
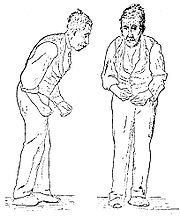
Parkinsonian gait
Encyclopedia
Gait
Gait is the pattern of movement of the limbs of animals, including humans, during locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on speed, terrain, the need to maneuver, and energetic efficiency...
exhibited by patients suffering from Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease is a degenerative disorder of the central nervous system...
(PD). This disorder
Gait abnormality
Gait abnormality is a deviation from normal walking . Watching a patient walk is the most important part of the neurological examination. Normal gait requires that many systems, including strength, sensation and coordination, function in an integrated fashion...
is caused by a deficiency
Deficiency (medicine)
In medicine, a deficiency is a lack or shortage of a functional entity, by less than normal or necessary supply or function.-Nutrients:Malnutrition can cause various effects by deficiency of one or more nutrients...
of dopamine
Dopamine
Dopamine is a catecholamine neurotransmitter present in a wide variety of animals, including both vertebrates and invertebrates. In the brain, this substituted phenethylamine functions as a neurotransmitter, activating the five known types of dopamine receptors—D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5—and their...
in the basal ganglia
Basal ganglia
The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei of varied origin in the brains of vertebrates that act as a cohesive functional unit. They are situated at the base of the forebrain and are strongly connected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus and other brain areas...
circuit leading to motor
Motor system
The motor system is the part of the central nervous system that is involved with movement. It consists of the pyramidal and extrapyramidal system....
deficits. Gait is one of the most affected motor characteristics of this disorder although symptoms of Parkinson's disease
Signs and symptoms of Parkinson's disease
Signs and symptoms of Parkinson's disease are varied. Parkinson's disease affects movement, producing motor symptoms. Non-motor symptoms, which include autonomic dysfunction, cognitive and neurobehavioral problems, and sensory and sleep difficulties, are also common.-Motor symptoms:Four motor...
are varied.
Parkinsonian gait is characterized by small shuffling steps
Walking
Walking is one of the main gaits of locomotion among legged animals, and is typically slower than running and other gaits. Walking is defined by an 'inverted pendulum' gait in which the body vaults over the stiff limb or limbs with each step...
and a general slowness of movement (hypokinesia
Hypokinesia
Hypokinesia refers to decreased bodily movement. It is associated with basal ganglia diseases , mental health disorders and prolonged inactivity due to illness, amongst other diseases.Hypokinesia describes a spectrum of disorders:...
), or even the total loss of movement (akinesia) in the extreme cases. Patients with PD demonstrate reduced stride
Gait
Gait is the pattern of movement of the limbs of animals, including humans, during locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on speed, terrain, the need to maneuver, and energetic efficiency...
length and walking speed during free ambulation while double support duration and cadence
Cadence (gait)
Cadence in sports involving running is the total number of 'revolutions per minute' , or number of full cycles taken within a minute, by the pair of feet, and is used as a measure of athletic performance. It is very similar in respect to cadence in cycling, however it is often overlooked in its...
rate are increased. The patient has difficulty starting, but also has difficulty stopping after starting. This is due to muscle hypertonicity.
Abnormal gait characteristics
Patients with Parkinson's disease exhibit gait characteristics that are markedly different from normal gait. While the list of abnormal gait characteristics given below is the most discussed, it is certainly not exhaustive.Heel to toe characteristics
Whereas in normal gait, the heelHeel
In human anatomy, the heel is the prominence at the posterior end of the foot. It is based on the projection of one bone, the calcaneus or heel bone, behind the articulation of the bones of the lower leg.- Human anatomy :...
strikes the ground before the toe
Toe
Toes are the digits of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being digitigrade. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being plantigrade; unguligrade animals are those that walk on hooves at the tips of...
s (also called heel-to-toe walking), in Parkinsonian gait, motion is characterised by flat foot strike (where the entire foot is placed on the ground at the same time) or less often and in the more advanced stages of the disease by toe-to-heel walking (where the toes touch the ground the before the heel). In addition, PD patients have reduced foot lifting during the swing phase of gait, which produces smaller clearance between the toes and the ground.
