonGeorge WashingtonGeorge Washington was the dominant military and political leader of the new United States of America from 1775 to 1799. He led the American victory over Great Britain in the American Revolutionary War as commander-in-chief of the Continental Army from 1775 to 1783, and presided over the writing of...
becomes the first President of the United StatesPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
on April 30, 1789 - Separation of the Commonwealth of Kentucky, 1792
- Thomas JeffersonThomas JeffersonThomas Jefferson was the principal author of the United States Declaration of Independence and the Statute of Virginia for Religious Freedom , the third President of the United States and founder of the University of Virginia...
becomes the third President of the United StatesPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
on March 4, 1801 - James MadisonJames MadisonJames Madison, Jr. was an American statesman and political theorist. He was the fourth President of the United States and is hailed as the “Father of the Constitution” for being the primary author of the United States Constitution and at first an opponent of, and then a key author of the United...
becomes the fourth President of the United StatesPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
on March 4, 1809 - War of 1812War of 1812The War of 1812 was a military conflict fought between the forces of the United States of America and those of the British Empire. The Americans declared war in 1812 for several reasons, including trade restrictions because of Britain's ongoing war with France, impressment of American merchant...
, 1812–1815 - Treaty of GhentTreaty of GhentThe Treaty of Ghent , signed on 24 December 1814, in Ghent , was the peace treaty that ended the War of 1812 between the United States of America and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland...
, December 24, 1814 - James MonroeJames MonroeJames Monroe was the fifth President of the United States . Monroe was the last president who was a Founding Father of the United States, and the last president from the Virginia dynasty and the Republican Generation...
becomes the fifth President of the United StatesPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
on March 4, 1817 - William Henry HarrisonWilliam Henry HarrisonWilliam Henry Harrison was the ninth President of the United States , an American military officer and politician, and the first president to die in office. He was 68 years, 23 days old when elected, the oldest president elected until Ronald Reagan in 1980, and last President to be born before the...
becomes ninth President of the United StatesPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
on March 4, 1841 - John TylerJohn TylerJohn Tyler was the tenth President of the United States . A native of Virginia, Tyler served as a state legislator, governor, U.S. representative, and U.S. senator before being elected Vice President . He was the first to succeed to the office of President following the death of a predecessor...
becomes the tenth President of the United StatesPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
on April 4, 1841 - Mexican-American War, April 25, 1846 – February 2, 1848
- Zachary TaylorZachary TaylorZachary Taylor was the 12th President of the United States and an American military leader. Initially uninterested in politics, Taylor nonetheless ran as a Whig in the 1848 presidential election, defeating Lewis Cass...
becomes 12th President of the United StatesPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
on March 4, 1849 - Virginia in the American Civil War, 1861–1865
- Confederate States of AmericaConfederate States of AmericaThe Confederate States of America was a government set up from 1861 to 1865 by 11 Southern slave states of the United States of America that had declared their secession from the U.S...
, 1861–1865- Eighth state to declare secession from the United States on April 17, 1861
- Eighth state admitted to the Confederate States of AmericaConfederate States of AmericaThe Confederate States of America was a government set up from 1861 to 1865 by 11 Southern slave states of the United States of America that had declared their secession from the U.S...
on May 7, 1861
- Manassas CampaignFirst Battle of Bull RunFirst Battle of Bull Run, also known as First Manassas , was fought on July 21, 1861, in Prince William County, Virginia, near the City of Manassas...
, July 2–21, 1861- First Battle of Bull RunFirst Battle of Bull RunFirst Battle of Bull Run, also known as First Manassas , was fought on July 21, 1861, in Prince William County, Virginia, near the City of Manassas...
, July 21, 1861
- First Battle of Bull Run
- Battle of Hampton RoadsBattle of Hampton RoadsThe Battle of Hampton Roads, often referred to as either the Battle of the Monitor and Merrimack or the Battle of Ironclads, was the most noted and arguably most important naval battle of the American Civil War from the standpoint of the development of navies...
, March 8–9, 1862 - Valley CampaignValley CampaignJackson's Valley Campaign was Confederate Maj. Gen. Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson's famous spring 1862 campaign through the Shenandoah Valley in Virginia during the American Civil War...
, March 23 – June 9, 1862 - Peninsula CampaignPeninsula CampaignThe Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War was a major Union operation launched in southeastern Virginia from March through July 1862, the first large-scale offensive in the Eastern Theater. The operation, commanded by Maj. Gen. George B...
, March – July 1862- Battle of Seven PinesBattle of Seven PinesThe Battle of Seven Pines, also known as the Battle of Fair Oaks or Fair Oaks Station, took place on May 31 and June 1, 1862, in Henrico County, Virginia, as part of the Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War. It was the culmination of an offensive up the Virginia Peninsula by Union Maj. Gen....
