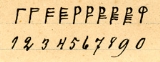
Pentimal system
Encyclopedia
The pentimal system is a notation for presenting numbers, usually by inscribing in wood or stone. The notation has been used in Scandinavia
, usually in conjunction to runes.
The notation is similar to the older Roman numerals
for numbers up to 9 (I - VIIII). Unlike the Roman notation, the notches are placed vertically on the stem or stav of the rune. The number 4 is represented by four horizontal lines on the stem, 5 is represented by what looks like an inverted letter U
. 10 is represented by two U's opposing each other. Numbers up to 19, or even 20, can be represented by a combination of I's and U's, just like the Roman numerals are represented by combinations of I's and V's. (A Roman 10 is represented by two V's opposing each other).
The widest use of the notation is in presenting the Golden Numbers
, 1 - 19 on Runic calendar
s . The numbers are commonly found in Modern Age
and possibly Early Modern Age calendar sticks. It is unknown if they were in use in the Middle Ages
, let alone in the Viking Age
. On older runic calendars, a different notation for representing the Golden Numbers was used; the 16 runes of Younger Futhark
represented the numbers from 1 to 16 and three ad hoc runes were used for the numbers 17 to 19. For example, the Computus Runicus
manuscript, originally from 1328, but collected and published by the Dane Ole Worm
(1588-1654), uses this futhark notation, and not the pentadic numerals under discussion here.
Most runic texts, including the Viking age runestones, do not use any numeral system
; instead, numbers are simply spelled out.
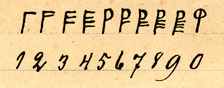 In some peculiar instances runic numbers have been used as numeral
In some peculiar instances runic numbers have been used as numeral
s in a base ten positional system
, replacing the Arabic numerals. It is unknown if this use existed before the 19th century.
The oldest authenticated use of this notation is in the notes of an 18-year-old journeyman tailor, Edward Larsson, that are dated to 1885 in pentimal runes. A copy of the note was first published by the Institute for Dialectology, Onomastics and Folklore Research in Umeå
in 2004.
This positional notation however appears on two unrelated sets of rune stones allegedly discovered in North America
. The first is the Kensington Runestone
found in 1898, the second are the three Spirit Pond runestones
found in 1971. All refer to pre-Columbian Norse exploration of the Americas.
The authors of the North American rune stones do not seem to understand the positional notation or the concept of zero
. The rune for 10 is used interchangeably for 0, 10
, and <1,0>
with little consistency. The inscription stone from Spirit Pond contains the sequences ahr:011 and ahr:00, which have been read as year 1011 and year 1010 respectively. It is unclear if the notation can represent all numbers unambiguously; for example, it may not be possible to distinguish 1010 from 100.
The use of this otherwise unknown numeral system has been seen as evidence that the North American rune stones are hoax
es.
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
, usually in conjunction to runes.
The notation is similar to the older Roman numerals
Roman numerals
The numeral system of ancient Rome, or Roman numerals, uses combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet to signify values. The numbers 1 to 10 can be expressed in Roman numerals as:...
for numbers up to 9 (I - VIIII). Unlike the Roman notation, the notches are placed vertically on the stem or stav of the rune. The number 4 is represented by four horizontal lines on the stem, 5 is represented by what looks like an inverted letter U
U
U is the twenty-first letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The letter U ultimately comes from the Semitic letter Waw by way of the letter Y. See the letter Y for details....
. 10 is represented by two U's opposing each other. Numbers up to 19, or even 20, can be represented by a combination of I's and U's, just like the Roman numerals are represented by combinations of I's and V's. (A Roman 10 is represented by two V's opposing each other).
The widest use of the notation is in presenting the Golden Numbers
Golden numbers
A golden number is a number assigned to each year in sequence to indicate the year's position in a 19-year Metonic cycle. They are used in the computus and also in the Runic calendar. The golden number of any Julian or Gregorian calendar year can be calculated by dividing the year by 19, taking...
, 1 - 19 on Runic calendar
Runic calendar
A Runic calendar is a perpetual calendar based on the 19 year long Metonic cycle of the Moon. Runic calendars were written on parchment or carved onto staves of wood, bone, or horn. The oldest one known, and the only one from the Middle Ages, is the Nyköping staff, believed to date from the 13th...
s . The numbers are commonly found in Modern Age
Modern Age
Modern Age is an American conservative academic quarterly journal, founded in 1957 by Russell Kirk in close collaboration with Henry Regnery...
and possibly Early Modern Age calendar sticks. It is unknown if they were in use in the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
, let alone in the Viking Age
Viking Age
Viking Age is the term for the period in European history, especially Northern European and Scandinavian history, spanning the late 8th to 11th centuries. Scandinavian Vikings explored Europe by its oceans and rivers through trade and warfare. The Vikings also reached Iceland, Greenland,...
