
PCI Express
Encyclopedia
PCI Express officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a computer
expansion card
standard designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X
, and AGP
bus standards. PCIe has numerous improvements over the aforementioned bus standards, including higher maximum system bus throughput, lower I/O pin count and smaller physical footprint, better performance-scaling for bus devices, a more detailed error detection and reporting mechanism, and native hot plug functionality. More recent revisions of the PCIe standard support hardware I/O virtualization.
The PCIe electrical interface is also used in a variety of other standards, most notably ExpressCard
, a laptop
expansion card interface.
Format specifications are maintained and developed by the PCI-SIG
(PCI Special Interest Group
), a group of more than 900 companies that also maintain the Conventional PCI specifications. PCIe 3.0 is the latest standard for expansion cards that is available on mainstream personal computer
s.
interface for add-in boards.
In virtually all modern PCs, from consumer laptops and desktops to enterprise data servers, the PCIe bus serves as the primary motherboard-level interconnect, connecting the host system processor with both integrated-peripherals (surface mounted ICs) and add-on peripherals (expansion cards.) In most of these systems, the PCIe bus co-exists with 1 or more legacy PCI busses, for backward compatibility with the large body of legacy PCI peripherals.
replacement of the older PCI/PCI-X bus, an interconnect bus using shared address/data lines.
A key difference between PCIe bus and the older PCI is the bus topology. PCI uses a shared parallel
bus architecture, where the PCI host and all devices share a common set of address/data/control lines. In contrast, PCIe is based on point-to-point topology
, with separate serial
links connecting every device to the root complex
(host). Due to its shared bus topology, access to the older PCI bus is arbitrated (in the case of multiple masters), and limited to 1 master at a time, in a single direction. Furthermore, the older PCI's clocking scheme limits the bus clock to the slowest peripheral on the bus (regardless of the devices involved in the bus transaction). In contrast, a PCIe bus link supports full-duplex communication between any two endpoints, with no inherent limitation on concurrent access across multiple endpoints.
In terms of bus protocol, PCIe communication is encapsulated in packets. The work of packetizing and de-packetizing data and status-message traffic is handled by the transaction layer of the PCIe port (described later). Radical differences in electrical signaling and bus protocol require the use of a different mechanical form factor and expansion connectors (and thus, new motherboards and new adapter boards); PCI slots and PCIe slots are not interchangeable. At the software level, PCIe preserves backward compatibility with PCI; legacy PCI system software can detect and configure newer PCIe devices without explicit support for the PCIe standard, though PCIe's new features are inaccessible.
The PCIe link between 2 devices can consist of anywhere from 1 to 32 lanes. In a multi-lane link, the packet data is striped across lanes, and peak data-throughput scales with the overall link width. The lane count is automatically negotiated during device initialization, and can be restricted by either endpoint. For example, a single-lane PCIe (x1) card can be inserted into a multi-lane slot (x4, x8, etc.), and the initialization cycle auto-negotiates the highest mutually supported lane count. The link can dynamically down-configure the link to use fewer lanes, thus providing some measure of failure tolerance in the presence of bad or unreliable lanes. The PCIe standard defines slots and connectors for multiple widths: x1, x4, x8, x16, x32. This allows PCIe bus to serve both cost-sensitive applications where high throughput is not needed, as well as performance-critical applications such as 3D graphics, network (10 Gigabit Ethernet
, multiport Gigabit Ethernet
), and enterprise storage (SAS
, Fibre Channel
.)
As a point of reference, a PCI-X (133 MHz 64 bit) device and PCIe device at 4-lanes (x4), Gen1 speed have roughly the same peak transfer rate in a single-direction: 1064MB/sec. The PCIe bus has the potential to perform better than the PCI-X bus in cases where multiple devices are transferring data communicating simultaneously, or if communication with the PCIe peripheral is bidirectional
.
s (INTx, MSI, MSI-X
). At the physical level, a link is composed of 1 or more lanes. Low-speed peripherals (such as an 802.11
Wi-Fi
card
) use a single-lane (×1) link, while a graphics adapter typically uses a much wider (and thus, faster) 16-lane link.
, transporting data packets in 8 bit 'byte' format, between endpoints of a link, in both directions simultaneously. Physical PCIe slots may contain from one to thirty-two lanes, in powers of two (1, 2, 4, 8, 16 and 32). Lane counts are written with an x prefix (e.g., x16 represents a sixteen-lane card or slot), with x16 being the largest size in common use.
due to timing skew. Timing skew results from separate electrical signals within a parallel interface traveling down different-length conductors, on potentially different printed circuit board
layers, at possibly different signal velocities
. Despite being transmitted simultaneously as a single word, signals on a parallel interface experience different travel times and arrive at their destinations at different moments. When the interface clock rate
is increased to a point where its inverse (i.e., its clock period) is shorter than the largest possible time between signal arrivals, the signals no longer arrive with sufficient coincidence to make recovery of the transmitted word possible. Since timing skew over a parallel bus can amount to a few nanoseconds, the resulting bandwidth limitation is in the range of hundreds of megahertz.
A serial interface does not exhibit timing skew because there is only one differential signal in each direction within each lane, and there is no external clock signal since clocking information is embedded within the serial signal. As such, typical bandwidth limitations on serial signals are in the multi-gigahertz range. PCIe is just one example of a general trend away from parallel buses to serial interconnects. Other examples include Serial ATA
, USB
, SAS
, FireWire and RapidIO
.
Multichannel serial design increases flexibility by allocating slow devices to fewer lanes than fast devices.
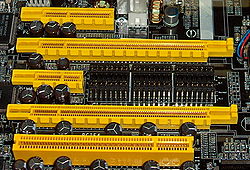 A PCIe card fits into a slot of its physical size or larger (maximum x16), but may not fit into a smaller PCIe slot (x16 in a x8 slot). Some slots use open-ended sockets to permit physically longer cards and negotiates the best available electrical connection. The number of lanes actually connected to a slot may also be less than the number supported by the physical slot size.
A PCIe card fits into a slot of its physical size or larger (maximum x16), but may not fit into a smaller PCIe slot (x16 in a x8 slot). Some slots use open-ended sockets to permit physically longer cards and negotiates the best available electrical connection. The number of lanes actually connected to a slot may also be less than the number supported by the physical slot size.
An example is a ×8 slot that actually only runs at ×1. These slots allow any ×1, ×2, ×4 or ×8 card, though only running at ×1 speed. This type of socket is called a ×8 (×1 mode) slot, meaning it physically accepts up to ×8 cards but only runs at ×1 speed. The advantage is that it can accommodate a larger range of PCIe cards without requiring motherboard hardware to support the full transfer rate. This keeps design and implementation costs down.
on a x4 PCI Express card. The solder side of the printed circuit board
(PCB) is the A side, and the component side is the B side.
An ×1 slot is a shorter version of this, ending after pin 18. ×8 and ×16 slots extend the pattern.

 PCI Express Mini Card (also known as Mini PCI Express, Mini PCIe, and Mini PCI-E) is a replacement for the Mini PCI form factor, based on PCI Express. It is developed by the PCI-SIG
PCI Express Mini Card (also known as Mini PCI Express, Mini PCIe, and Mini PCI-E) is a replacement for the Mini PCI form factor, based on PCI Express. It is developed by the PCI-SIG
. The host device supports both PCI Express and USB 2.0 connectivity, and each card may use either standard. Most laptop computers built after 2005 are based on PCI Express and can have several Mini Card slots.
Each row has 8 contacts, a gap equivalent to 4 contacts, then a further 18 contacts. A half-length card is also specified 30×26.8 mm. Cards have a thickness of 1.0 mm (excluding components).
Notebooks like Lenovo's newest T-Series, W-Series, and X-Series ThinkPads released in March-April of 2011 have support for an mSATA SSD card in their WWAN card slot. The ThinkPad Edge E220s/E420s, and the Lenovo IdeaPad Y460/Y560 also support mSATA.
Some notebooks (notably the Asus Eee PC
, the MacBook Air
, and the Dell mini9 and mini10) use a variant of the PCI Express Mini Card as an SSD
. This variant uses the reserved and several non-reserved pins to implement SATA and IDE interface passthrough, keeping only USB, ground lines, and sometimes the core PCIe 1x bus intact. This makes the 'miniPCIe' flash and solid state drives sold for netbooks largely incompatible with true PCI Express Mini implementations.
Also, the typical Asus miniPCIe SSD is 71mm long, causing the Dell 51mm model to often be (incorrectly) referred to as half length. A true 51mm Mini PCIe SSD was announced in 2009, with two stacked PCB layers, which allows for higher storage capacity. The announced design preserves the PCIe interface, making it compatible with the standard mini PCIe slot. No working product has yet been developed, likely as a result of the popularity of the alternative variant.
in February 2007.
Standard cables and connectors have been defined for x1, x4, x8, and x16 link widths, with a transfer rate of 250 MB/s per lane. The PCI-SIG also expects the norm will evolve to reach the 500 MB/s, as in PCI Express 2.0. The maximum cable length remains undetermined. An example of the uses of Cabled PCI Express is a metal enclosure, containing a number of PCI slots and PCI-to-ePCIe adapter circuitry. This device would not be possible had it not been for the ePCIe spec.
name PCI Express. It was first drawn up by a technical working group named the Arapaho Work Group (AWG) that, for initial drafts, consisted only of Intel engineers. Subsequently the AWG expanded to include industry partners.
