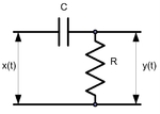
Passive differentiator circuit
Encyclopedia
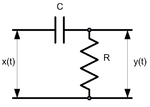
High-pass filter
A high-pass filter is a device that passes high frequencies and attenuates frequencies lower than its cutoff frequency. A high-pass filter is usually modeled as a linear time-invariant system...
.
Transfer function
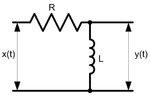
The analysis here is for the capacitive circuit in Figure 1. The inductive case in Figure 2 can be handled in a similar way.The transfer function
Transfer function
A transfer function is a mathematical representation, in terms of spatial or temporal frequency, of the relation between the input and output of a linear time-invariant system. With optical imaging devices, for example, it is the Fourier transform of the point spread function i.e...
shows the dependence of the network gain on the signal frequency for sinusoidal signals.
According to Ohm's law
Ohm's law
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points...
,
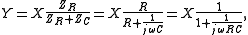
where
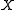 and
and 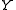 are input and output signals' amplitudes respectively, and
are input and output signals' amplitudes respectively, and 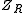 and
and 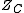 are the resistor's
are the resistor'sResistor
A linear resistor is a linear, passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.The current through a resistor is in direct proportion to the voltage across the resistor's terminals. Thus, the ratio of the voltage applied across a resistor's...
and capacitor's
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
s.
Therefore, the complex transfer function is
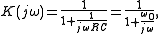
where
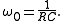
The amplitude transfer function
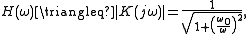
and the phase transfer function
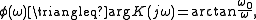
which are both shown in Figure 3.
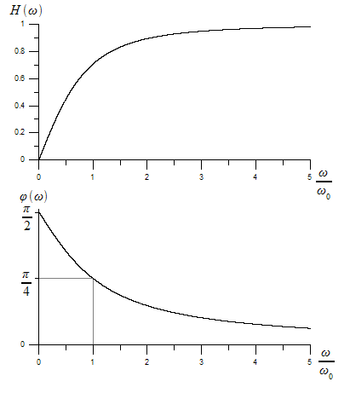
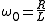 ).
).Impulse response
The circuit's impulse responseImpulse response
In signal processing, the impulse response, or impulse response function , of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an impulse. More generally, an impulse response refers to the reaction of any dynamic system in response to some external change...
, which is shown in Figure 4, can be derived as an inverse Laplace transform of the complex transfer function:
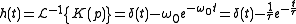
where
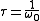 is a time constant, and
is a time constant, and 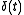 is a Dirac delta function.
is a Dirac delta function.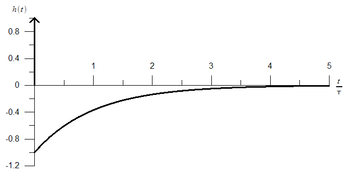
Applications
A passive differentiator circuit is one of the basic electronic circuitElectronic circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow...
s, being widely used in circuit analysis based on the equivalent circuit
Equivalent circuit
In electrical engineering and science, an equivalent circuit refers to a theoretical circuit that retains all of the electrical characteristics of a given circuit. Often, an equivalent circuit is sought that is the simplest form of a more complex circuit in order to aid analysis. In its most common...
method.

