
Parabolic SAR
Encyclopedia
In the field of technical analysis
, Parabolic SAR (SAR - stop and reverse) is a method devised by J. Welles Wilder, Jr., to find trends in market price
s or securities
. It may be used as a trailing stop loss based on prices tending to stay within a parabolic
curve during a strong trend.
The concept draws on the idea that time
is the enemy (similar to option theory's concept of time decay), and unless a security can continue to generate more profits over time, it should be liquidated. The indicator generally works well in trending markets, but provides "whipsaws" during non-trending, sideways phases; as such, Wilder recommended establishing the strength and direction of the trend first through the use of things such as the Average Directional Index
, and then using the Parabolic SAR to trade that trend.
A parabola below the price is generally bullish, while a parabola above is generally bearish.
in the price. When the price is in an uptrend, the SAR appears below the price and converges upwards towards it. Similarly, on a downtrend, the SAR appears above the price and converges downwards.
At each step within a trend, the SAR is calculated ahead of time. That is, tomorrow's SAR value is built using data available today. The general formula used for this is:
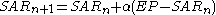
Where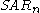 and
and 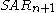 represent today's and tomorrow's SAR values, respectively.
represent today's and tomorrow's SAR values, respectively.
The extreme point,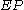 , is a record kept during each trend that represents the highest value reached by the price during the current uptrend — or lowest value during a downtrend. On each period, if a new maximum (or minimum) is observed, the EP is updated with that value.
, is a record kept during each trend that represents the highest value reached by the price during the current uptrend — or lowest value during a downtrend. On each period, if a new maximum (or minimum) is observed, the EP is updated with that value.
The value represents the acceleration factor. Usually, this is set to a value of 0.02 initially. This factor is increased by 0.02 each time a new EP is recorded. In other words, each time a new EP is observed, it will increase the acceleration factor. This will then quicken the rate at which the SAR converges towards the price. To keep it from getting too large, a maximum value for the acceleration factor is normally set at 0.20, so that it never goes beyond that. For stocks trading, it is preferable to set the acceleration factor to 0.01, in order to be less sensitive to local decreases. For commodity or currency trading, it is preferable to use a value of 0.02.
value represents the acceleration factor. Usually, this is set to a value of 0.02 initially. This factor is increased by 0.02 each time a new EP is recorded. In other words, each time a new EP is observed, it will increase the acceleration factor. This will then quicken the rate at which the SAR converges towards the price. To keep it from getting too large, a maximum value for the acceleration factor is normally set at 0.20, so that it never goes beyond that. For stocks trading, it is preferable to set the acceleration factor to 0.01, in order to be less sensitive to local decreases. For commodity or currency trading, it is preferable to use a value of 0.02.
The SAR is iteratively calculated for each new period using this recursive definition. There are, however, two special cases that will modify the SAR value:
Upon a trend switch, several things happen. The first SAR value for this new trend is set to the last EP recorded on the previous trend. The EP is then reset accordingly to this period's maximum. The acceleration factor is reset to its initial value of 0.02.
Technical analysis
In finance, technical analysis is security analysis discipline for forecasting the direction of prices through the study of past market data, primarily price and volume. Behavioral economics and quantitative analysis incorporate technical analysis, which being an aspect of active management stands...
, Parabolic SAR (SAR - stop and reverse) is a method devised by J. Welles Wilder, Jr., to find trends in market price
Market price
In economics, market price is the economic price for which a good or service is offered in the marketplace. It is of interest mainly in the study of microeconomics...
s or securities
Security (finance)
A security is generally a fungible, negotiable financial instrument representing financial value. Securities are broadly categorized into:* debt securities ,* equity securities, e.g., common stocks; and,...
. It may be used as a trailing stop loss based on prices tending to stay within a parabolic
Parabola
In mathematics, the parabola is a conic section, the intersection of a right circular conical surface and a plane parallel to a generating straight line of that surface...
curve during a strong trend.
The concept draws on the idea that time
Time
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
is the enemy (similar to option theory's concept of time decay), and unless a security can continue to generate more profits over time, it should be liquidated. The indicator generally works well in trending markets, but provides "whipsaws" during non-trending, sideways phases; as such, Wilder recommended establishing the strength and direction of the trend first through the use of things such as the Average Directional Index
Average Directional Index
The Average Directional Index was developed in 1978 by J. Welles Wilder as an indicator of trend strength in a series of prices of a financial instrument...
, and then using the Parabolic SAR to trade that trend.
A parabola below the price is generally bullish, while a parabola above is generally bearish.
Construction
The Parabolic SAR is calculated almost independently for each trendMarket trends
A market trend is a putative tendency of a financial market to move in a particular direction over time. These trends are classified as secular for long time frames, primary for medium time frames, and secondary for short time frames...
in the price. When the price is in an uptrend, the SAR appears below the price and converges upwards towards it. Similarly, on a downtrend, the SAR appears above the price and converges downwards.
At each step within a trend, the SAR is calculated ahead of time. That is, tomorrow's SAR value is built using data available today. The general formula used for this is:
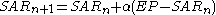
Where
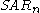 and
and 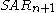 represent today's and tomorrow's SAR values, respectively.
represent today's and tomorrow's SAR values, respectively.The extreme point,
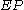 , is a record kept during each trend that represents the highest value reached by the price during the current uptrend — or lowest value during a downtrend. On each period, if a new maximum (or minimum) is observed, the EP is updated with that value.
, is a record kept during each trend that represents the highest value reached by the price during the current uptrend — or lowest value during a downtrend. On each period, if a new maximum (or minimum) is observed, the EP is updated with that value.The
 value represents the acceleration factor. Usually, this is set to a value of 0.02 initially. This factor is increased by 0.02 each time a new EP is recorded. In other words, each time a new EP is observed, it will increase the acceleration factor. This will then quicken the rate at which the SAR converges towards the price. To keep it from getting too large, a maximum value for the acceleration factor is normally set at 0.20, so that it never goes beyond that. For stocks trading, it is preferable to set the acceleration factor to 0.01, in order to be less sensitive to local decreases. For commodity or currency trading, it is preferable to use a value of 0.02.
value represents the acceleration factor. Usually, this is set to a value of 0.02 initially. This factor is increased by 0.02 each time a new EP is recorded. In other words, each time a new EP is observed, it will increase the acceleration factor. This will then quicken the rate at which the SAR converges towards the price. To keep it from getting too large, a maximum value for the acceleration factor is normally set at 0.20, so that it never goes beyond that. For stocks trading, it is preferable to set the acceleration factor to 0.01, in order to be less sensitive to local decreases. For commodity or currency trading, it is preferable to use a value of 0.02.The SAR is iteratively calculated for each new period using this recursive definition. There are, however, two special cases that will modify the SAR value:
- If tomorrow's SAR value lies within (or beyond) today's or yesterday's price range, the SAR must be set to the closest price bound. For example, if in an uptrend, the new SAR value is calculated and it results to be greater than today's or yesterday's lowest price, the SAR must be set equal to that lower boundary.
- If tomorrow's SAR value lies within (or beyond) tomorrow's price range, a new trend direction is then signaled, and the SAR must "switch sides."
Upon a trend switch, several things happen. The first SAR value for this new trend is set to the last EP recorded on the previous trend. The EP is then reset accordingly to this period's maximum. The acceleration factor is reset to its initial value of 0.02.