PCIe is a technology under constant development and improvement. The current PCI Express implementation is version 3.0.
announced the availability of the PCI Express Base 2.0 specification on 15 January 2007. The PCIe 2.0 standard doubles the transfer rate compared with PCIe 1.0 to 5 GT/s and the per-lane throughput rises from 250 MB/s to 500 MB/s. This means a 32-lane PCI connector (x32) can support throughput up to 16 GB/s aggregate.
PCIe 2.0 motherboard slots are fully backward compatible with PCIe v1.x cards. PCIe 2.0 cards are also generally backward compatible with PCIe 1.x motherboards, using the available bandwidth of PCI Express 1.1. Overall, graphic cards or motherboards designed for v2.0 will work with the other being v1.1 or v1.0.
The PCI-SIG also said that PCIe 2.0 features improvements to the point-to-point data transfer protocol and its software architecture.
Intel
's first PCIe 2.0 capable chipset was the X38 and boards began to ship from various vendors (Abit
, Asus
, Gigabyte
) as of October 21, 2007. AMD started supporting PCIe 2.0 with its AMD 700 chipset series
and nVidia started with the MCP72
. All of Intel's prior chipsets, including the Intel P35
chipset, supported PCIe 1.1 or 1.0a.
improvements, clock data recovery, and channel enhancements for currently supported topologies.
Following a six-month technical analysis of the feasibility of scaling the PCIe interconnect bandwidth, PCI-SIG's analysis found out that 8 gigatransfers per second can be manufactured in mainstream silicon process technology, and can be deployed with existing low-cost materials and infrastructure, while maintaining full compatibility (with negligible impact) to the PCIe protocol stack.
PCIe 2.0 delivers 5 GT/s, but uses an 8b/10b encoding
scheme that results in a 20 percent ((10-8)/10) overhead on the raw bit rate. PCIe 3.0 removes the requirement for 8b/10b encoding, and instead uses a technique called "scrambling" that applies a known binary polynomial to a data stream in a feedback topology. Because the scrambling polynomial is known, the data can be recovered by running it through a feedback topology using the inverse polynomial. and also uses a 128b/130b encoding scheme, reducing the overhead to approximately 1.5% ((130-128)/130), as opposed to the 20% overhead of 8b/10b encoding used by PCIe 2.0. PCIe 3.0's 8 GT/s bit rate effectively delivers double PCIe 2.0 bandwidth. PCI-SIG expects the PCIe 3.0 specifications to undergo rigorous technical vetting and validation before being released to the industry. This process, which was followed in the development of prior generations of the PCIe Base and various form factor specifications, includes the corroboration of the final electrical parameters with data derived from test silicon and other simulations conducted by multiple members of the PCI-SIG.
On November 18, 2010, the PCI Special Interest Group officially published the finalized PCI Express 3.0 specification to its members to build devices based on this new version of PCI Express.
as the default interface for graphics cards on new systems. With a few exceptions, all graphics cards being released as of 2009 and 2010 from AMD (ATI) and NVIDIA
use PCI Express. NVIDIA uses the high bandwidth data transfer of PCIe for its Scalable Link Interface
(SLI) technology, which allows multiple graphics cards of the same chipset and model number to run in tandem, allowing increased performance. ATI has also developed a multi-GPU system based on PCIe called CrossFire
. AMD and NVIDIA have released motherboard chipsets that support up to four PCIe ×16 slots, allowing tri-GPU and quad-GPU card configurations.
PCI Express has displaced a major portion of the add-in card market. PCI Express was originally only common in disk array controller
s, onboard gigabit Ethernet
, Wi-Fi
and graphics cards. Most sound cards, TV/capture-cards, modems, serial port/USB/Firewire cards, network/WiFi cards that would have used the conventional PCI in the past have moved to PCI Express x8, x4, or x1. While some motherboards have conventional PCI slots, these are primarily for legacy cards and are being phased out.
PCI Express is a layered protocol, consisting of a transaction layer, a data link layer, and a physical layer. The Data Link Layer is subdivided to include a media access control
(MAC) sublayer. The Physical Layer is subdivided into logical and electrical sublayers. The Physical logical-sublayer contains a physical coding sublayer (PCS). The terms are borrowed from the IEEE 802
networking protocol model.
and other analog circuitry; however, since SerDes implementations vary greatly among ASIC
vendors, PIPE does not specify an interface between the PCS and PMA.
At the electrical level, each lane consists of two unidirectional LVDS or PCML
pairs at 2.525 Gbit
/s. Transmit and receive are separate differential pair
s, for a total of 4 data wires per lane.
A connection between any two PCIe devices is known as a link, and is built up from a collection of 1 or more lanes. All devices must minimally support single-lane (x1) link. Devices may optionally support wider links composed of 2, 4, 8, 12, 16, or 32 lanes. This allows for very good compatibility in two ways:
In both cases, PCIe negotiates the highest mutually supported number of lanes. Many graphics cards, motherboards and bios versions are verified to support ×1, ×4, ×8 and ×16 connectivity on the same connection.
Even though the two would be signal-compatible, it is not usually possible to place a physically larger PCIe card (e.g., a ×16 sized card) into a smaller slot —though if the PCIe slots are open-ended, by design or by hack, some motherboards will allow this.
The width of a PCIe connector is 8.8 mm, while the height is 11.25 mm, and the length is variable. The fixed section of the connector is 11.65 mm in length and contains 2 rows of 11 (22 pins total), while the length of the other section is variable depending on the number of lanes. The pins are spaced at 1 mm intervals, and the thickness of the card going into the connector is 1.8 mm.
Data transmitted on multiple-lane links is interleaved, meaning that each successive byte is sent down successive lanes. The PCIe specification refers to this interleaving as data striping. While requiring significant hardware complexity to synchronize (or deskew
) the incoming striped data, striping can significantly reduce the latency of the nth byte on a link. Due to padding requirements, striping may not necessarily reduce the latency of small data packets on a link.
As with other high data rate serial transmission protocols, clocking information is embedded
in the signal. At the physical level, PCI Express 2.0 utilizes the 8b/10b encoding
scheme to ensure that strings of consecutive ones or consecutive zeros are limited in length. This was used to prevent the receiver from losing track of where the bit edges are. In this coding scheme every 8 (uncoded) payload bits of data are replaced with 10 (encoded) bits of transmit data, causing a 20% overhead in the electrical bandwidth. To improve the available bandwidth, PCI Express version 3.0 employs 128b/130b encoding instead: similar but with much lower overhead.
Many other protocols (such as SONET
) use a different form of encoding known as scrambling to embed clock information into data streams. The PCIe specification also defines a scrambling algorithm, but it is used to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) by preventing repeating data patterns in the transmitted data stream.
(1) sequence the transaction layer packets (TLPs) that are generated by the transaction layer,
(2) ensure reliable delivery of TLPs between two endpoints via an acknowledgement protocol (ACK
and NAK
signaling) that explicitly requires replay of unacknowledged/bad TLPs,
(3) initialize and manage flow control credits
On the transmit side, the data link layer generates an incrementing sequence number for each outgoing TLP. It serves as a unique identification tag for each transmitted TLP, and is inserted into the header of the outgoing TLP. A 32-bit cyclic redundancy check
code (known in this context as Link CRC or LCRC) is also appended to the end of each outgoing TLP.
On the receive side, the received TLP's LCRC and sequence number are both validated in the link layer. If either the LCRC check fails (indicating a data error), or the sequence-number is out of range (non-consecutive from the last valid received TLP), then the bad TLP, as well as any TLPs received after the bad TLP, are considered invalid and discarded. The receiver sends a negative acknowledgement message (NAK) with the sequence-number of the invalid TLP, requesting re-transmission of all TLPs forward of that sequence-number. If the received TLP passes the LCRC check and has the correct sequence number, it is treated as valid. The link receiver increments the sequence-number (which tracks the last received good TLP), and forwards the valid TLP to the receiver's transaction layer. An ACK message is sent to remote transmitter, indicating the TLP was successfully received (and by extension, all TLPs with past sequence-numbers.)
If the transmitter receives a NAK message, or no acknowledgement (NAK or ACK) is received until a timeout period expires, the transmitter must retransmit all TLPs that lack a positive acknowledgement (ACK). Barring a persistent malfunction of the device or transmission medium, the link-layer presents a reliable connection to the transaction layer, since the transmission protocol ensures delivery of TLPs over an unreliable medium.
In addition to sending and receiving TLPs generated by the transaction layer, the data-link layer also generates and consumes DLLPs, data link layer packets. ACK and NAK signals are communicated via (DLLP), as are flow control credit information, some power management messages and flow control credit information (on behalf of the transaction layer.)
In practice, the number of in-flight, unacknowledged TLPs on the link is limited by two factors: the size of the transmitter's replay buffer (which must store a copy of all transmitted TLPs until they the remote receiver ACKs them), and the flow control credits issued by the receiver to a transmitter. PCI Express requires all receivers to issue a minimum number of credits, to guarantee a link allows sending PCIConfig TLPs and message TLPs.
PCI Express uses credit-based flow control. In this scheme, a device advertises an initial amount of credit for each received buffer in its transaction layer. The device at the opposite end of the link, when sending transactions to this device, counts the number of credits each TLP consumes from its account. The sending device may only transmit a TLP when doing so does not make its consumed credit count exceed its credit limit. When the receiving device finishes processing the TLP from its buffer, it signals a return of credits to the sending device, which increases the credit limit by the restored amount. The credit counters are modular counters, and the comparison of consumed credits to credit limit requires modular arithmetic
. The advantage of this scheme (compared to other methods such as wait states or handshake-based transfer protocols) is that the latency of credit return does not affect performance, provided that the credit limit is not encountered. This assumption is generally met if each device is designed with adequate buffer sizes.