Patients with Parkinson's disease have reduced impact at heel strike and this mechanism has been found to be related to the disease severity with impact decreasing as the disease progresses. Also, Parkinson patients show a trend towards higher relative loads in the forefoot
Toe
Toes are the digits of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being digitigrade. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being plantigrade; unguligrade animals are those that walk on hooves at the tips of...
regions combined with a load shift towards medial foot areas. This load shift is believed to help in compensating for postural imbalance
Balance disorder
A balance disorder is a disturbance that causes an individual to feel unsteady, for example when standing or walking. It may be accompanied by feelings of giddiness or wooziness, or having a sensation of movement, spinning, or floating...
. The intra-individual variability in foot strike pattern is found to be surprisingly lower in PD patients compared with normal people.
Vertical ground reaction force
In normal gait, the vertical ground reaction forceGround reaction force
In physics, and in particular in biomechanics, the ground reaction force is the force exerted by the ground on a body in contact with it.For example, a person standing on the ground exerts a contact force on it and at the same time an equal and opposite ground reaction force is exerted by the...
(GRF) plot has two peaks – one when the foot strikes the ground and the second peak is caused by push-off force from the ground. The shape of the vertical GRF signal is abnormal in PD. In the earlier stages of the disease, reduced forces (or peak heights) are found for heel contact and the push-off phase resembling that of elderly subjects. In the more advanced stages of the disorder where gait is characterized by small shuffling steps, PD patients show only one narrow peak in the vertical GRF signal.
Falls and freezing of gait
Falls and freezing of gait are two episodic phenomena that are common in Parkinsonian gait. Falls and freezing of gait in PD are generally thought to be closely intertwined for several reasons, most importantly : both symptoms are common in the advanced stages of the disease and are less common in the earlier stages, with freezing of gait leading to falls in many instances. Both symptoms often respond poorly and sometimes paradoxically to treatment with dopaminergic medication, perhaps pointing to a common underlying pathophysiologyPathophysiology
Pathophysiology is the study of the changes of normal mechanical, physical, and biochemical functions, either caused by a disease, or resulting from an abnormal syndrome...
.
Freezing of Gait:
Freezing of Gait (FOG) is typically a transient episode – lasting less than a minute, in which gait is halted and the patient complains that his/her feet are glued to the ground. When the patient overcomes the block, walking can be performed relatively smoothly. The most common form of FOG is 'start hesitation' (which happens when the patient wants to start walking) followed in frequency by 'turning hesitation' FOG can also be experienced in narrow or tight quarters such as a doorway, whilst adjusting one’s steps when reaching a destination, and in stressful situations such as when the telephone or the doorbell rings or when the elevator door opens. As the disease progresses, FOG can appear spontaneously even in an open runway space.
Falls:
Falls, like FOG are rare in the earlier stages of the disorder and becomes more frequent as the disease progresses. Falls result mainly due to sudden changes in posture, in particular turning movements of the trunk, or attempts to perform more than one activity simultaneously with walking or balancing. Falls are also common during transfers, such as rising from a chair or bed. PD patients fall mostly forward (45% of all falls) and about 20% fall laterally.
Postural sway
PosturalHuman position
Human positions refers to the different positions that the human body can take.There are several synonyms that refer to the human position, often used interchangeably, but having specific flavors....
instability in upright stance is common in end-stage PD and compromises the ability to maintain balance during everyday tasks such as walking
Walking
Walking is one of the main gaits of locomotion among legged animals, and is typically slower than running and other gaits. Walking is defined by an 'inverted pendulum' gait in which the body vaults over the stiff limb or limbs with each step...
, turning and standing up from sitting
Sitting
Sitting is a rest position supported by the buttocks or thighs where the torso is more or less upright.- Sitting on the floor :The most common way of sitting on the floor involves bending the knees...
. An inability to adequately balance the body's center of mass
Center of mass
In physics, the center of mass or barycenter of a system is the average location of all of its mass. In the case of a rigid body, the position of the center of mass is fixed in relation to the body...
over the base of support combined with inflexibility in body movements (due to increased rigidity) causes patients with advanced PD to fall. Whereas postural sway in normal stance usually increases in patients with balance disorders arising from stroke
Stroke
A stroke, previously known medically as a cerebrovascular accident , is the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This can be due to ischemia caused by blockage , or a hemorrhage...
