
Pacific decadal oscillation
Encyclopedia
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
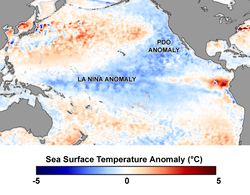
, north of 20° N. During a "warm", or "positive", phase, the west Pacific becomes cool and part of the eastern ocean warms; during a "cool" or "negative" phase, the opposite pattern occurs.
The Pacific (inter-)decadal oscillation was named by Steven R. Hare, who noticed it while studying salmon
Salmon
Salmon is the common name for several species of fish in the family Salmonidae. Several other fish in the same family are called trout; the difference is often said to be that salmon migrate and trout are resident, but this distinction does not strictly hold true...
production pattern results in 1997.
The prevailing hypothesis is that the PDO is caused by a "reddening" of ENSO
Enso
Ensō is a Japanese word meaning "circle" and a concept strongly associated with Zen. Ensō is one of the most common subjects of Japanese calligraphy even though it is a symbol and not a character. It symbolizes the Absolute enlightenment, strength, elegance, the Universe, and the void; it can...
combined with stochastic
Stochastic
Stochastic refers to systems whose behaviour is intrinsically non-deterministic. A stochastic process is one whose behavior is non-deterministic, in that a system's subsequent state is determined both by the process's predictable actions and by a random element. However, according to M. Kac and E...
atmospheric forcing.
A PDO signal has been reconstructed to 1661 through tree-ring chronologies in the Baja California
Baja California
Baja California officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is both the northernmost and westernmost state of Mexico. Before becoming a state in 1953, the area was known as the North...
area.
The interdecadal Pacific oscillation (IPO or ID) display similar sea-surface temperature (SST) and sea-level pressure (SLP) patterns, with a cycle of 15–30 years, but affects both the north and south Pacific. In the tropical Pacific, maximum SST anomalies are found away from the equator. This is quite different from the quasi-decadal oscillation (QDO) with a period of 8-to-12 years and maximum SST anomalies straddling the equator, thus resembling the El Niño-Southern Oscillation
El Niño-Southern Oscillation
El Niño/La Niña-Southern Oscillation, or ENSO, is a quasiperiodic climate pattern that occurs across the tropical Pacific Ocean roughly every five years...
(ENSO).
Mechanisms
Several studies have indicated that the PDO index can be reconstructed as the superimposition of tropical forcing and extra-tropical processes. Thus, unlike ENSOEnso
Ensō is a Japanese word meaning "circle" and a concept strongly associated with Zen. Ensō is one of the most common subjects of Japanese calligraphy even though it is a symbol and not a character. It symbolizes the Absolute enlightenment, strength, elegance, the Universe, and the void; it can...
, the PDO is not a single physical mode of ocean variability, but rather the sum of several processes with different dynamical origins.
At inter-annual time scales the PDO index is reconstructed as the sum of random and ENSO induced variability in the Aleutian low
Aleutian low
The Aleutian Low is a semi-permanent low pressure center located near the Aleutian Islands during the winter. It is one of the main centers of action in the atmospheric circulation of the Northern Hemisphere...
, on decadal timescales ENSO teleconnections, stochastic atmospheric forcing and changes in the North Pacific oceanic gyre
Gyre
A gyre in oceanography is any large system of rotating ocean currents, particularly those involved with large wind movements. Gyres are caused by the Coriolis Effect; planetary vorticity along with horizontal and vertical friction, which determine the circulation patterns from the wind curl...
circulation contribute approximately equally, additionally sea surface temperature anomalies have some winter to winter persistence due to the reemergence mechanism.