PCIe 1.x is often quoted to support a data rate of 250 MB/s in each direction, per lane. This figure is a calculation from the physical signaling rate (2.5 Gbaud
) divided by the encoding overhead (10 bits per byte.) This means a sixteen lane (x16) PCIe card would then be theoretically capable of 16×250 MB/s = 4 GB/s in each direction. While this is correct in terms of data bytes, more meaningful calculations are based on the usable data payload rate, which depends on the profile of the traffic, which is a function of the high-level (software) application and intermediate protocol levels.
Like other high data rate serial interconnect systems, PCIe has a protocol and processing overhead due to the additional transfer robustness (CRC and acknowledgements). Long continuous unidirectional transfers (such as those typical in high-performance storage controllers) can approach >95% of PCIe's raw (lane) data rate. These transfers also benefit the most from increased number of lanes (×2, ×4, etc.) But in more typical applications (such as a USB
or Ethernet
controller), the traffic profile is characterized as short data packets with frequent enforced acknowledgements. This type of traffic reduces the efficiency of the link, due to overhead from packet parsing and forced interrupts (either in the device's host interface or the PC's CPU.) Being a protocol for devices connected to the same printed circuit board
, it does not require the same tolerance for transmission errors as a protocol for communication over longer distances, and thus, this loss of efficiency is not particular to PCIe.
IBM/Lenovo has also included a PCI-Express slot in their Advanced Docking Station 250310U. It provides a half sized slot with an x16 length slot, but only x1 connectivity. However, docking stations with expansion slots are becoming less common as the laptops are getting more advanced video cards and either DVI-D interfaces, or DVI-D pass through for port replicators and docking stations.
Additionally, Nvidia
has developed Quadro Plex
external PCIe Video Cards that can be used for advanced graphic applications. These video cards require a PCI Express x8 or x16 slot for the interconnection cable. In 2008, AMD announced the ATI XGP
technology, based on a proprietary cabling solution that is compatible with PCIe x8 signal transmissions. This connector is available on the Fujitsu Amilo and the Acer Ferrari One notebooks. Only Fujitsu has an actual external box available, which also works on the Ferrari One. Recently Acer launched the Dynavivid graphics dock for XGP.
There are now card hubs in development that one can connect to a laptop through an ExpressCard slot, though they are currently rare, obscure, or unavailable on the open market. These hubs can have full-sized cards placed in them.
Magma and ViDock also makes use of ExpressCard and implements the usage of External graphic solutions .ViDock are expansion chassis tailored specifically for adapting PCI Express graphics cards for use with ExpressCard equipped laptop PCs. This enables user to make use of connecting PCIe cards externally.
Although, the developments in these technologies are still ongoing. Other examples that underwent are - MSI GUS, Asus XG Station.
Recently, Intel and Apple introduced Thunderbolt, which allows for external PCI(e) devices.
, RapidIO
, HyperTransport
, QPI and StarFabric. The differences are based on the tradeoffs between flexibility and extensibility vs latency and overhead. An example of such a tradeoff is adding complex header information to a transmitted packet to allow for complex routing (PCI Express is not capable of this). The additional overhead reduces the effective bandwidth of the interface and complicates bus discovery and initialization software. Also making the system hot-pluggable requires that software track network topology changes. Examples of buses suited for this purpose are InfiniBand and StarFabric.
Another example is making the packets shorter to decrease latency (as is required if a bus must operate as a memory interface). Smaller packets mean packet headers consume a higher percentage of the packet, thus decreasing the effective bandwidth. Examples of bus protocols designed for this purpose are RapidIO and HyperTransport.
PCI Express falls somewhere in the middle, targeted by design as a system interconnect (local bus
) rather than a device interconnect or routed network protocol. Additionally, its design goal of software transparency constrains the protocol and raises its latency somewhat.
s are tools that collect, analyze, decode, store signals so people can view the high-speed waveforms at their leisure.
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
expansion card
Expansion card
The expansion card in computing is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an expansion slot of a computer motherboard or backplane to add functionality to a computer system via the expansion bus.One edge of the expansion card holds the contacts that fit exactly into the slot...
standard designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X
PCI-X
PCI-X, short for PCI-eXtended, is a computer bus and expansion card standard that enhances the 32-bit PCI Local Bus for higher bandwidth demanded by servers. It is a double-wide version of PCI, running at up to four times the clock speed, but is otherwise similar in electrical implementation and...
, and AGP
Accelerated Graphics Port
The Accelerated Graphics Port is a high-speed point-to-point channel for attaching a video card to a computer's motherboard, primarily to assist in the acceleration of 3D computer graphics. Since 2004 AGP has been progressively phased out in favor of PCI Express...
bus standards. PCIe has numerous improvements over the aforementioned bus standards, including higher maximum system bus throughput, lower I/O pin count and smaller physical footprint, better performance-scaling for bus devices, a more detailed error detection and reporting mechanism, and native hot plug functionality. More recent revisions of the PCIe standard support hardware I/O virtualization.
The PCIe electrical interface is also used in a variety of other standards, most notably ExpressCard
ExpressCard
ExpressCard is an interface to allow peripheral devices to be connected to a computer, usually a laptop computer. Formerly called NEWCARD, the ExpressCard standard specifies the design of slots built into the computer and of cards which can be inserted into ExpressCard slots. The cards contain...
, a laptop
Laptop
A laptop, also called a notebook, is a personal computer for mobile use. A laptop integrates most of the typical components of a desktop computer, including a display, a keyboard, a pointing device and speakers into a single unit...
expansion card interface.
Format specifications are maintained and developed by the PCI-SIG
PCI-SIG
The PCI-SIG or Peripheral Component Interconnect Special Interest Group is an electronics industry consortium responsible for specifying the Peripheral Component Interconnect , PCI-X, and PCI Express computer buses....
(PCI Special Interest Group
Special Interest Group
A Special Interest Group is a community with an interest in advancing a specific area of knowledge, learning or technology where members cooperate to effect or to produce solutions within their particular field, and may communicate, meet, and organize conferences...
), a group of more than 900 companies that also maintain the Conventional PCI specifications. PCIe 3.0 is the latest standard for expansion cards that is available on mainstream personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
s.
Applications
PCI Express is used in consumer, server, and industrial applications, as a motherboard-level interconnect (to link motherboard-mounted peripherals), a passive backplane interconnect and as an expansion cardExpansion card
The expansion card in computing is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an expansion slot of a computer motherboard or backplane to add functionality to a computer system via the expansion bus.One edge of the expansion card holds the contacts that fit exactly into the slot...
interface for add-in boards.
In virtually all modern PCs, from consumer laptops and desktops to enterprise data servers, the PCIe bus serves as the primary motherboard-level interconnect, connecting the host system processor with both integrated-peripherals (surface mounted ICs) and add-on peripherals (expansion cards.) In most of these systems, the PCIe bus co-exists with 1 or more legacy PCI busses, for backward compatibility with the large body of legacy PCI peripherals.
Architecture
Conceptually, the PCIe bus is like a high-speed serialSerial communication
In telecommunication and computer science, serial communication is the process of sending data one bit at a time, sequentially, over a communication channel or computer bus. This is in contrast to parallel communication, where several bits are sent as a whole, on a link with several parallel channels...
replacement of the older PCI/PCI-X bus, an interconnect bus using shared address/data lines.
A key difference between PCIe bus and the older PCI is the bus topology. PCI uses a shared parallel
Parallel communications
In telecommunication and computer science, parallel communication is a method of sending several data signals simultaneously over several parallel channels...
bus architecture, where the PCI host and all devices share a common set of address/data/control lines. In contrast, PCIe is based on point-to-point topology
Network topology
Network topology is the layout pattern of interconnections of the various elements of a computer or biological network....
, with separate serial
Serial communication
In telecommunication and computer science, serial communication is the process of sending data one bit at a time, sequentially, over a communication channel or computer bus. This is in contrast to parallel communication, where several bits are sent as a whole, on a link with several parallel channels...
links connecting every device to the root complex
Root complex
In a PCI Express system, a root complex device connects the processor and memory subsystem to the PCI Express switch fabric composed of one or more switch devices....
(host). Due to its shared bus topology, access to the older PCI bus is arbitrated (in the case of multiple masters), and limited to 1 master at a time, in a single direction. Furthermore, the older PCI's clocking scheme limits the bus clock to the slowest peripheral on the bus (regardless of the devices involved in the bus transaction). In contrast, a PCIe bus link supports full-duplex communication between any two endpoints, with no inherent limitation on concurrent access across multiple endpoints.
In terms of bus protocol, PCIe communication is encapsulated in packets. The work of packetizing and de-packetizing data and status-message traffic is handled by the transaction layer of the PCIe port (described later). Radical differences in electrical signaling and bus protocol require the use of a different mechanical form factor and expansion connectors (and thus, new motherboards and new adapter boards); PCI slots and PCIe slots are not interchangeable. At the software level, PCIe preserves backward compatibility with PCI; legacy PCI system software can detect and configure newer PCIe devices without explicit support for the PCIe standard, though PCIe's new features are inaccessible.