. On older runic calendars, a different notation for representing the Golden Numbers was used; the 16 runes of Younger Futhark
Younger Futhark
The Younger Futhark, also called Scandinavian runes, is a runic alphabet, a reduced form of the Elder Futhark, consisting of only 16 characters, in use from ca. 800 CE...
represented the numbers from 1 to 16 and three ad hoc runes were used for the numbers 17 to 19. For example, the Computus Runicus
Computus Runicus
The Computus Runicus refers to a runic calendar produced in 1328 and found on the Swedish island of Gotland. A transcription/description of the text - called Computus Runicus - was published in 1626 by the Danish physician and antiquarian Ole Worm .-References:...
manuscript, originally from 1328, but collected and published by the Dane Ole Worm
Ole Worm
Ole Worm , who often went by the Latinized form of his name Olaus Wormius, was a Danish physician and antiquary.-Life:...
(1588-1654), uses this futhark notation, and not the pentadic numerals under discussion here.
Most runic texts, including the Viking age runestones, do not use any numeral system
Numeral system
A numeral system is a writing system for expressing numbers, that is a mathematical notation for representing numbers of a given set, using graphemes or symbols in a consistent manner....
; instead, numbers are simply spelled out.
Positional notation
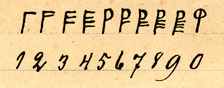
Numeral system
A numeral system is a writing system for expressing numbers, that is a mathematical notation for representing numbers of a given set, using graphemes or symbols in a consistent manner....
s in a base ten positional system
Positional notation
Positional notation or place-value notation is a method of representing or encoding numbers. Positional notation is distinguished from other notations for its use of the same symbol for the different orders of magnitude...
, replacing the Arabic numerals. It is unknown if this use existed before the 19th century.
The oldest authenticated use of this notation is in the notes of an 18-year-old journeyman tailor, Edward Larsson, that are dated to 1885 in pentimal runes. A copy of the note was first published by the Institute for Dialectology, Onomastics and Folklore Research in Umeå
Institute for Dialectology, Onomastics and Folklore Research in Umeå
DAUM, the Institute for Dialectology, Onomastics and Folklore Research in Umeå, is a Swedish governmental archive bureau which collects, preserves, works up and provides information about dialects, place names, folklore culture and local history. DAUM is part of the Swedish Institute for Language...
in 2004.
This positional notation however appears on two unrelated sets of rune stones allegedly discovered in North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
. The first is the Kensington Runestone
Kensington Runestone
The Kensington Runestone is a 200-pound slab of greywacke covered in runes on its face and side which, if genuine, would suggest that Scandinavian explorers reached the middle of North America in the 14th century. It was found in 1898 in the largely rural township of Solem, Douglas County,...
found in 1898, the second are the three Spirit Pond runestones
Spirit Pond runestones
The Spirit Pond runestones are three stones with runic inscriptions, allegedly found at Spirit Pond in Phippsburg, Maine in 1971 by a Walter J. Elliott, Jr., a carpenter born in Bath, Maine. The stones, currently housed at the Maine State Museum, are widely dismissed as a hoax or a fraud...
found in 1971. All refer to pre-Columbian Norse exploration of the Americas.
The authors of the North American rune stones do not seem to understand the positional notation or the concept of zero
0 (number)
0 is both a numberand the numerical digit used to represent that number in numerals.It fulfills a central role in mathematics as the additive identity of the integers, real numbers, and many other algebraic structures. As a digit, 0 is used as a placeholder in place value systems...
. The rune for 10 is used interchangeably for 0, 10
10 (number)
10 is an even natural number following 9 and preceding 11.-In mathematics:Ten is a composite number, its proper divisors being , and...
, and <1,0>
Tuple
In mathematics and computer science, a tuple is an ordered list of elements. In set theory, an n-tuple is a sequence of n elements, where n is a positive integer. There is also one 0-tuple, an empty sequence. An n-tuple is defined inductively using the construction of an ordered pair...
with little consistency. The inscription stone from Spirit Pond contains the sequences ahr:011 and ahr:00, which have been read as year 1011 and year 1010 respectively. It is unclear if the notation can represent all numbers unambiguously; for example, it may not be possible to distinguish 1010 from 100.
The use of this otherwise unknown numeral system has been seen as evidence that the North American rune stones are hoax
Hoax
A hoax is a deliberately fabricated falsehood made to masquerade as truth. It is distinguishable from errors in observation or judgment, or rumors, urban legends, pseudosciences or April Fools' Day events that are passed along in good faith by believers or as jokes.-Definition:The British...
es.