, May 31 – June 1, 1862 - Seven Days BattlesSeven Days BattlesThe Seven Days Battles was a series of six major battles over the seven days from June 25 to July 1, 1862, near Richmond, Virginia during the American Civil War. Confederate General Robert E. Lee drove the invading Union Army of the Potomac, commanded by Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan, away from...
, June 25 – July 1, 1862
- Battle of Seven Pines
- Northern Virginia CampaignNorthern Virginia CampaignThe Northern Virginia Campaign, also known as the Second Bull Run Campaign or Second Manassas Campaign, was a series of battles fought in Virginia during August and September 1862 in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. Confederate General Robert E...
, July 19 – September 1, 1862- Second Battle of Bull RunSecond Battle of Bull RunThe Second Battle of Bull Run or Second Manassas was fought August 28–30, 1862, as part of the American Civil War. It was the culmination of an offensive campaign waged by Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia against Union Maj. Gen...
, August 29–30, 1862
- Second Battle of Bull Run
- Battle of FredericksburgBattle of FredericksburgThe Battle of Fredericksburg was fought December 11–15, 1862, in and around Fredericksburg, Virginia, between General Robert E. Lee's Confederate Army of Northern Virginia and the Union Army of the Potomac, commanded by Maj. Gen. Ambrose E. Burnside...
, December 11–15, 1862 - Battle of ChancellorsvilleBattle of ChancellorsvilleThe Battle of Chancellorsville was a major battle of the American Civil War, and the principal engagement of the Chancellorsville Campaign. It was fought from April 30 to May 6, 1863, in Spotsylvania County, Virginia, near the village of Chancellorsville. Two related battles were fought nearby on...
, May 1–4, 1863 - Separation of the State of West Virginia, 1863
- Bristoe CampaignBristoe CampaignThe Bristoe Campaign was a series of minor battles fought in Virginia during October and November 1863, in the American Civil War. Maj. Gen. George G. Meade, commanding the Union Army of the Potomac, began to maneuver in an unsuccessful attempt to defeat Gen. Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern...
, October 14 – November 9, 1863 - Overland CampaignOverland CampaignThe Overland Campaign, also known as Grant's Overland Campaign and the Wilderness Campaign, was a series of battles fought in Virginia during May and June 1864, in the American Civil War. Lt. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant, general-in-chief of all Union armies, directed the actions of the Army of the...
, May 5 – June 24, 1864- Battle of the WildernessBattle of the WildernessThe Battle of the Wilderness, fought May 5–7, 1864, was the first battle of Lt. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant's 1864 Virginia Overland Campaign against Gen. Robert E. Lee and the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia. Both armies suffered heavy casualties, a harbinger of a bloody war of attrition by...
, May 5–7, 1864 - Battle of Spotsylvania Court HouseBattle of Spotsylvania Court HouseThe Battle of Spotsylvania Court House, sometimes simply referred to as the Battle of Spotsylvania , was the second major battle in Lt. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant's 1864 Overland Campaign of the American Civil War. Following the bloody but inconclusive Battle of the Wilderness, Grant's army disengaged...
, May 8–21, 1864 - Battle of Cold HarborBattle of Cold HarborThe Battle of Cold Harbor was fought from May 31 to June 12, 1864 . It was one of the final battles of Union Lt. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant's Overland Campaign during the American Civil War, and is remembered as one of American history's bloodiest, most lopsided battles...
, May 31 – June 12, 1864
- Battle of the Wilderness
- Valley CampaignsValley Campaigns of 1864The Valley Campaigns of 1864 were American Civil War operations and battles that took place in the Shenandoah Valley of Virginia from May to October 1864. Military historians divide this period into three separate campaigns, but it is useful to consider the three together and how they...
, May 15 – October 19, 1864 - Bermuda Hundred CampaignBermuda Hundred CampaignThe Bermuda Hundred Campaign was a series of battles fought at the town of Bermuda Hundred, outside Richmond, Virginia, during May 1864 in the American Civil War. Union Maj. Gen. Benjamin Butler, commanding the Army of the James, threatened Richmond from the east but was stopped by forces under ...
, May 6–20, 1864 - Siege of PetersburgSiege of PetersburgThe Richmond–Petersburg Campaign was a series of battles around Petersburg, Virginia, fought from June 9, 1864, to March 25, 1865, during the American Civil War...
, June 9, 1864 – March 25, 1865 - Appomattox CampaignAppomattox CampaignThe Appomattox Campaign was a series of battles fought March 29 – April 9, 1865, in Virginia that culminated in the surrender of Confederate General Robert E...