, head injury and cerebellar ataxia
Ataxia
Ataxia is a neurological sign and symptom that consists of gross lack of coordination of muscle movements. Ataxia is a non-specific clinical manifestation implying dysfunction of the parts of the nervous system that coordinate movement, such as the cerebellum...
it is often reduced in patients with PD. The reason for this because in PD the problem appears to be a lack of flexibility in shifting postural responses. This inflexibility increases the tendency to fall in these patients.
Electromyographic studies
ElectromyographicElectromyography
Electromyography is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph, to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyograph detects the electrical potential generated by muscle...
(EMG) studies of the leg muscles in PD patients have shown an extreme reduction in the activation of the tibialis anterior muscle
Tibialis anterior muscle
In human anatomy, the tibialis anterior is a muscle that originates in the upper two-thirds of the lateral surface of the tibia and inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. Its acts to dorsiflex and invert the foot. This muscle is mostly located near the shin.It is...
in the early stance and in the early and late swing phases , and a reduction in triceps surae muscle
Triceps surae muscle
The triceps surae is a pair of muscles located at the calf - the gastrocnemius and the soleus...
bursting at push-off. The quadriceps and hamstring
Hamstring
In human anatomy, the hamstring refers to any one of the three posterior thigh muscles, or to the tendons that make up the borders of the space behind the knee. In modern anatomical contexts, however, they usually refer to the posterior thigh muscles, or the tendons of the semitendinosus, the...
muscles on the other hand, show prolonged activation in the stance phase of gait. This implies that PD patients have higher passive stiffness of ankle joints, show larger background EMG activity and more co-contraction of leg muscles in stance. Stiffer joints lead to abnormal postural sway in the PD patients.
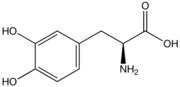
Drugs
Blood-brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier is a separation of circulating blood and the brain extracellular fluid in the central nervous system . It occurs along all capillaries and consists of tight junctions around the capillaries that do not exist in normal circulation. Endothelial cells restrict the diffusion...
as a prodrug and is decarboxylated in the brain to the neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
dopamine by the enzyme aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase. In this way, L-DOPA can replace the some of the deficit in dopamine seen in Parkinsonism. Due to feedback inhibition, L-dopa results in a reduction in the endogenous formation of L-dopa, and so eventually becomes counterproductive.
Effect on gait parameters:
The stride length and the kinematic
Kinematics
Kinematics is the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of bodies and systems without consideration of the forces that cause the motion....
parameters (swing velocity, peak velocity) related to the energy are Dopa-sensitive. Temporal parameters (stride and swing duration, stride duration variability), related to rhythm, are Dopa-resistant.
Effect on falls and freezing of gait:
Levodopa treatment decreases the frequency and the akinetic type of FOG, with a tendency
for shorter FOG episodes. Results indicate that this is primarily because L-dopa increases the threshold for FOG to occur but the fundamental pathophysiology for FOG did not change. It has also been shown that other dopamine agonists like ropinirole
Ropinirole
Ropinirole is a non-ergoline dopamine agonist. It is manufactured by GlaxoSmithKline , Cipla and Sun Pharmaceutical. It is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease...
, pramipexole
Pramipexole
Pramipexole is a non-ergoline dopamine agonist indicated for treating early-stage Parkinson's disease and restless legs syndrome...
and pergolide
Pergolide
Pergolide is an ergoline-based dopamine receptor agonist used in some countries for the treatment of Parkinson's disease....
that have a strong affinity to D2
Dopamine receptor D2
Dopamine receptor D2, also known as D2R, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the DRD2 gene.- Function :This gene encodes the D2 subtype of the dopamine receptor. This G protein-coupled receptor inhibits adenylyl cyclase activity...
receptors (as opposed to L-dopa which has a strong D1
Dopamine receptor D1
Dopamine receptor D1, also known as DRD1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD1 gene.- Function :This gene encodes the D1 subtype of the dopamine receptor. The D1 subtype is the most abundant dopamine receptor in the central nervous system. This G-protein-coupled receptor stimulates...
receptor affinity) increase the frequency of FOGs.
Effects on postural sway:
Parkinson’s disease have abnormal postural sway in stance and treatment with levodopa increases postural sway abnormalities. During movement, it has been shown that early autonomic postural disturbances are only partially corrected while the later occurring postural corrections are not affected by dopamine. These results indicate that non-dopaminergic lesion
Lesion
A lesion is any abnormality in the tissue of an organism , usually caused by disease or trauma. Lesion is derived from the Latin word laesio which means injury.- Types :...
s play a role in postural imbalance in PD patients.