The PCIe link between 2 devices can consist of anywhere from 1 to 32 lanes. In a multi-lane link, the packet data is striped across lanes, and peak data-throughput scales with the overall link width. The lane count is automatically negotiated during device initialization, and can be restricted by either endpoint. For example, a single-lane PCIe (x1) card can be inserted into a multi-lane slot (x4, x8, etc.), and the initialization cycle auto-negotiates the highest mutually supported lane count. The link can dynamically down-configure the link to use fewer lanes, thus providing some measure of failure tolerance in the presence of bad or unreliable lanes. The PCIe standard defines slots and connectors for multiple widths: x1, x4, x8, x16, x32. This allows PCIe bus to serve both cost-sensitive applications where high throughput is not needed, as well as performance-critical applications such as 3D graphics, network (10 Gigabit Ethernet
10 Gigabit Ethernet
The 10 gigabit Ethernet computer networking standard was first published in 2002. It defines a version of Ethernet with a nominal data rate of 10 Gbit/s , ten times faster than gigabit Ethernet.10 gigabit Ethernet defines only full duplex point to point links which are generally connected by...
, multiport Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet is a term describing various technologies for transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second , as defined by the IEEE 802.3-2008 standard. It came into use beginning in 1999, gradually supplanting Fast Ethernet in wired local networks where it performed...
), and enterprise storage (SAS
Serial Attached SCSI
Serial Attached SCSI is a computer bus used to move data to and from computer storage devices such as hard drives and tape drives. SAS depends on a point-to-point serial protocol that replaces the parallel SCSI bus technology that first appeared in the mid 1980s in data centers and workstations,...
, Fibre Channel
Fibre Channel
Fibre Channel, or FC, is a gigabit-speed network technology primarily used for storage networking. Fibre Channel is standardized in the T11 Technical Committee of the InterNational Committee for Information Technology Standards , an American National Standards Institute –accredited standards...
.)
As a point of reference, a PCI-X (133 MHz 64 bit) device and PCIe device at 4-lanes (x4), Gen1 speed have roughly the same peak transfer rate in a single-direction: 1064MB/sec. The PCIe bus has the potential to perform better than the PCI-X bus in cases where multiple devices are transferring data communicating simultaneously, or if communication with the PCIe peripheral is bidirectional
Bi-directional
Bi-directional may refer to:* Bi-directional text* Two-way communication* Bi-directional railway signalling* Controls at each end of a tram or railcar...
.
Interconnect
PCIe devices communicate via a logical connection called an interconnect or link. A link is a point-to-point communication channel between 2 PCIe ports, allowing both to send/receive ordinary PCI-requests (configuration read/write, I/O read/write, memory read/write) and interruptInterrupt
In computing, an interrupt is an asynchronous signal indicating the need for attention or a synchronous event in software indicating the need for a change in execution....
s (INTx, MSI, MSI-X
Message Signaled Interrupts
Message Signaled Interrupts, in PCI 2.2and later in PCI Express, are an alternative way of generating an interrupt. Traditionally, a device has an interrupt pin which it asserts when it wants to interrupt the host CPU. While PCI Express does not have separate interrupt pins, it has special...
). At the physical level, a link is composed of 1 or more lanes. Low-speed peripherals (such as an 802.11
IEEE 802.11
IEEE 802.11 is a set of standards for implementing wireless local area network computer communication in the 2.4, 3.6 and 5 GHz frequency bands. They are created and maintained by the IEEE LAN/MAN Standards Committee . The base version of the standard IEEE 802.11-2007 has had subsequent...
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi or Wifi, is a mechanism for wirelessly connecting electronic devices. A device enabled with Wi-Fi, such as a personal computer, video game console, smartphone, or digital audio player, can connect to the Internet via a wireless network access point. An access point has a range of about 20...
card
Wireless network interface card
A wireless network interface controller is a network interface controller which connects to a radio-based computer network rather than a wire-based network such as Token Ring or Ethernet. A WNIC, just like other NICs, works on the Layer 1 and Layer 2 of the OSI Model. A WNIC is an essential...
) use a single-lane (×1) link, while a graphics adapter typically uses a much wider (and thus, faster) 16-lane link.
Lane
A lane is composed of a transmit and receive pair of differential lines. Each lane is composed of 4 wires or signal paths, meaning conceptually, each lane is a full-duplex byte streamByte stream
In computer science, a byte stream is a bit stream, in which data bits are grouped into units, called bytes.In computer networking the term octet stream is sometimes used to refer to the same thing; it emphasizes the use of bytes having the length of 8 bits, known as octets.Formally, a byte stream...
, transporting data packets in 8 bit 'byte' format, between endpoints of a link, in both directions simultaneously. Physical PCIe slots may contain from one to thirty-two lanes, in powers of two (1, 2, 4, 8, 16 and 32). Lane counts are written with an x prefix (e.g., x16 represents a sixteen-lane card or slot), with x16 being the largest size in common use.
Serial bus
The bonded serial format was chosen over a traditional parallel bus format due to the latter's inherent limitations, including single-duplex operation, excess signal count and an inherently lower bandwidthBandwidth (computing)
In computer networking and computer science, bandwidth, network bandwidth, data bandwidth, or digital bandwidth is a measure of available or consumed data communication resources expressed in bits/second or multiples of it .Note that in textbooks on wireless communications, modem data transmission,...
due to timing skew. Timing skew results from separate electrical signals within a parallel interface traveling down different-length conductors, on potentially different printed circuit board
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
layers, at possibly different signal velocities
Signal velocity
The signal velocity is the speed at which a wave carries information. It describes how quickly a message can be communicated between two separated parties...
. Despite being transmitted simultaneously as a single word, signals on a parallel interface experience different travel times and arrive at their destinations at different moments. When the interface clock rate
Clock rate
The clock rate typically refers to the frequency that a CPU is running at.For example, a crystal oscillator frequency reference typically is synonymous with a fixed sinusoidal waveform, a clock rate is that frequency reference translated by electronic circuitry into a corresponding square wave...
is increased to a point where its inverse (i.e., its clock period) is shorter than the largest possible time between signal arrivals, the signals no longer arrive with sufficient coincidence to make recovery of the transmitted word possible. Since timing skew over a parallel bus can amount to a few nanoseconds, the resulting bandwidth limitation is in the range of hundreds of megahertz.
A serial interface does not exhibit timing skew because there is only one differential signal in each direction within each lane, and there is no external clock signal since clocking information is embedded within the serial signal. As such, typical bandwidth limitations on serial signals are in the multi-gigahertz range. PCIe is just one example of a general trend away from parallel buses to serial interconnects. Other examples include Serial ATA
Serial ATA
Serial ATA is a computer bus interface for connecting host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives and optical drives...
, USB
Universal Serial Bus
USB is an industry standard developed in the mid-1990s that defines the cables, connectors and protocols used in a bus for connection, communication and power supply between computers and electronic devices....
, SAS
Serial Attached SCSI
Serial Attached SCSI is a computer bus used to move data to and from computer storage devices such as hard drives and tape drives. SAS depends on a point-to-point serial protocol that replaces the parallel SCSI bus technology that first appeared in the mid 1980s in data centers and workstations,...
, FireWire and RapidIO
RapidIO
The RapidIO architecture is a high-performance packet-switched, interconnect technology for interconnecting chips on a circuit board, and also circuit boards to each other using a backplane...
.
Multichannel serial design increases flexibility by allocating slow devices to fewer lanes than fast devices.
PCI Express (standard)

An example is a ×8 slot that actually only runs at ×1. These slots allow any ×1, ×2, ×4 or ×8 card, though only running at ×1 speed. This type of socket is called a ×8 (×1 mode) slot, meaning it physically accepts up to ×8 cards but only runs at ×1 speed. The advantage is that it can accommodate a larger range of PCIe cards without requiring motherboard hardware to support the full transfer rate. This keeps design and implementation costs down.
Pinout
The following table identifies the conductors on each side of the edge connectorEdge connector
An edge connector is the portion of a printed circuit board consisting of traces leading to the edge of the board that are intended to plug into a matching socket. The edge connector is a money-saving device because it only requires a single discrete female connector , and they also tend to be...
on a x4 PCI Express card. The solder side of the printed circuit board
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
(PCB) is the A side, and the component side is the B side.
| Pin | Side B | Side A | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | +12V | PRSNT1# | Pulled low to indicate card inserted |
| 2 | +12V | +12V | |
| 3 | Reserved | +12V | |
| 4 | Ground | Ground | |
| 5 | SMCLK | TCK | SMBus and JTAG JTAG Joint Test Action Group is the common name for what was later standardized as the IEEE 1149.1 Standard Test Access Port and Boundary-Scan Architecture. It was initially devised for testing printed circuit boards using boundary scan and is still widely used for this application.Today JTAG is also... port pins |
| 6 | SMDAT | TDI | |
| 7 | Ground | TDO | |
| 8 | +3.3V | TMS | |
| 9 | TRST# | +3.3V | |
| 10 | +3.3Vaux | +3.3V | Standby power Standby power Standby power, also called vampire power, vampire draw, phantom load, or leaking electricity , refers to the electric power consumed by electronic and electrical appliances while they are switched off Standby power, also called vampire power, vampire draw, phantom load, or leaking electricity... |
| 11 | WAKE# | PWRGD | Link reactivation, power good. |
| Key notch | |||
| 12 | Reserved | Ground | |
| 13 | Ground | REFCLK+ | Reference clock differential pair |
| 14 | HSOp(0) | REFCLK- | Lane 0 transmit data, + and − |
| 15 | HSOn(0) | Ground | |
| 16 | Ground | HSIp(0) | Lane 0 receive data, + and − |
| 17 | PRSNT2# | HSIn(0) | |
| 18 | Ground | Ground | |
| 19 | HSOp(1) | Reserved | Lane 1 transmit data, + and − |
| 20 | HSOn(1) | Ground | |
| 21 | Ground | HSIp(1) | Lane 1 receive data, + and − |
| 22 | Ground | HSIn(1) | |
| 23 | HSOp(2) | Ground | Lane 2 transmit data, + and − |
| 24 | HSOn(2) | Ground | |
| 25 | Ground | HSIp(2) | Lane 2 receive data, + and − |
| 26 | Ground | HSIn(2) | |
| 27 | HSOp(3) | Ground | Lane 3 transmit data, + and − |
| 28 | HSOn(3) | Ground | |
| 29 | Ground | HSIp(3) | Lane 3 receive data, + and − |
| 30 | Reserved | HSIn(3) | |
| 31 | PRSNT2# | Ground | |
| 32 | Ground | Reserved | |
An ×1 slot is a shorter version of this, ending after pin 18. ×8 and ×16 slots extend the pattern.
