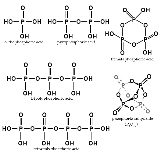
Phosphoric acids and Phosphates
Encyclopedia
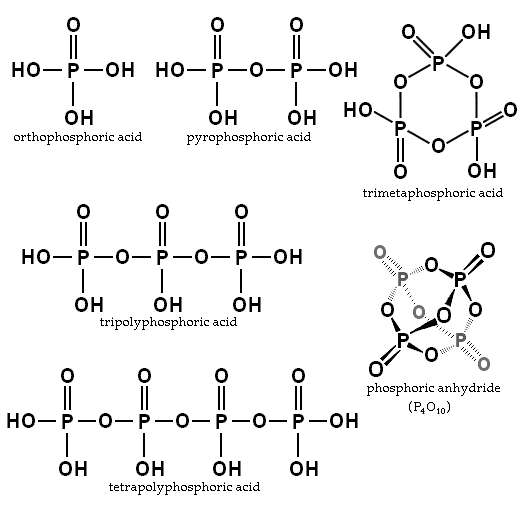
There are various kinds of phosphoric acids and phosphates. Of the many phosphorus oxoacids, the phosphoric acid
s constitute the largest and most diverse group. The simplest phosphoric acid series begins with monophosphoric (orthophosphoric) acid, continues with many oligophosphoric acids such as diphosphoric (pyrophosphoric) acid and concludes in the polyphosphoric acids. But, phosphoric acid units can bind together into rings or cyclic structures, chains (catenas), or branched structures, with various combinations possible. Each of these can form phosphates (salts or esters).
of a series of phosphoric acids is sometimes called by its common name, orthophosphoric acid
, but more often called by its IUPAC name, simply phosphoric acid, by both non-technical people and even many chemist
s. It has also been called monophosphoric acid. The chemical formula
of orthophosphoric acid is H3PO4 and its chemical structure
is shown in the illustration below. There is a separate article on this most important compound in the series under Phosphoric Acid
. However, two or more orthophosphoric acid molecule
s can be joined by condensation
into larger molecules by elimination of water. This way, a series of polyphosphoric acids can be obtained.
atom
s bonded
to oxygen
atoms in its structure. All three hydrogens are acid
ic to varying degrees and can be lost from the molecule
as H+ ions (alternatively referred to as protons). When all three H+ ions are lost from orthophosphoric acid, an orthophosphate ion (PO43−) is formed. Orthophosphate is the simplest in a series of phosphates, and is usually just called phosphate by both non-technical people and many chemist
s alike; see a separate article on phosphate
for details.
Because orthophosphoric acid can undergo as many as three dissociations or ionizations (losses of H+ ions), it has three acid dissociation constant
s called Ka1, Ka2, and Ka3. Another way to provide acid dissociation constant data is to list pKa1, pKa2, and pKa3 instead. Orthophosphate is in a sense the triple conjugate base of phosphoric acid and has three related basicity constants, Kb1, Kb2, and Kb3, which likewise have corresponding pKb1, pKb2, and pKb3 values.
The chemical structure of pyrophosphoric acid is also shown in the illustration. There is also a separate article on Pyrophosphoric acid
. Three orthophosphoric acid molecules can condense in a row to obtain tripolyphosphoric acid (H5P3O10), which is also shown in the illustration. This condensation process can continue with additional orthophosphoric acid units to obtain tetrapolyphosphoric acid (H6P4O13, pictured) and so on. Note that each extra phosphoric unit adds 1 extra H (hydrogen
) atom, 1 extra P (phosphorus
) atom, and 3 extra O (oxygen
) atoms. The "backbone" chain of these types of molecules consists of alternating P and O atoms covalently bonded
together. Polyphosphoric acid molecules can have dozens of such phosphoric units bonded in a row. A general formula for such poly-acid compounds is HO(PO2OH)xH, where x = number of phosphoric units in the molecule. The four oxygen atoms bonded to each phosphorus atom are in a tetrahedral configuration with the phosphorus in the center of the tetrahedron
and the oxygens in each of the four corners.
