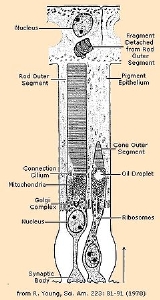
Photoreceptor
Overview
A photoreceptor cell is a specialized type of neuron
found in the eye
's retina
that is capable of phototransduction. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light (electromagnetic radiation
) into signals that can stimulate biological processes. To be more specific, photoreceptor protein
s in the cell absorb photon
s, triggering a change in the cell's membrane potential
.
The two classic photoreceptor cells are rods
and cones
, each contributing information used by the visual system
to form a representation of the visual world, sight
.
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
found in the eye
Human eye
The human eye is an organ which reacts to light for several purposes. As a conscious sense organ, the eye allows vision. Rod and cone cells in the retina allow conscious light perception and vision including color differentiation and the perception of depth...
's retina
Retina
The vertebrate retina is a light-sensitive tissue lining the inner surface of the eye. The optics of the eye create an image of the visual world on the retina, which serves much the same function as the film in a camera. Light striking the retina initiates a cascade of chemical and electrical...
that is capable of phototransduction. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light (electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space...
) into signals that can stimulate biological processes. To be more specific, photoreceptor protein
Photoreceptor protein
Photoreceptors are light-sensitive proteins involved in the sensing and response to light in a variety of organisms. Some examples are rhodopsin in the photoreceptor cells of the vertebrate retina, phytochrome in plants, and bacteriorhodopsin and bacteriophytochromes in some bacteria...
s in the cell absorb photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
s, triggering a change in the cell's membrane potential
Membrane potential
Membrane potential is the difference in electrical potential between the interior and exterior of a biological cell. All animal cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane composed of a lipid bilayer with a variety of types of proteins embedded in it...
.
The two classic photoreceptor cells are rods
Rod cell
Rod cells, or rods, are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye that can function in less intense light than can the other type of visual photoreceptor, cone cells. Named for their cylindrical shape, rods are concentrated at the outer edges of the retina and are used in peripheral vision. On...
and cones
Cone cell
Cone cells, or cones, are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye that are responsible for color vision; they function best in relatively bright light, as opposed to rod cells that work better in dim light. If the retina is exposed to an intense visual stimulus, a negative afterimage will be...
, each contributing information used by the visual system
Visual system
The visual system is the part of the central nervous system which enables organisms to process visual detail, as well as enabling several non-image forming photoresponse functions. It interprets information from visible light to build a representation of the surrounding world...
to form a representation of the visual world, sight
Visual perception
Visual perception is the ability to interpret information and surroundings from the effects of visible light reaching the eye. The resulting perception is also known as eyesight, sight, or vision...
.