ENSO teleconnections, the atmospheric bridge
ENSO can influence the global circulation pattern thousands of kilometers away from the equatorial Pacific through the "atmospheric bridge". During El Nino
Enso
Ensō is a Japanese word meaning "circle" and a concept strongly associated with Zen. Ensō is one of the most common subjects of Japanese calligraphy even though it is a symbol and not a character. It symbolizes the Absolute enlightenment, strength, elegance, the Universe, and the void; it can...
events deep convection
Deep convection
Deep convection is a convective process in a medium, usually in an atmosphere or ocean, that in some sense spans the vertical.Within the atmosphere, this means from the surface to above the 500 hPa level, generally stopping at or defining the tropopause at around 200 hPa...
and heat transfer to the troposphere is enhanced over the anomalously warm sea surface temperature
Sea surface temperature
Sea surface temperature is the water temperature close to the oceans surface. The exact meaning of surface varies according to the measurement method used, but it is between and below the sea surface. Air masses in the Earth's atmosphere are highly modified by sea surface temperatures within a...
, this ENSO related tropical forcing generates Rossby waves that propagates poleward and eastward and are subsequently refracted back from the pole to the tropics. The planetary waves forms at preferred locations both in the North and South Pacific Ocean and the teleconnection pattern is established within 2–6 weeks. ENSO driven patterns modify surface temperature,humidity, wind and the distribution of cloud over the North Pacific that alter surface heat, momentum and freshwater fluxes and thus induce sea surface temperature,salinity and mixed layer
Mixed layer
The oceanic or limnological mixed layer is a layer in which active turbulence has homogenized some range of depths. The surface mixed layer is a layer where this turbulence is generated by winds, cooling, or processes such as evaporation or sea ice formation which result in an increase in salinity...
depth (MLD) anomalies.
The atmospheric bridge is more effective during boreal winter when the deepened Aleutian low
Aleutian low
The Aleutian Low is a semi-permanent low pressure center located near the Aleutian Islands during the winter. It is one of the main centers of action in the atmospheric circulation of the Northern Hemisphere...
results in stronger and cold northwesterly winds over the central Pacific and warm/humid southerly winds along the North American west coast, the associated changes in the surface heat fluxes and to a lesser extent Ekman transport
Ekman transport
Ekman transport, part of Ekman motion theory first investigated in 1902 by Vagn Walfrid Ekman , is the term given for the 90 degree net transport of the surface layer due to wind forcings...
creates negative sea surface temperature anomalies and a deepened MLD in the central pacific and warm the ocean from the Hawaii to the Bering Sea
Bering Sea
The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves....
.
SST reemergence
Midlatitude SST
Sea surface temperature
Sea surface temperature is the water temperature close to the oceans surface. The exact meaning of surface varies according to the measurement method used, but it is between and below the sea surface. Air masses in the Earth's atmosphere are highly modified by sea surface temperatures within a...
anomaly patterns tend to recur from one winter to the next but not during the intervening summer, this process occurs because of the strong mixed layer
Mixed layer
The oceanic or limnological mixed layer is a layer in which active turbulence has homogenized some range of depths. The surface mixed layer is a layer where this turbulence is generated by winds, cooling, or processes such as evaporation or sea ice formation which result in an increase in salinity...
seasonal cycle. The mixed layer depth over the North Pacific is deeper, typically 100-200m, in winter than it is in summer and thus SST anomalies that forms during winter and extend to the base of the mixed layer are sequestered beneath the shallow summer mixed layer when it reforms in late spring and are effectively insulated from the air-sea heat flux. When the mixed layer deepens again in the following autumn/early winter the anomalies may influence again the surface. This process has been named "reemergence mechanism" by Alexander and Deser and is observed over much of the North Pacific Ocean although is more effective in the west where the winter mixed layer is deeper and the seasonal cycle greater.
Stochastic atmospheric forcing
Long term sea surface temperature variation may be induced by random atmospheric forcings that are integrated and reddened into the ocean mixed layer. The stochastic climate model paradigm was proposed by Frankignoul and Hasselmann, in this model a stochastic forcing represented by the passage of storms alter the ocean mixed layer temperature via surface energy fluxes and Ekman currents and the system is damped due to the enhanced (reduced) heat loss to the atmosphere over the anomalously warm (cold) SST via turbulent energy and longwave
Longwave
In radio, longwave refers to parts of radio spectrum with relatively long wavelengths. The term is a historic one dating from the early 20th century, when the radio spectrum was considered to consist of long, medium and short wavelengths...
radiative fluxes, in the simple case of a linear negative feedback
Feedback
Feedback describes the situation when output from an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or occurrences of the same Feedback describes the situation when output from (or information about the result of) an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or...
the model can be written as:
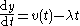
where v is the random atmospheric forcing, λ is the damping rate (positive and constant) and y is the response.