Used in organic synthesis for cyclizations and acylations.
The situation with higher order polyphosphoric acids and polyphosphate
s continues in a similar way. Tripolyphosphoric acid can lose up to five H+ ions to form a tripolyphosphate ion, tetrapolyphosphoric acid can lose up to six H+ ions to form tetrapolyphosphate, etc. As more dissociations per molecule are possible, the intervals between individual pKa and pKb values now start becoming smaller on the pH
scale.
As the polyphosphoric molecules grow increasingly larger and more complex, practically any number of the somewhat acidic -OH groups in them can dissociate to become negatively charged oxygens, forming numerous combinations of multiple-charged polyphosphoric/polyphosphate anions. Generally in an aqueous solution
, the degree or percentage of dissociation depends on the pH
of the solution.
Ortho-, pyro-, and tripolyphosphate compounds have been commonly used in detergent
s (i. e. cleaners) formulations. For example, see Sodium tripolyphosphate
. Sometimes pyrophosphate, tripolyphosphate, tetrapolyphosphate, etc. are called diphosphate, triphosphate, tetraphosphate, etc. , especially when they are part of phosphate esters in biochemistry
. They are also used for scale and corrosion control
by potable water providers. As a corrosion inhibitor, polyphosphates work by forming a protective film on the interior surface of pipes.
When these metaphosphoric acids lose their hydrogens as H+, cyclic anions called metaphosphates are formed. An example of a compound with such an anion is sodium hexametaphosphate
(Na6P6O18) used as a sequestrant
and a food additive
.
-soluble considering the polarity
of the molecules. Ammonium
and alkali
phosphates are also quite soluble in water. The alkaline earth salts start becoming less soluble and phosphate salts of various other metals are even less soluble. In aqueous solutions (solutions of water), water gradually (over the course of hours) hydrolyzes
polyphosphates into smaller phosphates and finally into ortho-phosphate, given enough water. Higher temperature or acidic conditions can speed up the hydrolysis reaction
s considerably.
Conversely, polyphosphoric acids or polyphosphates are often formed by dehydrating a phosphoric acid solution; in other words, removing water from it often by heating and evaporating the water off.
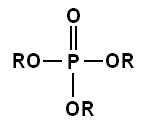 The -OH groups in phosphoric acids can also condense with the hydroxyl groups of alcohols to form phosphate esters. Since orthophosphoric acid has three -OH groups, it can esterify with one, two, or three alcohol molecules to form a mono-, di-, or triester. See the general structure image of an ortho- (or mono-) phosphate ester
The -OH groups in phosphoric acids can also condense with the hydroxyl groups of alcohols to form phosphate esters. Since orthophosphoric acid has three -OH groups, it can esterify with one, two, or three alcohol molecules to form a mono-, di-, or triester. See the general structure image of an ortho- (or mono-) phosphate ester
below on the left, where any of the R groups can be a hydrogen or an organic radical. Pyro- (or di-) phosphate esters and tripoly- (or tri-) phosphate esters, etc. are also possible. Any -OH groups on the phosphates in these ester molecules may lose H+ ions to form anions, again depending on the pH in a solution. In the biochemistry of living organisms, there are many kinds of (mono)phosphate, diphosphate, and triphosphate compounds (essentially ester
s), many of which play a significant role in metabolism such as adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
and triphosphate (ATP)
.
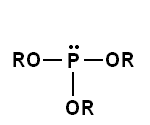 Similarly, phosphorous acid
Similarly, phosphorous acid
can bond with alcohol molecules to form a phosphite ester
. See the general structure image below on the right. The two dots on the P represent the lone electron pair of the phosphorus atom.
Phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid, also known as orthophosphoric acid or phosphoric acid, is a mineral acid having the chemical formula H3PO4. Orthophosphoric acid molecules can combine with themselves to form a variety of compounds which are also referred to as phosphoric acids, but in a more general way...
s constitute the largest and most diverse group. The simplest phosphoric acid series begins with monophosphoric (orthophosphoric) acid, continues with many oligophosphoric acids such as diphosphoric (pyrophosphoric) acid and concludes in the polyphosphoric acids. But, phosphoric acid units can bind together into rings or cyclic structures, chains (catenas), or branched structures, with various combinations possible. Each of these can form phosphates (salts or esters).
Orthophosphoric acid
The simplest compoundChemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
of a series of phosphoric acids is sometimes called by its common name, orthophosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid, also known as orthophosphoric acid or phosphoric acid, is a mineral acid having the chemical formula H3PO4. Orthophosphoric acid molecules can combine with themselves to form a variety of compounds which are also referred to as phosphoric acids, but in a more general way...
, but more often called by its IUPAC name, simply phosphoric acid, by both non-technical people and even many chemist
Chemist
A chemist is a scientist trained in the study of chemistry. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties such as density and acidity. Chemists carefully describe the properties they study in terms of quantities, with detail on the level of molecules and their component atoms...
s. It has also been called monophosphoric acid. The chemical formula
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
of orthophosphoric acid is H3PO4 and its chemical structure
Chemical structure
A chemical structure includes molecular geometry, electronic structure and crystal structure of molecules. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together. Molecular geometry can range from the very simple, such as...
is shown in the illustration below. There is a separate article on this most important compound in the series under Phosphoric Acid
Phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid, also known as orthophosphoric acid or phosphoric acid, is a mineral acid having the chemical formula H3PO4. Orthophosphoric acid molecules can combine with themselves to form a variety of compounds which are also referred to as phosphoric acids, but in a more general way...
. However, two or more orthophosphoric acid molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
s can be joined by condensation
Condensation
Condensation is the change of the physical state of matter from gaseous phase into liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. When the transition happens from the gaseous phase into the solid phase directly, the change is called deposition....
into larger molecules by elimination of water. This way, a series of polyphosphoric acids can be obtained.

Orthophosphate
Orthophosphoric acid has three hydrogenHydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s bonded
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electromagnetic force attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction...
to oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
atoms in its structure. All three hydrogens are acid
Acid
An acid is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically stronger, and turn blue litmus paper red...
ic to varying degrees and can be lost from the molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
as H+ ions (alternatively referred to as protons). When all three H+ ions are lost from orthophosphoric acid, an orthophosphate ion (PO43−) is formed. Orthophosphate is the simplest in a series of phosphates, and is usually just called phosphate by both non-technical people and many chemist
Chemist
A chemist is a scientist trained in the study of chemistry. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties such as density and acidity. Chemists carefully describe the properties they study in terms of quantities, with detail on the level of molecules and their component atoms...
s alike; see a separate article on phosphate
Phosphate
A phosphate, an inorganic chemical, is a salt of phosphoric acid. In organic chemistry, a phosphate, or organophosphate, is an ester of phosphoric acid. Organic phosphates are important in biochemistry and biogeochemistry or ecology. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in...
for details.
Because orthophosphoric acid can undergo as many as three dissociations or ionizations (losses of H+ ions), it has three acid dissociation constant
Acid dissociation constant
An acid dissociation constant, Ka, is a quantitative measure of the strength of an acid in solution. It is the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction known as dissociation in the context of acid-base reactions...
s called Ka1, Ka2, and Ka3. Another way to provide acid dissociation constant data is to list pKa1, pKa2, and pKa3 instead. Orthophosphate is in a sense the triple conjugate base of phosphoric acid and has three related basicity constants, Kb1, Kb2, and Kb3, which likewise have corresponding pKb1, pKb2, and pKb3 values.