| Ground pin | Zero volt reference |
|---|---|
| Power pin | Supplies power to the PCIe card |
| Output pin | Signal from the card to the motherboard |
| Input pin | Signal from the motherboard to the card |
| Open drain | May be pulled low and/or sensed by multiple cards |
| Sense pin | Tied together on card |
| Reserved | Not presently used, do not connect |
Power
PCI Express cards are allowed a maximum power consumption of 25W (×1: 10W for power-up). Low profile cards are limited to 10W (×16 to 25W). PCI Express Graphics (PEG) cards may increase power (from slot) to 75W after configuration (3.3V/3A + 12V/5.5A). Optional connectors add 75W (6-pin) or 150W (8-pin) power for up to 300W total.PCI Express Mini Card


PCI-SIG
The PCI-SIG or Peripheral Component Interconnect Special Interest Group is an electronics industry consortium responsible for specifying the Peripheral Component Interconnect , PCI-X, and PCI Express computer buses....
. The host device supports both PCI Express and USB 2.0 connectivity, and each card may use either standard. Most laptop computers built after 2005 are based on PCI Express and can have several Mini Card slots.
Physical dimensions
PCI Express Mini Cards are 30×50.95 mm. There is a 52 pin edge connector, consisting of two staggered rows on a 0.8 mm pitch.Each row has 8 contacts, a gap equivalent to 4 contacts, then a further 18 contacts. A half-length card is also specified 30×26.8 mm. Cards have a thickness of 1.0 mm (excluding components).
Electrical interface
PCI Express Mini Card edge connector provide multiple connections and buses:- PCIe x1
- USB 2.0
- SMBus
- Wires to diagnostics LEDs for wireless network (i.e., WiFiWIFIWIFI is a radio station broadcasting a brokered format. Licensed to Florence, New Jersey, USA, the station is currently operated by Florence Broadcasting Partners, LLC.This station was previously owned by Real Life Broadcasting...
) status on computer's chassis - SIMSubscriber Identity ModuleA subscriber identity module or subscriber identification module is an integrated circuit that securely stores the International Mobile Subscriber Identity and the related key used to identify and authenticate subscriber on mobile telephony devices .A SIM is held on a removable SIM card, which...
card for GSM and WCDMA applications. (UIM signals on spec) - Future extension for another PCIe lane
- 1.5 and 3.3 volt power
Mini PCI Express & mSATA
Despite the mini-PCI Express form factor, a mini-PCI Express slot must have support for the electrical connections an mSATA drive requires. For this reason, only certain notebooks are compatible with mSATA drives. Most compatible systems are based on Intel's newest Sandy Bridge processor architecture, using the new Huron River platform.Notebooks like Lenovo's newest T-Series, W-Series, and X-Series ThinkPads released in March-April of 2011 have support for an mSATA SSD card in their WWAN card slot. The ThinkPad Edge E220s/E420s, and the Lenovo IdeaPad Y460/Y560 also support mSATA.
Some notebooks (notably the Asus Eee PC
ASUS Eee PC
The Asus Eee PC is a subnotebook/netbook computer line from ASUSTeK Computer Incorporated, and a part of the Asus Eee product family. At the time of its introduction in late 2007, it was noted for its combination of a light weight, Linux operating system, solid-state drive , and relatively low cost...
, the MacBook Air
MacBook Air
The MacBook Air family is a line of Apple ultraportable Macintosh notebook computers.The first-generation MacBook Air was a 13.3"-only model, previously promoted as the World's Thinnest Notebook, introduced at the Macworld Conference & Expo on January 15, 2008. It featured a custom Intel Merom CPU...
, and the Dell mini9 and mini10) use a variant of the PCI Express Mini Card as an SSD
Solid-state drive
A solid-state drive , sometimes called a solid-state disk or electronic disk, is a data storage device that uses solid-state memory to store persistent data with the intention of providing access in the same manner of a traditional block i/o hard disk drive...
. This variant uses the reserved and several non-reserved pins to implement SATA and IDE interface passthrough, keeping only USB, ground lines, and sometimes the core PCIe 1x bus intact. This makes the 'miniPCIe' flash and solid state drives sold for netbooks largely incompatible with true PCI Express Mini implementations.
Also, the typical Asus miniPCIe SSD is 71mm long, causing the Dell 51mm model to often be (incorrectly) referred to as half length. A true 51mm Mini PCIe SSD was announced in 2009, with two stacked PCB layers, which allows for higher storage capacity. The announced design preserves the PCIe interface, making it compatible with the standard mini PCIe slot. No working product has yet been developed, likely as a result of the popularity of the alternative variant.
PCI Express External Cabling
PCI Express External Cabling (also known as External PCI Express, Cabled PCI Express, or ePCIe) specifications were released by the PCI-SIGPCI-SIG
The PCI-SIG or Peripheral Component Interconnect Special Interest Group is an electronics industry consortium responsible for specifying the Peripheral Component Interconnect , PCI-X, and PCI Express computer buses....
in February 2007.
Standard cables and connectors have been defined for x1, x4, x8, and x16 link widths, with a transfer rate of 250 MB/s per lane. The PCI-SIG also expects the norm will evolve to reach the 500 MB/s, as in PCI Express 2.0. The maximum cable length remains undetermined. An example of the uses of Cabled PCI Express is a metal enclosure, containing a number of PCI slots and PCI-to-ePCIe adapter circuitry. This device would not be possible had it not been for the ePCIe spec.
Derivative forms
There are several other expansion card types derived from PCIe. These include:- Low height card
- ExpressCardExpressCardExpressCard is an interface to allow peripheral devices to be connected to a computer, usually a laptop computer. Formerly called NEWCARD, the ExpressCard standard specifies the design of slots built into the computer and of cards which can be inserted into ExpressCard slots. The cards contain...
: successor to the PC cardPC cardIn computing, PC Card is the form factor of a peripheral interface designed for laptop computers. The PC Card standard was defined and developed by the Personal Computer Memory Card International Association which itself was created by a number of computer industry companies in the United States...
form factor (with ×1 PCIe and USB 2.0; hot-pluggable) - PCI Express ExpressModule: a hot-pluggable modular form factor defined for servers and workstations
- XMC: similar to the CMC/PMCPCI mezzanine cardA PCI Mezzanine Card or PMC is a printed circuit board manufactured to the IEEE P1386.1 standard. This standard combines the electrical characteristics of the PCI bus with the mechanical dimensions of the Common Mezzanine Card or CMC format .A mezzanine connector connects two parallel printed...
form factor (with ×4 PCIe or Serial RapidI/O) - AdvancedTCAAdvanced Telecommunications Computing ArchitectureAdvanced Telecommunications Computing Architecture is the largest specification effort in the history of the PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group , with more than 100 companies participating. Known as AdvancedTCA, the official specification designation PICMG 3.x was ratified by the PICMG...
: a complement to CompactPCICompactPCIA CompactPCI system is a 3U or 6U Eurocard-based industrial computer, where all boards are connected via a passive PCI backplane. The connector pin assignments are standardized by the PICMG US and PICMG Europe organizations. PICMG stands for PCI Industrial Computers Manufacturers Group...
for larger applications; supports serial based backplane topologies - AMCAdvanced Mezzanine CardAdvanced Mezzanine Cards are printed circuit boards that follow a specification of the PCI Industrial Computers Manufacturers Group , with more than 100 companies participating. Known as AdvancedMC, the official specification designation is AMC.x . AdvancedMC is targeted to requirements for the...
: a complement to the AdvancedTCAAdvanced Telecommunications Computing ArchitectureAdvanced Telecommunications Computing Architecture is the largest specification effort in the history of the PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group , with more than 100 companies participating. Known as AdvancedTCA, the official specification designation PICMG 3.x was ratified by the PICMG...
specification; supports processor and I/O modules on ATCA boards (×1, ×2, ×4 or ×8 PCIe). - FeaturePakFeaturePakThe FeaturePak standard defines a small form factor card for I/O expansion of embedded systems and other space-constrained computing applications. The cards are intended to be used for adding a wide range of capabilities, such as A/D, D/A, digital I/O, counter/timers, serial I/O, wired or wireless...
: a tiny expansion card format (43 x 65 mm) for embedded and small form factor applications; it implements two x1 PCIe links on a high-density connector along with USB, I2C, and up to 100 points of I/O. - Universal IO: A variant from Super Micro Computer Inc designed for use in low profile rack mounted chassis. It has the connector bracket reversed so it cannot fit in a normal PCI Express socket, but is pin compatible and may be inserted if the bracket is removed.