The variance spectrum of y is:
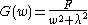
where F is the variance of the white noise forcing and w is the frequency, an implication of this equation is that at short time scales (w>>λ) the variance of the ocean temperature increase with the square of the period while at longer timescales(w<<λ, ~150 months) the damping process dominates and limits sea surface temperature anomalies so that the spectra became white.
Thus an atmospheric white noise generates SST anomalies at much longer timescales but without spectral peaks. Modeling studies suggest that this process contribute to as much as 1/3 of the PDO variability at decadal timescales.
Ocean dynamics
Several dynamic oceanic mechanisms and SST-air feedback may contribute to the observed decadal variability in the North Pacific Ocean. SST variability is stronger in the Kuroshio
Kuroshio Current
The Kuroshio is a north-flowing ocean current on the west side of the North Pacific Ocean. It is similar to the Gulf Stream in the North Atlantic and is part of the North Pacific ocean gyre...
Oyashio
Oyashio Current
, also known as Oya Siwo, Okhotsk or the Kurile current, is a cold subarctic ocean current that flows south and circulates counterclockwise in the western North Pacific Ocean. It collides with the Kuroshio Current off the eastern shore of Japan to form the North Pacific Current...
extension (KOE) region and is associated with changes in the KOE axis and strength, that generates decadal and longer time scales SST variance but without the observed magnitude of the spectral peak at ~10 years, and SST-air feedback. Remote reemergence occurs in regions of strong current such as the Kuroshio extension and the anomalies created near the Japan may reemerge the next winter in the central pacific.
- Advective resonance
Saravanan and McWilliams have demonstrated that the interaction between spatially coherent atmospheric forcing patterns and an advective ocean shows periodicities at preferred time scales when non-local advective effects dominates over the local sea surface temperature damping. This "advective resonance" mechanism may generate decadal SST variability in the Eastern North Pacific associated with the anomalous Ekman advection and surface heat flux.
- North Pacific oceanic gyre circulation
Dynamic gyre adjustments are essential to generate decadal SST
Sea surface temperature
Sea surface temperature is the water temperature close to the oceans surface. The exact meaning of surface varies according to the measurement method used, but it is between and below the sea surface. Air masses in the Earth's atmosphere are highly modified by sea surface temperatures within a...
peaks in the North Pacific, the process occurs via westward propagating oceanic Rossby waves that are forced by wind anomalies in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean. The quasigeostrophic equation for long non-dispersive Rossby Waves forced by large scale wind stress can be written as:
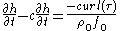
where h is the upper-layer thickness anomaly, curl(τ) is the wind stress, c is the Rossby waves speed that depends on latitudes, ρ0 is the density of sea water and f0 is the Coriolis parameter at a reference latitude. The response time scale is set by the Rossby waves speed, the location of the wind forcing and the basin width, at the latitude of the Kuroshio Extension c is 2.5 cm s−1 and the dynamic gyre adjustement timescale is ~(5)10 years if the Rossby wave was initiated in the (central)eastern Pacific Ocean.
If the wind white forcing is zonally uniform it should generate a red spectrum in which h variance increase with the period and reaches a constant amplitude at lower frequencies without decadal and interdecadal peaks, however low frequencies atmospheric circulation tends to be dominated by fixed spatial patterns so that wind forcing is not zonally uniform, if the wind forcing is zonally sinusoidal then decadal peaks occurs due to resonance of the forced basin-scale Rossby waves.