Polyphosphoric acids
When two orthophosphoric acid molecules are condensed into one molecule, pyrophosphoric acid (H4P2O7) is obtained as follows:-
-
-
-
-
- 2 H3PO4 → H4P2O7 + H2O
-
-
-
-
The chemical structure of pyrophosphoric acid is also shown in the illustration. There is also a separate article on Pyrophosphoric acid
Pyrophosphoric acid
Pyrophosphoric acid, also known under the name diphosphoric acid, is colorless, odorless, hygroscopic and is soluble in water, diethyl ether, and ethyl alcohol. It is produced from phosphoric acid by dehydration. Pyrophosphoric acid slowly hydrolyzes in the presence of water into phosphoric...
. Three orthophosphoric acid molecules can condense in a row to obtain tripolyphosphoric acid (H5P3O10), which is also shown in the illustration. This condensation process can continue with additional orthophosphoric acid units to obtain tetrapolyphosphoric acid (H6P4O13, pictured) and so on. Note that each extra phosphoric unit adds 1 extra H (hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
) atom, 1 extra P (phosphorus
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks...
) atom, and 3 extra O (oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
) atoms. The "backbone" chain of these types of molecules consists of alternating P and O atoms covalently bonded
Covalent bond
A covalent bond is a form of chemical bonding that is characterized by the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they share electrons is known as covalent bonding....
together. Polyphosphoric acid molecules can have dozens of such phosphoric units bonded in a row. A general formula for such poly-acid compounds is HO(PO2OH)xH, where x = number of phosphoric units in the molecule. The four oxygen atoms bonded to each phosphorus atom are in a tetrahedral configuration with the phosphorus in the center of the tetrahedron
Tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids...
and the oxygens in each of the four corners.
Used in organic synthesis for cyclizations and acylations.
Linear polyphosphates
In a pyrophosphoric acid molecule, there are four hydrogens bonded to oxygens, and one, two, three, or all four can be lost as H+ ions. When all four are lost from pyrophosphoric acid, a pyrophosphate ion is formed. Because pyrophosphoric acids can undergo four dissociations, there are four Ka values for it, as well as four corresponding pKa values. Similarly, pyrophosphate is a base with four Kb and, of course, four pKb values for regaining the H+ ions in reverse order.The situation with higher order polyphosphoric acids and polyphosphate
Polyphosphate
Triphosphates are salts or esters of polymeric oxyanions formed from tetrahedral PO4 structural units linked together by sharing oxygen atoms. When two corners are shared the polyphosphate may have a linear chain structure or a cyclic ring structure. In biology the polyphosphate esters AMP, ADP...
s continues in a similar way. Tripolyphosphoric acid can lose up to five H+ ions to form a tripolyphosphate ion, tetrapolyphosphoric acid can lose up to six H+ ions to form tetrapolyphosphate, etc. As more dissociations per molecule are possible, the intervals between individual pKa and pKb values now start becoming smaller on the pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
scale.
As the polyphosphoric molecules grow increasingly larger and more complex, practically any number of the somewhat acidic -OH groups in them can dissociate to become negatively charged oxygens, forming numerous combinations of multiple-charged polyphosphoric/polyphosphate anions. Generally in an aqueous solution
Solution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
, the degree or percentage of dissociation depends on the pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
of the solution.
Ortho-, pyro-, and tripolyphosphate compounds have been commonly used in detergent
Detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with "cleaning properties in dilute solutions." In common usage, "detergent" refers to alkylbenzenesulfonates, a family of compounds that are similar to soap but are less affected by hard water...
s (i. e. cleaners) formulations. For example, see Sodium tripolyphosphate
Sodium tripolyphosphate
Sodium triphosphate is an inorganic compound with formula Na5P3O10. It is the sodium salt of the polyphosphate penta-anion, which is the conjugate base of triphosphoric acid. It is produced on a large scale as a component of many domestic and industrial products, especially detergents...