- Thunderbolt: A variant from Intel that combines DisplayPortDisplayPortDisplayPort is a digital display interface standard produced by the Video Electronics Standards Association . The specification defines a royalty-free digital interconnect for audio and video. The interface is primarily used to connect a video source to a display device such as a computer monitor...
and PCIe protocols in a form factor compatible with Mini DisplayPortMini DisplayPortThe Mini DisplayPort is a miniaturized version of the DisplayPort digital audio-visual interface. Apple, Inc. announced the development in the fourth quarter of 2008, and now applies it in the LED Cinema Display and in all new Macintosh computers: MacBook, MacBook Pro, MacBook Air, iMac, Mac mini,...
.
History
While in early development, PCIe was initially referred to as HSI (for High Speed Interconnect), and underwent a name change to 3GIO (for 3rd Generation I/O) before finally settling on its PCI-SIGPCI-SIG
The PCI-SIG or Peripheral Component Interconnect Special Interest Group is an electronics industry consortium responsible for specifying the Peripheral Component Interconnect , PCI-X, and PCI Express computer buses....
name PCI Express. It was first drawn up by a technical working group named the Arapaho Work Group (AWG) that, for initial drafts, consisted only of Intel engineers. Subsequently the AWG expanded to include industry partners.
PCIe is a technology under constant development and improvement. The current PCI Express implementation is version 3.0.
PCI Express 1.0a
In 2003, PCI-SIG introduced PCIe 1.0a, with a data rate of 250 MB/s and a transfer rate of 2.5 GT/s.PCI Express 1.1
In 2005, PCI-SIG introduced PCIe 1.1. This updated specification includes clarifications and several improvements, but is fully compatible with PCI Express 1.0a. No changes were made to the data rate.PCI Express 2.0
PCI-SIGPCI-SIG
The PCI-SIG or Peripheral Component Interconnect Special Interest Group is an electronics industry consortium responsible for specifying the Peripheral Component Interconnect , PCI-X, and PCI Express computer buses....
announced the availability of the PCI Express Base 2.0 specification on 15 January 2007. The PCIe 2.0 standard doubles the transfer rate compared with PCIe 1.0 to 5 GT/s and the per-lane throughput rises from 250 MB/s to 500 MB/s. This means a 32-lane PCI connector (x32) can support throughput up to 16 GB/s aggregate.
PCIe 2.0 motherboard slots are fully backward compatible with PCIe v1.x cards. PCIe 2.0 cards are also generally backward compatible with PCIe 1.x motherboards, using the available bandwidth of PCI Express 1.1. Overall, graphic cards or motherboards designed for v2.0 will work with the other being v1.1 or v1.0.
The PCI-SIG also said that PCIe 2.0 features improvements to the point-to-point data transfer protocol and its software architecture.
Intel
Intel Corporation
Intel Corporation is an American multinational semiconductor chip maker corporation headquartered in Santa Clara, California, United States and the world's largest semiconductor chip maker, based on revenue. It is the inventor of the x86 series of microprocessors, the processors found in most...
's first PCIe 2.0 capable chipset was the X38 and boards began to ship from various vendors (Abit
Abit
Abit may refer to:*Universal abit, a Defunct Taiwanese computer firm*Abit, Burma, a village in Burma*Abit , an asphalt production company in Surenavan, Armenia...
, Asus
ASUS
ASUSTeK Computer Incorporated is a multinational computer technology and consumer electronics product manufacturer headquartered in Taipei, Taiwan. Its product range includes motherboards, desktops, laptops, monitors, tablet PCs, servers and mobile phones...
, Gigabyte
Gigabyte Technology
Gigabyte Technology Co., Ltd. is a Taiwan-based manufacturer of computer hardware products best known for its motherboards. The company is publicly held and traded on the Taiwan Stock Exchange .-Company:...
) as of October 21, 2007. AMD started supporting PCIe 2.0 with its AMD 700 chipset series
AMD 700 chipset series
The AMD 700 chipset series is a set of chipsets designed by ATI for AMD Phenom processors to be sold under the AMD brand...
and nVidia started with the MCP72
NForce 700
The nForce 700 is a chipset series designed by Nvidia first released in December 2007. The series supports both Intel Core 2 and AMD Phenom processors, and replaces the nForce 600 series chipsets...
. All of Intel's prior chipsets, including the Intel P35
Intel P35
The P35 Express is a mainstream desktop computer chipset from Intel released in June 2007, although motherboards featuring the chipset were available a month earlier. The P35 Express chipset supports Intel's LGA 775 socket and Core 2 Duo and Quad processors, and is also known to support...
chipset, supported PCIe 1.1 or 1.0a.
PCI Express 2.1
PCI Express 2.1 supports a large proportion of the management, support, and troubleshooting systems planned for full implementation in PCI Express 3.0. However, the speed is the same as PCI Express 2.0. Most motherboards sold currently come with PCI Express 2.1 connectors.PCI Express 3.0
PCI Express 3.0 Base specification revision 3.0 was made available in November 2010, after multiple delays. In August 2007, PCI-SIG announced that PCI Express 3.0 would carry a bit rate of 8 gigatransfers per second, and that it would be backwards compatible with existing PCIe implementations. At that time, it was also announced that the final specification for PCI Express 3.0 would be delayed until 2011. New features for the PCIe 3.0 specification include a number of optimizations for enhanced signaling and data integrity, including transmitter and receiver equalization, PLLPhase-locked loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input "reference" signal. It is an electronic circuit consisting of a variable frequency oscillator and a phase detector...
improvements, clock data recovery, and channel enhancements for currently supported topologies.
Following a six-month technical analysis of the feasibility of scaling the PCIe interconnect bandwidth, PCI-SIG's analysis found out that 8 gigatransfers per second can be manufactured in mainstream silicon process technology, and can be deployed with existing low-cost materials and infrastructure, while maintaining full compatibility (with negligible impact) to the PCIe protocol stack.
PCIe 2.0 delivers 5 GT/s, but uses an 8b/10b encoding
8B/10B encoding
In telecommunications, 8b/10b is a line code that maps 8-bit symbols to 10-bit symbols to achieve DC-balance and bounded disparity, and yet provide enough state changes to allow reasonable clock recovery. This means that the difference between the count of 1s and 0s in a string of at least 20 bits...
scheme that results in a 20 percent ((10-8)/10) overhead on the raw bit rate. PCIe 3.0 removes the requirement for 8b/10b encoding, and instead uses a technique called "scrambling" that applies a known binary polynomial to a data stream in a feedback topology. Because the scrambling polynomial is known, the data can be recovered by running it through a feedback topology using the inverse polynomial. and also uses a 128b/130b encoding scheme, reducing the overhead to approximately 1.5% ((130-128)/130), as opposed to the 20% overhead of 8b/10b encoding used by PCIe 2.0. PCIe 3.0's 8 GT/s bit rate effectively delivers double PCIe 2.0 bandwidth. PCI-SIG expects the PCIe 3.0 specifications to undergo rigorous technical vetting and validation before being released to the industry. This process, which was followed in the development of prior generations of the PCIe Base and various form factor specifications, includes the corroboration of the final electrical parameters with data derived from test silicon and other simulations conducted by multiple members of the PCI-SIG.
On November 18, 2010, the PCI Special Interest Group officially published the finalized PCI Express 3.0 specification to its members to build devices based on this new version of PCI Express.
Current status
PCI Express has replaced AGPAccelerated Graphics Port
The Accelerated Graphics Port is a high-speed point-to-point channel for attaching a video card to a computer's motherboard, primarily to assist in the acceleration of 3D computer graphics. Since 2004 AGP has been progressively phased out in favor of PCI Express...
as the default interface for graphics cards on new systems. With a few exceptions, all graphics cards being released as of 2009 and 2010 from AMD (ATI) and NVIDIA
NVIDIA
Nvidia is an American global technology company based in Santa Clara, California. Nvidia is best known for its graphics processors . Nvidia and chief rival AMD Graphics Techonologies have dominated the high performance GPU market, pushing other manufacturers to smaller, niche roles...
use PCI Express. NVIDIA uses the high bandwidth data transfer of PCIe for its Scalable Link Interface
Scalable Link Interface
Scalable Link Interface is a brand name for a multi-GPU solution developed by NVIDIA for linking two or more video cards together to produce a single output...
(SLI) technology, which allows multiple graphics cards of the same chipset and model number to run in tandem, allowing increased performance. ATI has also developed a multi-GPU system based on PCIe called CrossFire
ATI CrossFire
AMD CrossFireX is a brand name for the multi-GPU solution by Advanced Micro Devices, originally developed by ATI Technologies. The technology allows up to four GPUs to be used in a single computer to improve graphics performance.-First-generation:CrossFire was first made available to the public...
. AMD and NVIDIA have released motherboard chipsets that support up to four PCIe ×16 slots, allowing tri-GPU and quad-GPU card configurations.
PCI Express has displaced a major portion of the add-in card market. PCI Express was originally only common in disk array controller
Disk array controller
A disk array controller is a device which manages the physical disk drives and presents them to the computer as logical units. It almost always implements hardware RAID, thus it is sometimes referred to as RAID controller. It also often provides additional disk cache.A disk array controller name is...
s, onboard gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet is a term describing various technologies for transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second , as defined by the IEEE 802.3-2008 standard. It came into use beginning in 1999, gradually supplanting Fast Ethernet in wired local networks where it performed...
, Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi or Wifi, is a mechanism for wirelessly connecting electronic devices. A device enabled with Wi-Fi, such as a personal computer, video game console, smartphone, or digital audio player, can connect to the Internet via a wireless network access point. An access point has a range of about 20...
and graphics cards. Most sound cards, TV/capture-cards, modems, serial port/USB/Firewire cards, network/WiFi cards that would have used the conventional PCI in the past have moved to PCI Express x8, x4, or x1. While some motherboards have conventional PCI slots, these are primarily for legacy cards and are being phased out.
Hardware protocol summary
The PCIe link is built around dedicated unidirectional couples of serial (1-bit), point-to-point connections known as lanes. This is in sharp contrast to the earlier PCI connection, which is a bus-based system where all the devices share the same bidirectional, 32-bit or 64-bit parallel bus.PCI Express is a layered protocol, consisting of a transaction layer, a data link layer, and a physical layer. The Data Link Layer is subdivided to include a media access control
Media Access Control
The media access control data communication protocol sub-layer, also known as the medium access control, is a sublayer of the data link layer specified in the seven-layer OSI model , and in the four-layer TCP/IP model...
(MAC) sublayer. The Physical Layer is subdivided into logical and electrical sublayers. The Physical logical-sublayer contains a physical coding sublayer (PCS). The terms are borrowed from the IEEE 802
IEEE 802
IEEE 802 refers to a family of IEEE standards dealing with local area networks and metropolitan area networks.More specifically, the IEEE 802 standards are restricted to networks carrying variable-size packets. IEEE 802 refers to a family of IEEE standards dealing with local area networks and...
networking protocol model.
Physical layer
The PCIe Physical Layer (PHY, PCIEPHY, PCI Express PHY, or PCIe PHY) specification is divided into two sub-layers, corresponding to electrical and logical specifications. The logical sublayer is sometimes further divided into a MAC sublayer and a PCS, although this division is not formally part of the PCIe specification. A specification published by Intel, the PHY Interface for PCI Express (PIPE), defines the MAC/PCS functional partitioning and the interface between these two sub-layers. The PIPE specification also identifies the physical media attachment (PMA) layer, which includes the serializer/deserializer (SerDes)SerDes
A Serializer/Deserializer is a pair of functional blocks commonly used in high speed communications to compensate for limited input/output. These blocks convert data between serial data and parallel interfaces in each direction...
and other analog circuitry; however, since SerDes implementations vary greatly among ASIC
Application-specific integrated circuit
An application-specific integrated circuit is an integrated circuit customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use. For example, a chip designed solely to run a cell phone is an ASIC...
vendors, PIPE does not specify an interface between the PCS and PMA.
At the electrical level, each lane consists of two unidirectional LVDS or PCML
Current mode logic
Current mode logic , or source-coupled logic , is a differential digital logic family intended to transmit data at speeds between 312.5 Mbit/s and 3.125 Gbit/s over a standard printed circuit board....
pairs at 2.525 Gbit
Gigabit
The gigabit is a multiple of the unit bit for digital information or computer storage. The prefix giga is defined in the International System of Units as a multiplier of 109 , and therefore...
/s. Transmit and receive are separate differential pair
Differential pair
A differential pair is a pair of conductors used for differential signaling. Differential pairs are usually found on a printed circuit board, in cables , and in connectors...
s, for a total of 4 data wires per lane.
A connection between any two PCIe devices is known as a link, and is built up from a collection of 1 or more lanes. All devices must minimally support single-lane (x1) link. Devices may optionally support wider links composed of 2, 4, 8, 12, 16, or 32 lanes. This allows for very good compatibility in two ways:
- A PCIe card physically fits (and works correctly) in any slot that is at least as large as it is (e.g., an ×1 sized card will work in any sized slot);
- A slot of a large physical size (e.g., ×16) can be wired electrically with fewer lanes (e.g., ×1, ×4, ×8, or ×12) as long as it provides the ground connections required by the larger physical slot size.
In both cases, PCIe negotiates the highest mutually supported number of lanes. Many graphics cards, motherboards and bios versions are verified to support ×1, ×4, ×8 and ×16 connectivity on the same connection.
Even though the two would be signal-compatible, it is not usually possible to place a physically larger PCIe card (e.g., a ×16 sized card) into a smaller slot —though if the PCIe slots are open-ended, by design or by hack, some motherboards will allow this.
The width of a PCIe connector is 8.8 mm, while the height is 11.25 mm, and the length is variable. The fixed section of the connector is 11.65 mm in length and contains 2 rows of 11 (22 pins total), while the length of the other section is variable depending on the number of lanes. The pins are spaced at 1 mm intervals, and the thickness of the card going into the connector is 1.8 mm.
| Lanes | Pins | Length | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Variable | Total | Variable | |
| ×1 | 2×18 = 36 | 2×7 = 14 | 25 mm | 7.65 mm |
| ×4 | 2×32 = 64 | 2×21 = 42 | 39 mm | 21.65 mm |
| ×8 | 2×49 = 98 | 2×38 = 76 | 56 mm | 38.65 mm |
| ×16 | 2×82 = 164 | 2×71 = 142 | 89 mm | 71.65 mm |
Data transmission
PCIe sends all control messages, including interrupts, over the same links used for data. The serial protocol can never be blocked, so latency is still comparable to conventional PCI, which has dedicated interrupt lines.Data transmitted on multiple-lane links is interleaved, meaning that each successive byte is sent down successive lanes. The PCIe specification refers to this interleaving as data striping. While requiring significant hardware complexity to synchronize (or deskew
Skew
Skew may refer to:In mathematics:* Skew lines, lines that are neither parallel nor intersecting* Skew-symmetric matrix, a square matrix whose transpose is also its negative...
) the incoming striped data, striping can significantly reduce the latency of the nth byte on a link. Due to padding requirements, striping may not necessarily reduce the latency of small data packets on a link.
As with other high data rate serial transmission protocols, clocking information is embedded
Self-clocking signal
In telecommunications and electronics, a self-clocking signal is one that can be decoded without the need for a separate clock signal or other source of synchronization...
in the signal. At the physical level, PCI Express 2.0 utilizes the 8b/10b encoding
8B/10B encoding
In telecommunications, 8b/10b is a line code that maps 8-bit symbols to 10-bit symbols to achieve DC-balance and bounded disparity, and yet provide enough state changes to allow reasonable clock recovery. This means that the difference between the count of 1s and 0s in a string of at least 20 bits...
scheme to ensure that strings of consecutive ones or consecutive zeros are limited in length. This was used to prevent the receiver from losing track of where the bit edges are. In this coding scheme every 8 (uncoded) payload bits of data are replaced with 10 (encoded) bits of transmit data, causing a 20% overhead in the electrical bandwidth. To improve the available bandwidth, PCI Express version 3.0 employs 128b/130b encoding instead: similar but with much lower overhead.
Many other protocols (such as SONET
Sonet
Sonet may refer to:* Sonet Records, European record label* Synchronous optical networking * Saab Sonett...
) use a different form of encoding known as scrambling to embed clock information into data streams. The PCIe specification also defines a scrambling algorithm, but it is used to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) by preventing repeating data patterns in the transmitted data stream.
Data link layer
The Data Link Layer performs three vital services for the PCIe express link:(1) sequence the transaction layer packets (TLPs) that are generated by the transaction layer,
(2) ensure reliable delivery of TLPs between two endpoints via an acknowledgement protocol (ACK
Acknowledge character
In telecommunications, an acknowledge character is a transmission control character transmitted by the receiving station as an acknowledgement, i.e...
and NAK
Negative-acknowledge character
* In telecommunications, a negative-acknowledge character is a transmission control character sent by a station as a negative response to the station with which the connection has been set up....
signaling) that explicitly requires replay of unacknowledged/bad TLPs,
(3) initialize and manage flow control credits
On the transmit side, the data link layer generates an incrementing sequence number for each outgoing TLP. It serves as a unique identification tag for each transmitted TLP, and is inserted into the header of the outgoing TLP. A 32-bit cyclic redundancy check
Cyclic redundancy check
A cyclic redundancy check is an error-detecting code commonly used in digital networks and storage devices to detect accidental changes to raw data...
code (known in this context as Link CRC or LCRC) is also appended to the end of each outgoing TLP.
On the receive side, the received TLP's LCRC and sequence number are both validated in the link layer. If either the LCRC check fails (indicating a data error), or the sequence-number is out of range (non-consecutive from the last valid received TLP), then the bad TLP, as well as any TLPs received after the bad TLP, are considered invalid and discarded. The receiver sends a negative acknowledgement message (NAK) with the sequence-number of the invalid TLP, requesting re-transmission of all TLPs forward of that sequence-number. If the received TLP passes the LCRC check and has the correct sequence number, it is treated as valid. The link receiver increments the sequence-number (which tracks the last received good TLP), and forwards the valid TLP to the receiver's transaction layer. An ACK message is sent to remote transmitter, indicating the TLP was successfully received (and by extension, all TLPs with past sequence-numbers.)
If the transmitter receives a NAK message, or no acknowledgement (NAK or ACK) is received until a timeout period expires, the transmitter must retransmit all TLPs that lack a positive acknowledgement (ACK). Barring a persistent malfunction of the device or transmission medium, the link-layer presents a reliable connection to the transaction layer, since the transmission protocol ensures delivery of TLPs over an unreliable medium.
In addition to sending and receiving TLPs generated by the transaction layer, the data-link layer also generates and consumes DLLPs, data link layer packets. ACK and NAK signals are communicated via (DLLP), as are flow control credit information, some power management messages and flow control credit information (on behalf of the transaction layer.)