, March 29 – April 9, 1865- Battle of Five ForksBattle of Five ForksThe Battle of Five Forks was fought on April 1, 1865, southwest of Petersburg, Virginia, in Dinwiddie County, during the Appomattox Campaign of the American Civil War. The battle, sometimes referred to as the "Waterloo of the Confederacy," pitted Union Maj. Gen. Philip H. Sheridan against...
, April 1, 1865 - Battle of Appomattox Court House, April 9, 1865
- Battle of Five Forks
- Confederate States of America
- Virginia in Reconstruction, 1865–1870
- Eighth former Confederate state readmitted to the United States on January 26, 1870
- Woodrow WilsonWoodrow WilsonThomas Woodrow Wilson was the 28th President of the United States, from 1913 to 1921. A leader of the Progressive Movement, he served as President of Princeton University from 1902 to 1910, and then as the Governor of New Jersey from 1911 to 1913...
becomes 28th President of the United StatesPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
on March 4, 1913 - Shenandoah National ParkShenandoah National ParkShenandoah National Park encompasses part of the Blue Ridge Mountains in the U.S. state of Virginia. This national park is long and narrow, with the broad Shenandoah River and valley on the west side, and the rolling hills of the Virginia Piedmont on the east...
established on December 26, 1935
Culture of Virginia
Culture of VirginiaCulture of Virginia
The Culture of Virginia refers to the distinct human activities and values that take place in, or originate from the Commonwealth of Virginia. Virginia's historic culture was popularized and spread across America and the South by Washington, Jefferson, and Lee, and their homes represent Virginia as...
- Museums in Virginia
- Religion in Virginia
- The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in VirginiaThe Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in VirginiaAs of year-end 2007, The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints reported 83,225 members in 19 stakes, 183 Congregations , and 2 missions in Virginia.-History:A brief history can be found at -Membership History:-Stakes:...
- Episcopal Diocese of VirginiaEpiscopal Diocese of VirginiaThe Diocese of Virginia is a diocese of the Episcopal Church in the United States of America encompassing 38 counties in the northern and central parts of the state of Virginia. The diocese was organized in 1785 and is one of the Episcopal Church's nine original dioceses. However, the diocese has...
- The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in Virginia
- Scouting in VirginiaScouting in VirginiaScouting in Virginia has a long history, from the 1910s to the present day, serving thousands of youth in programs that suit the environment in which they live...
- State symbols of Virginia
- Flag of the Commonwealth of Virginia

- Great Seal of the Commonwealth of Virginia

- Flag of the Commonwealth of Virginia
Sports in Virginia
Sports in VirginiaEconomy and infrastructure of Virginia
Economy of VirginiaEconomy of Virginia
The Economy of Virginia is well balanced with diverse sources of income. From the Hampton Roads area to Richmond and down to Lee County in the southwest includes military installations, cattle, tobacco and peanut farming in Southside Virginia. Tomatoes recently surpassed soy as the most profitable...
- Communications in Virginia
- Health care in Virginia
- Transportation in VirginiaTransportation in VirginiaTransportation in the Commonwealth of Virginia is by land, sea and air. Virginia's extensive network of highways and railroads were developed and built over a period almost 400 years, beginning almost immediately after the founding of Jamestown in 1607, and often incorporating old established...
- Airports in Virginia
- Roads in Virginia
- Interstate Highways in Virginia
- State highways in VirginiaState highways in VirginiaThe state highway system of the U.S. state of Virginia is a network of roads maintained by the Virginia Department of Transportation . As of 2006, VDOT maintains 57,867 miles of state highways, making it the third-largest system in the United States.-Interstate and primary highways:Interstate...
Education in Virginia
- Main article: Education in VirginiaEducation in VirginiaEducation in Virginia addresses the needs of students from pre-kindergarten through adult education. The 1984 Virginia Assembly stated that, "Education is the cornerstone upon which Virginia's future rests." Virginia's educational system consistently ranks in the top ten states on the U.S...
- Schools in Virginia
- School districts in Virginia
- Colleges and universities in Virginia
- University of VirginiaUniversity of VirginiaThe University of Virginia is a public research university located in Charlottesville, Virginia, United States, founded by Thomas Jefferson...
- Virginia State UniversityVirginia State UniversityVirginia State University is a historically black and land-grant university located north of the Appomattox River in Chesterfield, in the Richmond area. Founded on , Virginia State was the United States's first fully state-supported four-year institution of higher learning for black Americans...
- University of Virginia
See also
- Outline of geographyOutline of geographyThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geography:Geography – science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth.- Geography is :...
- Outline of the United States
- Index of Virginia-related articles
- Outline of the United States