. Sometimes pyrophosphate, tripolyphosphate, tetrapolyphosphate, etc. are called diphosphate, triphosphate, tetraphosphate, etc. , especially when they are part of phosphate esters in biochemistry
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
. They are also used for scale and corrosion control
Corrosion inhibitor
A corrosion inhibitor is a chemical compound that, when added to a liquid or gas, decreases the corrosion rate of a material, typically a metal or an alloy. The effectiveness of a corrosion inhibitor depends on fluid composition, quantity of water, and flow regime...
by potable water providers. As a corrosion inhibitor, polyphosphates work by forming a protective film on the interior surface of pipes.
Metaphosphoric acids and metaphosphates
The phosphoric acid units can be bonded together in rings (cyclic structures) forming metaphosphoric acid molecules. The simplest such compound is trimetaphosphoric acid or cyclo-triphosphoric acid having the formula H3P3O9. Its structure is shown in the illustration. Since the ends are condensed, its formula has one less H2O (water) than tripolyphosphoric acid. What are commonly called trimetaphosphates actually have a mixture of ring sizes. A general formula for such cyclic compounds is (HPO3)x where x = number of phosphoric units in the molecule.When these metaphosphoric acids lose their hydrogens as H+, cyclic anions called metaphosphates are formed. An example of a compound with such an anion is sodium hexametaphosphate
Sodium hexametaphosphate
Sodium hexametaphosphate is a hexamer of composition 6. Sodium hexametaphosphate of commerce is typically a mixture of polymeric metaphosphates, of which the hexamer is one, and is usually the compound referred to by this name. It is more correctly termed sodium polymetaphosphate. It is prepared...
(Na6P6O18) used as a sequestrant
Sequestrant
A sequestrant is a food additive whose role is to improve the quality and stability of the food products. Sequestrants form chelate complexes with polyvalent metal ions, especially copper, iron and nickel, which serve as catalysts in the oxidation of the fats in the food...
and a food additive
Food additive
Food additives are substances added to food to preserve flavor or enhance its taste and appearance.Some additives have been used for centuries; for example, preserving food by pickling , salting, as with bacon, preserving sweets or using sulfur dioxide as in some wines...
.
Branched polyphosphates
The third -OH group on an orthophosphoric acid unit can also be used for condensation with other phosphoric groups to form branches in the polyphosphoric/polyphosphate chains. The ultimate example of cyclic and branching condensation would be the cyclic four-phosphate unit double-branched to form the phosphoric anhydride P4O10; see illustration.Hydrolysis of polyphosphoric/polyphosphates
These phosphoric acids series are generally waterWater
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
-soluble considering the polarity
Chemical polarity
In chemistry, polarity refers to a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole or multipole moment. Polar molecules interact through dipole–dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Molecular polarity is dependent on the difference in...
of the molecules. Ammonium
Ammonium
The ammonium cation is a positively charged polyatomic cation with the chemical formula NH. It is formed by the protonation of ammonia...
and alkali
Alkali
In chemistry, an alkali is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or alkaline earth metal element. Some authors also define an alkali as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7. The adjective alkaline is commonly used in English as a synonym for base,...
phosphates are also quite soluble in water. The alkaline earth salts start becoming less soluble and phosphate salts of various other metals are even less soluble. In aqueous solutions (solutions of water), water gradually (over the course of hours) hydrolyzes
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction during which molecules of water are split into hydrogen cations and hydroxide anions in the process of a chemical mechanism. It is the type of reaction that is used to break down certain polymers, especially those made by condensation polymerization...
polyphosphates into smaller phosphates and finally into ortho-phosphate, given enough water. Higher temperature or acidic conditions can speed up the hydrolysis reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
s considerably.
Conversely, polyphosphoric acids or polyphosphates are often formed by dehydrating a phosphoric acid solution; in other words, removing water from it often by heating and evaporating the water off.
