
Periodic summation
Encyclopedia
In signal processing
, any periodic function
 with period
with period  can be represented by a summation of an infinite number of instances of an aperiodic function,
can be represented by a summation of an infinite number of instances of an aperiodic function, 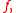 that are offset by integer multiples of
that are offset by integer multiples of  This representation is called periodic summation:
This representation is called periodic summation:

When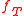 is alternatively represented as a complex Fourier series
is alternatively represented as a complex Fourier series
, the Fourier coefficients are proportional to the values (or "samples") of the continuous Fourier transform
of at intervals of
at intervals of  That identity is known as the Poisson summation formula
That identity is known as the Poisson summation formula
.
domain
 then one can write
then one can write
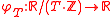

instead. The arguments of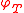 are equivalence classes of real number
are equivalence classes of real number
s that share the same fractional part
when divided by .
.
Signal processing
Signal processing is an area of systems engineering, electrical engineering and applied mathematics that deals with operations on or analysis of signals, in either discrete or continuous time...
, any periodic function
Periodic function
In mathematics, a periodic function is a function that repeats its values in regular intervals or periods. The most important examples are the trigonometric functions, which repeat over intervals of length 2π radians. Periodic functions are used throughout science to describe oscillations,...
 with period
with period  can be represented by a summation of an infinite number of instances of an aperiodic function,
can be represented by a summation of an infinite number of instances of an aperiodic function, 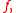 that are offset by integer multiples of
that are offset by integer multiples of  This representation is called periodic summation:
This representation is called periodic summation:
When
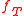 is alternatively represented as a complex Fourier series
is alternatively represented as a complex Fourier seriesFourier series
In mathematics, a Fourier series decomposes periodic functions or periodic signals into the sum of a set of simple oscillating functions, namely sines and cosines...
, the Fourier coefficients are proportional to the values (or "samples") of the continuous Fourier transform
Continuous Fourier transform
The Fourier transform is a mathematical operation that decomposes a function into its constituent frequencies, known as a frequency spectrum. For instance, the transform of a musical chord made up of pure notes is a mathematical representation of the amplitudes of the individual notes that make...
of
 at intervals of
at intervals of  That identity is known as the Poisson summation formula
That identity is known as the Poisson summation formulaPoisson summation formula
In mathematics, the Poisson summation formula is an equation that relates the Fourier series coefficients of the periodic summation of a function to values of the function's continuous Fourier transform. Consequently, the periodic summation of a function is completely defined by discrete samples...
.
Quotient space as domain
If a periodic function is represented using the quotient spaceQuotient space (linear algebra)
In linear algebra, the quotient of a vector space V by a subspace N is a vector space obtained by "collapsing" N to zero. The space obtained is called a quotient space and is denoted V/N ....
domain
 then one can write
then one can write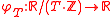

instead. The arguments of
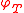 are equivalence classes of real number
are equivalence classes of real numberReal number
In mathematics, a real number is a value that represents a quantity along a continuum, such as -5 , 4/3 , 8.6 , √2 and π...
s that share the same fractional part
Fractional part
All real numbers can be written in the form n + r where n is an integer and the remaining fractional part r is a nonnegative real number less than one...
when divided by
 .
.