Auditory and visual cues
Basal gangliaBasal ganglia
The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei of varied origin in the brains of vertebrates that act as a cohesive functional unit. They are situated at the base of the forebrain and are strongly connected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus and other brain areas...
dysfunctioning in PD, causes it to stop acting as an internal cue for gait in Parkinson's patients. Hence various external sensory cues like auditory and visual cues have been developed to bypass the basal ganglia's cueing functions.
Visual cues:
The visual
Visual system
The visual system is the part of the central nervous system which enables organisms to process visual detail, as well as enabling several non-image forming photoresponse functions. It interprets information from visible light to build a representation of the surrounding world...
cues are commonly transverse lines or rods on the floor (floor markers).Such cues have been shown to improve stride length and velocity in Parkinsonian gait by susbtituting kinaesthetic feedback with visual feedback for regulating movement amplitude. In addition gait initiation has been shown to be significantly improved in PD patients compared with auditory cues. Virtual reality glasses have also been developed recently to aid walking in PD patients.
Auditory cues:
The auditory
Auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing.- Outer ear :The folds of cartilage surrounding the ear canal are called the pinna...
cues are commonly rhythm
Rhythm
Rhythm may be generally defined as a "movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions." This general meaning of regular recurrence or pattern in time may be applied to a wide variety of cyclical natural phenomena having a periodicity or...
ic cues generated by a metronome
Metronome
A metronome is any device that produces regular, metrical ticks — settable in beats per minute. These ticks represent a fixed, regular aural pulse; some metronomes also include synchronized visual motion...
or equivalent, sometimes embedded in music, set at or slightly above the subject’s usual cadence. Rhythmic auditory cues have been associated with increases in velocity and cadence and sometimes stride after gait has been initiated. Auditory cues have been shown to have little or no effect in gait initiation.
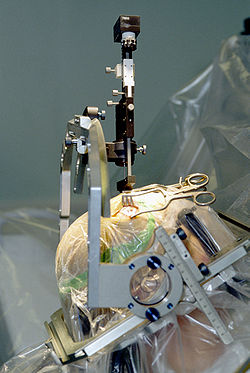
Deep brain stimulation
Deep brain stimulation
Deep brain stimulation is a surgical treatment involving the implantation of a medical device called a brain pacemaker, which sends electrical impulses to specific parts of the brain...
(DBS) in the subthalamic nucleus
Subthalamic nucleus
The subthalamic nucleus is a small lens-shaped nucleus in the brain where it is, from a functional point of view, part of the basal ganglia system. Anatomically, it is the major part of subthalamus. As suggested by its name, the subthalamic nucleus is located ventral to the thalamus. It is also...
(STN) and the globus pallidus
Globus pallidus
The globus pallidus also known as paleostriatum, is a sub-cortical structure of the brain. Topographically, it is part of the telencephalon, but retains close functional ties with the subthalamus - both of which are part of the extrapyramidal motor system...
have been shown to have positive effects on gait abnormalities presented by Parkinson's Disease patients. DBS in the STN has been reported to reduce freezing of gait significantly at 1 and 2 year follow up. Contradictory results have been reported on the effects on DBS on postural stability The results seem to be highly location specific. The studies which do report positive effects suggest that the effectiveness of DBS in improving postural stability is due to its ability to affect non-dopaminergic pathways (in addition to dopaminergic pathways) which are believed to cause postural sway in PD patients.
Other treatments strategies
Attention strategies:By consciously paying more attention to walking and rehearsing each step before actually making it, PD patients have shown to improve their gait. Sometimes, a companion walking alongside reminds the patient to concentrate on gait or they create a visual cue to step over by putting a foot in front of the person with PD over which the person must step. This causes the patient to focus their attention on the stepping action, thus making this a voluntary action and hence bypassing the faulty basal ganglia pathway (which is responsible for involuntary actions like walking). Avoidance of dual tasks that require motor attention or cognitive
Cognition
In science, cognition refers to mental processes. These processes include attention, remembering, producing and understanding language, solving problems, and making decisions. Cognition is studied in various disciplines such as psychology, philosophy, linguistics, and computer science...
attention has also been shown to normalize gait in the PD patients.