In practice, the number of in-flight, unacknowledged TLPs on the link is limited by two factors: the size of the transmitter's replay buffer (which must store a copy of all transmitted TLPs until they the remote receiver ACKs them), and the flow control credits issued by the receiver to a transmitter. PCI Express requires all receivers to issue a minimum number of credits, to guarantee a link allows sending PCIConfig TLPs and message TLPs.
Transaction layer
PCI Express implements split transactions (transactions with request and response separated by time), allowing the link to carry other traffic while the target device gathers data for the response.PCI Express uses credit-based flow control. In this scheme, a device advertises an initial amount of credit for each received buffer in its transaction layer. The device at the opposite end of the link, when sending transactions to this device, counts the number of credits each TLP consumes from its account. The sending device may only transmit a TLP when doing so does not make its consumed credit count exceed its credit limit. When the receiving device finishes processing the TLP from its buffer, it signals a return of credits to the sending device, which increases the credit limit by the restored amount. The credit counters are modular counters, and the comparison of consumed credits to credit limit requires modular arithmetic
Modular arithmetic
In mathematics, modular arithmetic is a system of arithmetic for integers, where numbers "wrap around" after they reach a certain value—the modulus....
. The advantage of this scheme (compared to other methods such as wait states or handshake-based transfer protocols) is that the latency of credit return does not affect performance, provided that the credit limit is not encountered. This assumption is generally met if each device is designed with adequate buffer sizes.
PCIe 1.x is often quoted to support a data rate of 250 MB/s in each direction, per lane. This figure is a calculation from the physical signaling rate (2.5 Gbaud
Baud
In telecommunications and electronics, baud is synonymous to symbols per second or pulses per second. It is the unit of symbol rate, also known as baud rate or modulation rate; the number of distinct symbol changes made to the transmission medium per second in a digitally modulated signal or a...
) divided by the encoding overhead (10 bits per byte.) This means a sixteen lane (x16) PCIe card would then be theoretically capable of 16×250 MB/s = 4 GB/s in each direction. While this is correct in terms of data bytes, more meaningful calculations are based on the usable data payload rate, which depends on the profile of the traffic, which is a function of the high-level (software) application and intermediate protocol levels.
Like other high data rate serial interconnect systems, PCIe has a protocol and processing overhead due to the additional transfer robustness (CRC and acknowledgements). Long continuous unidirectional transfers (such as those typical in high-performance storage controllers) can approach >95% of PCIe's raw (lane) data rate. These transfers also benefit the most from increased number of lanes (×2, ×4, etc.) But in more typical applications (such as a USB
Universal Serial Bus
USB is an industry standard developed in the mid-1990s that defines the cables, connectors and protocols used in a bus for connection, communication and power supply between computers and electronic devices....
or Ethernet
Ethernet
Ethernet is a family of computer networking technologies for local area networks commercially introduced in 1980. Standardized in IEEE 802.3, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies....
controller), the traffic profile is characterized as short data packets with frequent enforced acknowledgements. This type of traffic reduces the efficiency of the link, due to overhead from packet parsing and forced interrupts (either in the device's host interface or the PC's CPU.) Being a protocol for devices connected to the same printed circuit board
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
, it does not require the same tolerance for transmission errors as a protocol for communication over longer distances, and thus, this loss of efficiency is not particular to PCIe.
External PCIe cards
Theoretically, external PCIe could give a notebook the graphics power of a desktop, by connecting a notebook with any PCIe desktop video card (enclosed in its own external housing, with strong power supply and cooling); This is possible with an ExpressCard interface, which provides single lane v1.1 performance.IBM/Lenovo has also included a PCI-Express slot in their Advanced Docking Station 250310U. It provides a half sized slot with an x16 length slot, but only x1 connectivity. However, docking stations with expansion slots are becoming less common as the laptops are getting more advanced video cards and either DVI-D interfaces, or DVI-D pass through for port replicators and docking stations.
Additionally, Nvidia
NVIDIA
Nvidia is an American global technology company based in Santa Clara, California. Nvidia is best known for its graphics processors . Nvidia and chief rival AMD Graphics Techonologies have dominated the high performance GPU market, pushing other manufacturers to smaller, niche roles...
has developed Quadro Plex
NVIDIA Quadro Plex
The Nvidia Quadro Plex is an external graphics processing unit designed for large-scale 3D visualizations. The system consists of a box containing a pair of high-end Nvidia Quadro graphics cards featuring a variety of external video connectors...
external PCIe Video Cards that can be used for advanced graphic applications. These video cards require a PCI Express x8 or x16 slot for the interconnection cable. In 2008, AMD announced the ATI XGP
ATI XGP
ATI XGP is an external graphics solution for notebook computers. The technology was announced on June 4, 2008 on Computex 2008 trade show, following the announcement of the codenamed Puma notebook platform....
technology, based on a proprietary cabling solution that is compatible with PCIe x8 signal transmissions. This connector is available on the Fujitsu Amilo and the Acer Ferrari One notebooks. Only Fujitsu has an actual external box available, which also works on the Ferrari One. Recently Acer launched the Dynavivid graphics dock for XGP.
There are now card hubs in development that one can connect to a laptop through an ExpressCard slot, though they are currently rare, obscure, or unavailable on the open market. These hubs can have full-sized cards placed in them.
Magma and ViDock also makes use of ExpressCard and implements the usage of External graphic solutions .ViDock are expansion chassis tailored specifically for adapting PCI Express graphics cards for use with ExpressCard equipped laptop PCs. This enables user to make use of connecting PCIe cards externally.
Although, the developments in these technologies are still ongoing. Other examples that underwent are - MSI GUS, Asus XG Station.
Recently, Intel and Apple introduced Thunderbolt, which allows for external PCI(e) devices.
Competing protocols
Several communications standards have emerged based on high bandwidth serial architectures. These include InfiniBandInfiniBand
InfiniBand is a switched fabric communications link used in high-performance computing and enterprise data centers. Its features include high throughput, low latency, quality of service and failover, and it is designed to be scalable...
, RapidIO
RapidIO
The RapidIO architecture is a high-performance packet-switched, interconnect technology for interconnecting chips on a circuit board, and also circuit boards to each other using a backplane...
, HyperTransport
HyperTransport
HyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
, QPI and StarFabric. The differences are based on the tradeoffs between flexibility and extensibility vs latency and overhead. An example of such a tradeoff is adding complex header information to a transmitted packet to allow for complex routing (PCI Express is not capable of this). The additional overhead reduces the effective bandwidth of the interface and complicates bus discovery and initialization software. Also making the system hot-pluggable requires that software track network topology changes. Examples of buses suited for this purpose are InfiniBand and StarFabric.
Another example is making the packets shorter to decrease latency (as is required if a bus must operate as a memory interface). Smaller packets mean packet headers consume a higher percentage of the packet, thus decreasing the effective bandwidth. Examples of bus protocols designed for this purpose are RapidIO and HyperTransport.
PCI Express falls somewhere in the middle, targeted by design as a system interconnect (local bus
Local bus
In computer science, a local bus is a computer bus that connects directly, or almost directly, from the CPU to one or more slots on the expansion bus. The significance of direct connection to the CPU is avoiding the bottleneck created by the expansion bus, thus providing fast throughput...
) rather than a device interconnect or routed network protocol. Additionally, its design goal of software transparency constrains the protocol and raises its latency somewhat.
Development tools
When developing and/or troubleshooting the PCI Express bus, examination of hardware signals can be very important to find the problems. Logic analyzers and bus analyzerBus analyzer
A bus analyzer is a computer bus analysis tool, often a combination of hardware and software, used during development of hardware or device drivers for a specific bus, for diagnosing bus or device failures, or reverse engineering....
s are tools that collect, analyze, decode, store signals so people can view the high-speed waveforms at their leisure.
See also
- PCI Configuration SpacePCI Configuration SpacePCI configuration space is the underlying way that the Conventional PCI, PCI-X and PCI Express perform auto configuration of the cards inserted into their bus.- Technical information :...
- Conventional PCI
- PCI-XPCI-XPCI-X, short for PCI-eXtended, is a computer bus and expansion card standard that enhances the 32-bit PCI Local Bus for higher bandwidth demanded by servers. It is a double-wide version of PCI, running at up to four times the clock speed, but is otherwise similar in electrical implementation and...
- Root complexRoot complexIn a PCI Express system, a root complex device connects the processor and memory subsystem to the PCI Express switch fabric composed of one or more switch devices....
- Serial Digital Video Out for ADD2 DVI adapter cards
- Active State Power ManagementActive State Power ManagementActive State Power Management or ASPM is a power management protocol used to manage PCI Express-based serial link devices as links become less active over time...
(ASPM)
Further reading
- PCI Express System Architecture; 1st Ed; Ravi Budruk / Don Anderson / Tom Shanley; 1120 pages; 2003; ISBN 9780321156303.
- Introduction to PCI Express : A Hardware and Software Developer's Guide; 1st Ed; 325 pages; 2003; ISBN 9780970284693.
- Complete PCI Express Reference : Design Implications for Hardware and Software Developers; 1st Ed; 1056 pages; 2003; ISBN 9780971786196.
External links
- Introduction to PCI Protocol (Requires PCI-SIG membership)
- PCI-SIG, the industry organization that maintains and develops the various PCI standards
- An introduction to how PCIe works at the TLP level
- Intel Developer Network for PCI Express Architecture
- IDT + PCI Express solutions -> http://www.idt.com/go/pcie