Phosphate and phosphite esters

Ester
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
below on the left, where any of the R groups can be a hydrogen or an organic radical. Pyro- (or di-) phosphate esters and tripoly- (or tri-) phosphate esters, etc. are also possible. Any -OH groups on the phosphates in these ester molecules may lose H+ ions to form anions, again depending on the pH in a solution. In the biochemistry of living organisms, there are many kinds of (mono)phosphate, diphosphate, and triphosphate compounds (essentially ester
Ester
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
s), many of which play a significant role in metabolism such as adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
Adenosine diphosphate
Adenosine diphosphate, abbreviated ADP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside adenosine. ADP consists of the pyrophosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine....
and triphosphate (ATP)
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
.

Phosphorous acid
Phosphorous acid is the compound described by the formula H3PO3. This acid is diprotic , not triprotic as might be suggested by this formula. Phosphorous acid is as an intermediate in the preparation of other phosphorus compounds.-Nomenclature and tautomerism:H3PO3 is more clearly described with...
can bond with alcohol molecules to form a phosphite ester
Phosphite ester
A phosphite ester or organophosphite is a type of chemical compound with the general structure P3. Phosphite esters can be considered as esters of phosphorous acid, H3PO3. A simple phosphite ester is trimethylphosphite, P3...
. See the general structure image below on the right. The two dots on the P represent the lone electron pair of the phosphorus atom.
See also
- Adenosine monophosphateAdenosine monophosphateAdenosine monophosphate , also known as 5'-adenylic acid, is a nucleotide that is used as a monomer in RNA. It is an ester of phosphoric acid and the nucleoside adenosine. AMP consists of a phosphate group, the sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine...
- Adenosine diphosphateAdenosine diphosphateAdenosine diphosphate, abbreviated ADP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside adenosine. ADP consists of the pyrophosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine....
- Adenosine triphosphateAdenosine triphosphateAdenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
- List of biochemical phosphate reactions
- Nucleoside triphosphateNucleoside triphosphateNucleoside triphosphate is a nucleoside with three phosphates. Natural nucleoside triphosphates include adenosine triphosphate , guanosine triphosphate , cytidine triphosphate , 5-methyluridine triphosphate , and uridine triphosphate . These terms refer to those nucleoside triphosphates that...
- OrganophosphateOrganophosphateAn organophosphate is the general name for esters of phosphoric acid. Phosphates are probably the most pervasive organophosphorus compounds. Many of the most important biochemicals are organophosphates, including DNA and RNA as well as many cofactors that are essential for life...
- PhosphatePhosphateA phosphate, an inorganic chemical, is a salt of phosphoric acid. In organic chemistry, a phosphate, or organophosphate, is an ester of phosphoric acid. Organic phosphates are important in biochemistry and biogeochemistry or ecology. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in...
- Phosphate homeostasis
- Phosphate reaction
- Phosphonic acid
- PhosphoramidatePhosphoramidateA phosphoramidate is a phosphate that has an NR2 instead of an OH group. The structure of phosphoramidic acid , 2PONH2, is present in PubChem....
- Phosphoric acidPhosphoric acidPhosphoric acid, also known as orthophosphoric acid or phosphoric acid, is a mineral acid having the chemical formula H3PO4. Orthophosphoric acid molecules can combine with themselves to form a variety of compounds which are also referred to as phosphoric acids, but in a more general way...
- Phosphorus oxoacids
- PolyphosphatePolyphosphateTriphosphates are salts or esters of polymeric oxyanions formed from tetrahedral PO4 structural units linked together by sharing oxygen atoms. When two corners are shared the polyphosphate may have a linear chain structure or a cyclic ring structure. In biology the polyphosphate esters AMP, ADP...
- PyrophosphatePyrophosphateIn chemistry, the anion, the salts, and the esters of pyrophosphoric acid are called pyrophosphates. Any salt or ester containing two phosphate groups is called a diphosphate. As a food additive, diphosphates are known as E450.- Chemistry :...
- Ribonucleoside monophosphate
- Structural phosphate
- Superphosphate