Exercise:
Physical therapy
Physical therapy
Physical therapy , often abbreviated PT, is a health care profession. Physical therapy is concerned with identifying and maximizing quality of life and movement potential within the spheres of promotion, prevention, diagnosis, treatment/intervention,and rehabilitation...
and exercise have been shown to have positive effects on gait parameters in PD patients.
Physiotherapist's may help improve gait by creating training programs to lengthen a patient's stride length, broaden the base of support, improve the heel-toe gait
Gait
Gait is the pattern of movement of the limbs of animals, including humans, during locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on speed, terrain, the need to maneuver, and energetic efficiency...
pattern, straighten out a patient's posture, and increase arm swing patterns.
Research has shown gait training combining an overhead harness with walking on a treadmill has shown to improve both walking speed and stride length. The harness assists the patient in maintaining an upright posture by eliminating the need to use a mobility aid, a practice which normally promotes a forward flexed posture. It is believed the activation of the central pattern generator
Central pattern generator
Central pattern generators are neural networks that produce rhythmic patterned outputs without sensory feedback. CPGs have been shown to produce rhythmic outputs resembling normal "rhythmic motor pattern production" even in isolation from motor and sensory feedback from limbs and other muscle...
leads to the improvement in gait pattern.
Improving trunk flexibility, along with strengthening of the core muscles and lower extremities has been associated with increased balance and an improvement in gait pattern. Aerobic exercises such as tandem bicycling and water aerobics are also crucial in improving strength and overall balance. Due to PD’s progressive nature it is important to sustain an exercise routine to maintain its’ benefits.
Strategies such as using a vertical walking pole can also help to improve upright postural alignment. The therapist may also use tiles or footprints on the ground to improve foot placement and widen the patient's base of support. Creative visualization
Creative Visualization
Creative visualization refers to the practice of seeking to affect the outer world via changing one's thoughts. Creative Visualization is the basic technique underlying positive thinking and is frequently used by athletes to enhance their performance. The concept originally arose in the US with...
of walking with a more normalized gait pattern, and mentally rehearsing the desired movement has also shown to be affective.
The patient should also be challenged by walking on a variety of surfaces such as tile, carpet, grass, or foamed surfaces will also benefit the individual’s progress towards normalizing their gait pattern.
Comparison with other gait disorders
Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (SAE), also called lower-body parkinsonism, and cerebral ataxiaAtaxia
Ataxia is a neurological sign and symptom that consists of gross lack of coordination of muscle movements. Ataxia is a non-specific clinical manifestation implying dysfunction of the parts of the nervous system that coordinate movement, such as the cerebellum...
are two other gait disorders whose symptoms seem to closely resemble that of Parkinson's. However, through regression analysis
Regression analysis
In statistics, regression analysis includes many techniques for modeling and analyzing several variables, when the focus is on the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables...
studies have revealed that in Parkinson's, increasing the velocity
Velocity
In physics, velocity is speed in a given direction. Speed describes only how fast an object is moving, whereas velocity gives both the speed and direction of the object's motion. To have a constant velocity, an object must have a constant speed and motion in a constant direction. Constant ...
of walking changes the stride length linear
Linear
In mathematics, a linear map or function f is a function which satisfies the following two properties:* Additivity : f = f + f...
ly (which resembles that of controls). However in SAE and cerebellar ataxia stride length had a disproportionate contribution to increasing velocity, indicating that SAE and cerebellar ataxia have common underlying mechanisms different from those of Parkinson's.
Socio-economic impact
Mobility issues associated with falls and freezing of gait have a devastating impact in the lives of PD patients. Fear of falling in itself can have an incapacitating effect in PD patients and can result in social seclusion leaving patients largely isolated leading to depression. Immobility can also lead to osteoporosisOsteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease of bones that leads to an increased risk of fracture. In osteoporosis the bone mineral density is reduced, bone microarchitecture is deteriorating, and the amount and variety of proteins in bone is altered...
which in-turn facilitates future fracture development. This then becomes a vicious circle with falls leading to immobility and immobility facilitating future falls. Hip fracture
Fracture
A fracture is the separation of an object or material into two, or more, pieces under the action of stress.The word fracture is often applied to bones of living creatures , or to crystals or crystalline materials, such as gemstones or metal...
s from falls are the most common form of fracture among PD patients. Fractures increase treatment costs associated with health care expenditures in PD.

