
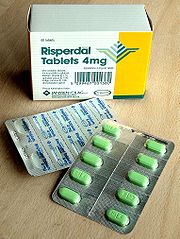
Pharmaceutical packaging
Encyclopedia
Contamination
Contamination is the presence of a minor and unwanted constituent in material, physical body, natural environment, at a workplace, etc.-Specifics:"Contamination" also has more specific meanings in science:...
, hinder microbial growth, and ensure product safety through the intended shelf life
Shelf life
Shelf life is the length of time that food, drink, medicine, chemicals, and many other perishable items are given before they are considered unsuitable for sale, use, or consumption...
for the pharmaceuticals. Packaging is a critical tool in the pharmaceutical industry for product delivery and regulatory compliance, many pharmaceutical companies will do all their packaging within a contamination free environment or Cleanroom. Some common pharmaceutical packaging techniques include foil and heat sealing; polyester and olefin package printing; polyethylene and polypropylene printing; and flat bed die cutting.
See also
- AuthenticationAuthenticationAuthentication is the act of confirming the truth of an attribute of a datum or entity...
- Counterfeit medicationsCounterfeit medicationsA counterfeit medication or a counterfeit drug is a medication or pharmaceutical product which is produced and sold with the intent to deceptively represent its origin, authenticity or effectiveness...
- Good Distribution PracticeGood distribution practiceGood Distribution Practice deals with the guidelines for the proper distribution of medicinal products for human use. GDP is a quality warranty system, which includes requirements for purchase, receiving, storage and export of drugs intended for human consumption.GDP regulates the division and...
- Tamper resistanceTamper resistanceTamper resistance is resistance to tampering by either the normal users of a product, package, or system or others with physical access to it. There are many reasons for employing tamper resistance....
- Package pilferagePackage pilferagePilferage is the theft of part of the contents of a package. It may also include theft of the contents but leaving the package, perhaps resealed with bogus contents. Small packages can be pilfered from a larger package such as a shipping container...
- Child-resistant packagingChild-resistant packagingChild-resistant packaging or C-R packaging is special packaging used to reduce the risk of children ingesting dangerous items. This is often accomplished by the use of a special safety cap. It is required by regulation for prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, pesticides, and household...
- Package testingPackage testingPackage testing or packaging testing involves the measurement of a characteristic or property involved with packaging. This includes packaging materials, packaging components, primary packages, shipping containers, and unit loads, as well as the associated processes.Testing measures the effects...
- Cold chainCold chainA cold chain is a temperature-controlled supply chain. An unbroken cold chain is an uninterrupted series of storage and distribution activities which maintain a given temperature range...
- Track and trace
- Verification and validationVerification and ValidationIn software project management, software testing, and software engineering, verification and validation is the process of checking that a software system meets specifications and that it fulfills its intended purpose...
General references
- anon, Guidance for Industry:Q8 (R2) Pharmaceutical Development, US FDA, 2009, http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/UCM073507.pdf
- Dean, D. A., 'Pharmaceutical Packaging Technology", 2000, ISBN 0748404406
- Lockhart, H., and Paine, F.A., "Packaging of Pharmaceuticals and Healthcare Products", 2006, Blackie, ISBN 0751401676
- Pilchik, R., "Validating Medical Packaging" 2002, ISBN 1566768071
- Rosette, J. L, "Improving Tamper-Evident Packaging: Problems, Tests and Solutions", 1992
- Soroka, W, "Fundamentals of Packaging Technology", IoPP, 2002, ISBN 1-930268-25-4
- Yam, K. L., "Encyclopedia of Packaging Technology", John Wiley & Sons, 2009, ISBN 978-0-470-08704-6