The propagation of h anomalies in the western pacific changes the KOE axis and strength and impact sst due to the anomalous geostrophic heat transport. Recent studies suggest that Rossby waves excited by the Aleutian low propagates the PDO signal from the North Pacific to the KOE through changes in the KOE axis while Rossby waves associated with the NPO
North Pacific Oscillation
The North Pacific Oscillation is a teleconnection pattern first described by Walker and Bliss and characterized by a north-south seesaw in sea level pressure over the North Pacific.Rogers, using surface atmospheric temperature from St...
propagates the North Pacific Gyre
North Pacific Gyre
The North Pacific Gyre, located in the northern Pacific Ocean, is one of the five major oceanic gyres. This gyre comprises most of the northern Pacific Ocean. It is the largest ecosystem on our planet...
oscillation signal through changes in the KOE strength.
Reconstructions and Regime shifts
The PDO index has been reconstructed using tree rings and other hydrologically sensitive proxiesProxy (climate)
In the study of past climates is known as paleoclimatology, climate proxies are preserved physical characteristics of the past that stand in for direct measurements , to enable scientists to reconstruct the climatic conditions that prevailed during much of the Earth's history...
from west North America and Asia.
MacDonald and Case reconstructed the PDO back to 993 using tree rings from California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
and Alberta
Alberta
Alberta is a province of Canada. It had an estimated population of 3.7 million in 2010 making it the most populous of Canada's three prairie provinces...
. The index shows a 50-70 year periodicity but this is a strong mode of variability only after 1800, a persistent negative phase occurred during medieval times
Medieval Warm Period
The Medieval Warm Period , Medieval Climate Optimum, or Medieval Climatic Anomaly was a time of warm climate in the North Atlantic region, that may also have been related to other climate events around the world during that time, including in China, New Zealand, and other countries lasting from...
(993-1300) which is consistent with la nina
La Niña
La Niña is a coupled ocean-atmosphere phenomenon that is the counterpart of El Niño as part of the broader El Niño-Southern Oscillation climate pattern. During a period of La Niña, the sea surface temperature across the equatorial Eastern Central Pacific Ocean will be lower than normal by 3–5 °C...
conditions reconstructed in the tropical Pacific and multi-century droughts in the South-West United States.
Several regime shifts are apparent both in the reconstructions and instrumental data, during the 20th century regime shifts associated with concurrent changes in SST
Sea surface temperature
Sea surface temperature is the water temperature close to the oceans surface. The exact meaning of surface varies according to the measurement method used, but it is between and below the sea surface. Air masses in the Earth's atmosphere are highly modified by sea surface temperatures within a...
, SLP, land precipitation and ocean cloud cover occurred in 1924/1925,1945/1946 and 1976/1977:
- 1750: PDO displays an unusually strong oscillation.
- 1924/1925: PDO changed to a "warm" phase.
- 1945/1946: The PDO changed to a "cool" phase, the pattern of this regime shift is similar to the 1970s episode with maximum amplitude in the subarctic and subtropical front but with a greater signature near the Japan while the 1970s shift was stronger near the American west coast.
- 1976/1977: PDO changed to a "warm" phase.
- 1988/1989:A weakening of the Aleutian low with associated SST changes was observed, in contrast to others regime shifts this change appears to be related to concurrent extratropical oscillation in the North Pacific and North Atlantic rather than tropical processes.
- 1997/1998: Several changes in Sea surface temperature and marine ecosystem occurred in the North Pacific after 1997/1998, in contrast to prevailing anomalies observed after the 1970s shift SST declined along the United States west coast and substantial changes in the populations of salmonSalmonSalmon is the common name for several species of fish in the family Salmonidae. Several other fish in the same family are called trout; the difference is often said to be that salmon migrate and trout are resident, but this distinction does not strictly hold true...
, anchovyAnchovyAnchovies are a family of small, common salt-water forage fish. There are 144 species in 17 genera, found in the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans. Anchovies are usually classified as an oily fish.-Description:...
and sardineSardineSardines, or pilchards, are several types of small, oily fish related to herrings, family Clupeidae. Sardines are named after the Mediterranean island of Sardinia, around which they were once abundant....
were observed, however the spatial pattern of the SST change was different with a meridional SST seesaw in the central and western Pacific that resemble a strong shift in the North Pacific Gyre Oscillation rather than the PDO structure, this pattern dominated much of the North Pacific SST variability after 1989.
