PUREX raffinate
Encyclopedia
The term PUREX raffinate
is a better term for the mixture of metals in nitric acid
which are left behind when the uranium
and plutonium
have been removed by the PUREX
process from a nuclear fuel
dissolution liquor. This mixture is often known as high level nuclear waste.
Two PUREX raffinates exist. The most highly active raffinate
from the first cycle is the one which is most commonly known as PUREX raffinate. The other is from the medium-active cycle in which the uranium and plutonium are refined by a second extraction with tributyl phosphate
.
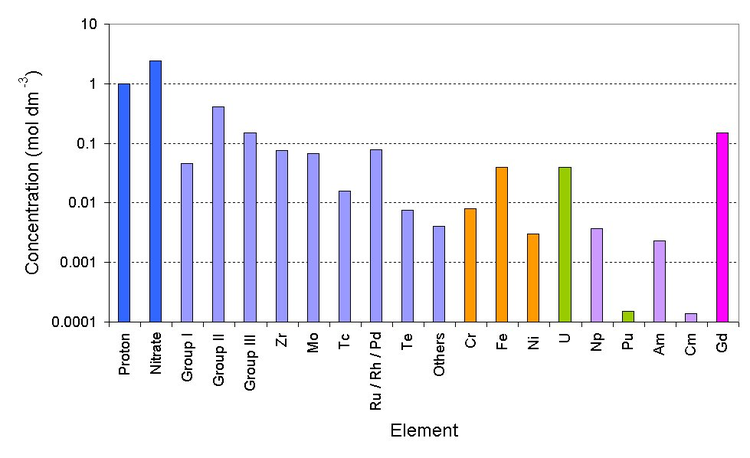 Deep blue is the bulk ions, light blue is the fission products (group I is Rb/Cs) (group II is Sr/Ba) (group III is Y and the lanthanides), orange is the corrosion
Deep blue is the bulk ions, light blue is the fission products (group I is Rb/Cs) (group II is Sr/Ba) (group III is Y and the lanthanides), orange is the corrosion
products (from stainless steel pipework), green are the major actinides, violet are the minor actinides
and magenta is the neutron poison)
Currently PUREX raffinate is stored in stainless steel
tanks before being converted into glass
. The first cycle PUREX raffinate is very radioactive. It has almost all of the fission products, corrosion
products such as iron
/nickel
, traces of uranium, plutonium and the minor actinides
.
Raffinate
Raffinating something is a technique used in metallurgy to remove impurities from liquid material. There are many different kinds of raffination, for example you can use vacuum to extract hydrogen from metals....
is a better term for the mixture of metals in nitric acid
Nitric acid
Nitric acid , also known as aqua fortis and spirit of nitre, is a highly corrosive and toxic strong acid.Colorless when pure, older samples tend to acquire a yellow cast due to the accumulation of oxides of nitrogen. If the solution contains more than 86% nitric acid, it is referred to as fuming...
which are left behind when the uranium
Uranium
Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons...
and plutonium
Plutonium
Plutonium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, forming a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation...
have been removed by the PUREX
PUREX
PUREX is an acronym standing for Plutonium - URanium EXtraction — de facto standard aqueous nuclear reprocessing method for the recovery of uranium and plutonium from used nuclear fuel. It is based on liquid-liquid extraction ion-exchange.The PUREX process was invented by Herbert H. Anderson and...
process from a nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel is a material that can be 'consumed' by fission or fusion to derive nuclear energy. Nuclear fuels are the most dense sources of energy available...
dissolution liquor. This mixture is often known as high level nuclear waste.
Two PUREX raffinates exist. The most highly active raffinate
Raffinate
Raffinating something is a technique used in metallurgy to remove impurities from liquid material. There are many different kinds of raffination, for example you can use vacuum to extract hydrogen from metals....
from the first cycle is the one which is most commonly known as PUREX raffinate. The other is from the medium-active cycle in which the uranium and plutonium are refined by a second extraction with tributyl phosphate
Tributyl phosphate
Tributyl phosphate, known commonly as TBP, is an organophosphorus compound with the formula 3PO. This colourless, odorless liquid finds some applications as an extractant and a plasticizer. It is an ester of orthophosphoric acid with n-butanol.- Production :Tributyl phosphate is manufactured by...
.

Corrosion
Corrosion is the disintegration of an engineered material into its constituent atoms due to chemical reactions with its surroundings. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metals in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen...
products (from stainless steel pipework), green are the major actinides, violet are the minor actinides
Minor actinides
The minor actinides are the actinide elements in used nuclear fuel other than uranium and plutonium, which are termed the major actinides. The minor actinides include neptunium, americium, curium, berkelium, californium, einsteinium, and fermium...
and magenta is the neutron poison)
Currently PUREX raffinate is stored in stainless steel
Stainless steel
In metallurgy, stainless steel, also known as inox steel or inox from French "inoxydable", is defined as a steel alloy with a minimum of 10.5 or 11% chromium content by mass....
tanks before being converted into glass
Glass
Glass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives...
. The first cycle PUREX raffinate is very radioactive. It has almost all of the fission products, corrosion
Corrosion
Corrosion is the disintegration of an engineered material into its constituent atoms due to chemical reactions with its surroundings. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metals in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen...
products such as iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
/nickel
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile...
, traces of uranium, plutonium and the minor actinides
Minor actinides
The minor actinides are the actinide elements in used nuclear fuel other than uranium and plutonium, which are termed the major actinides. The minor actinides include neptunium, americium, curium, berkelium, californium, einsteinium, and fermium...
.