Predictability
NOAANational Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration , pronounced , like "noah", is a scientific agency within the United States Department of Commerce focused on the conditions of the oceans and the atmosphere...
's forecast http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/forecasts/sstlim/for1pdo.html use a linear inverse modeling (LIM) method to predict the PDO, LIM assumes that the PDO can be separated into a linear deterministic component and a non-linear component represented by random fluctuations.
Much of the LIM PDO predictability arises from ENSO and the global trend rather than extra-tropical processes and is thus limited to ~4 season, the prediction is consistent with the seasonal footprinting mechanism in which an optimal SST structure evolve into the ENSO mature phase 6–10 months later that subsequently impact the North Pacific Ocean SST via the atmospheric bridge.
Skills in predicting decadal PDO variability could arise from taking into account the impact of the externally forced and internally generated pacific variability.
Related patterns
- ENSO tends to lead PDO/IPO cycling.
- Shifts in the IPO change the location and strength of ENSO activity. The South Pacific Convergence ZoneSouth Pacific convergence zoneThe South Pacific Convergence Zone , a reverse-oriented monsoon trough, is a band of low-level convergence, cloudiness and precipitation extending from the west Pacific warm pool south-eastwards towards French Polynesia...
moves northeast during El Niño and southwest during La Niña events. The same movement takes place during positive IPO and negative IPO phases respectively. (Folland et al., 2002) - Interdecadal temperature variations in ChinaChinaChinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
are closely related to those of the NAONorth Atlantic oscillationThe North Atlantic oscillation is a climatic phenomenon in the North Atlantic Ocean of fluctuations in the difference of atmospheric pressure at sea level between the Icelandic low and the Azores high. Through east-west oscillation motions of the Icelandic low and the Azores high, it controls the...
and the NPO. - The amplitudes of the NAONorth Atlantic oscillationThe North Atlantic oscillation is a climatic phenomenon in the North Atlantic Ocean of fluctuations in the difference of atmospheric pressure at sea level between the Icelandic low and the Azores high. Through east-west oscillation motions of the Icelandic low and the Azores high, it controls the...
and NPO increased in the 1960s and interannual variation patterns changed from 3–4 years to 8–15 years. - Sea level rise is affected when large areas of water warm and expand, or cool and contract.
See also
- California CurrentCalifornia CurrentThe California Current is a Pacific Ocean current that moves south along the western coast of North America, beginning off southern British Columbia, and ending off southern Baja California. There are five major coastal currents affiliated with upwelling zones...
- Hadley cellHadley cellThe Hadley cell, named after George Hadley, is a circulation pattern that dominates the tropical atmosphere, with rising motion near the equator, poleward flow 10–15 kilometers above the surface, descending motion in the subtropics, and equatorward flow near the surface...
- Pacific-North American teleconnection patternPacific-North American teleconnection patternThe Pacific-North American teleconnection pattern is a climatological term for a large-scale weather pattern with two modes, denoted positive and negative, and which relates the atmospheric circulation pattern over the North Pacific Ocean with the one over the North American continent.The positive...
Further reading
- Steven R. Hare and Nathan J. Mantua, 2001. An historical narrative on the Pacific Decadal Oscillation, interdecadal climate variability and ecosystem impacts, Report of a talk presented at the 20th NE Pacific Pink and Chum workshop, Seattle, WA, 22 March 2001. http://www.iphc.washington.edu/Staff/hare/html/papers/pcworkshop/pcworkshop.pdf
- Nathan J. Mantua and Steven R. Hare, 2002. The Pacific Decadal Oscillation, Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 58, p. 35–44. http://jisao.washington.edu/PNWimpacts/Publications/Pub166.pdf
- Kevin Ho, 2005. Salmon-omics: Effect of Pacific Decadal Oscillation on Alaskan Chinook Harvests and Market Price. Columbia University. http://www.columbia.edu/~kjh2103/Salmon-omics-PDO.pdf

