Phycoerythrin
Encyclopedia
Phycoerythrin is a red
protein
from the light-harvesting phycobiliprotein
family, present in cyanobacteria, red algae
and cryptomonad
s.
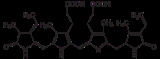
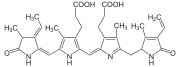 Like all phycobiliproteins, phycoerythrin is composed of a protein part, organised in a hexameric structure of alpha and beta chains, covalently binding chromophore
Like all phycobiliproteins, phycoerythrin is composed of a protein part, organised in a hexameric structure of alpha and beta chains, covalently binding chromophore
s called phycobilin
s. In the phycoerythrin family, the phycobilins are: phycoerythrobilin
, the typical phycoerythrin acceptor chromophore, and sometimes phycourobilin
(marine organisms). Phycoerythrins are the phycobiliproteins that bind the highest number of phycobilins (up to six per alpha-beta subunit dimer).
Absorption peaks in the visible light spectrum are at 495 and 545/566 nm, depending on the chromophores bound and the considered organism. A strong emission peak exists at 575 ± 10 nm. (i.e., phycoerythrin absorbs slightly blue-green/yellowish light and emits slightly orange-yellow light.)
Phycoerythrin is an accessory pigment to the main chlorophyll
pigments responsible for photosynthesis
. The light energy is captured by phycoerythrin and is then passed on to the reaction centre chlorophyll pair, most of the time via the phycobiliproteins phycocyanin
and allophycocyanin
.
R-Phycoerythrin, or PE, is useful in the laboratory as a fluorescence
-based indicator for the presence of cyanobacteria and for labeling antibodies
in a technique called immunofluorescence
, among other applications. There are also other types of phycoerythrins, such as B-Phycoerythrin, which has slightly different spectral properties. B-Phycoerythrin absorbs strongly at about 545 nm (slightly yellowish green) and emits strongly at 572 nm (yellow) instead and could be better suited for some instruments. B-Phycoerythrin may also be less "sticky" than R-Phycoerythrin and contributes less to background signal due to non-specific binding in certain applications.
R-Phycoerythrin and B-Phycoerythrin are among the brightest fluorescent dyes ever identified.
Red
Red is any of a number of similar colors evoked by light consisting predominantly of the longest wavelengths of light discernible by the human eye, in the wavelength range of roughly 630–740 nm. Longer wavelengths than this are called infrared , and cannot be seen by the naked eye...
protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
from the light-harvesting phycobiliprotein
Phycobiliprotein
Phycobiliproteins are water-soluble proteins present in cyanobacteria and certain algae that capture light energy, which is then passed on to chlorophylls during photosynthesis. Phycobiliproteins are formed of a complex between proteins and covalently bound phycobilins that act as chromophores...
family, present in cyanobacteria, red algae
Red algae
The red algae are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae, and also one of the largest, with about 5,000–6,000 species of mostly multicellular, marine algae, including many notable seaweeds...
and cryptomonad
Cryptomonad
The cryptomonads are a group of algae, most of which have plastids. They are common in freshwater, and also occur in marine and brackish habitats. Each cell is around 10-50 μm in size and flattened in shape, with an anterior groove or pocket...
s.

Chromophore
A chromophore is the part of a molecule responsible for its color. The color arises when a molecule absorbs certain wavelengths of visible light and transmits or reflects others. The chromophore is a region in the molecule where the energy difference between two different molecular orbitals falls...
s called phycobilin
Phycobilin
Phycobilins are chromophores found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of red algae, glaucophytes and some cryptomonads...
s. In the phycoerythrin family, the phycobilins are: phycoerythrobilin
Phycoerythrobilin
Phycoerythrobilin is a red phycobilin, i.e. an open tetrapyrrole chromophore found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of red algae, glaucophytes and some cryptomonads. Phycoerythrobilin is present in the phycobiliprotein phycoerythrin, of which it is the terminal acceptor of energy. The...
, the typical phycoerythrin acceptor chromophore, and sometimes phycourobilin
Phycourobilin
Phycourobilin is a tetrapyrrole orange molecule involved in photosynthesis in cyanobacteria and red algae. This chromophore is bound to the phycobiliprotein phycoerythrin, the distal component of the light-harvesting system of cyanobacteria and red algae .When bound to phycoerythrin, phycourobilin...
(marine organisms). Phycoerythrins are the phycobiliproteins that bind the highest number of phycobilins (up to six per alpha-beta subunit dimer).
Absorption peaks in the visible light spectrum are at 495 and 545/566 nm, depending on the chromophores bound and the considered organism. A strong emission peak exists at 575 ± 10 nm. (i.e., phycoerythrin absorbs slightly blue-green/yellowish light and emits slightly orange-yellow light.)
Phycoerythrin is an accessory pigment to the main chlorophyll
Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in almost all plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. Its name is derived from the Greek words χλωρος, chloros and φύλλον, phyllon . Chlorophyll is an extremely important biomolecule, critical in photosynthesis, which allows plants to obtain energy from light...
pigments responsible for photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a chemical process that converts carbon dioxide into organic compounds, especially sugars, using the energy from sunlight. Photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, and many species of bacteria, but not in archaea. Photosynthetic organisms are called photoautotrophs, since they can...
. The light energy is captured by phycoerythrin and is then passed on to the reaction centre chlorophyll pair, most of the time via the phycobiliproteins phycocyanin
Phycocyanin
Phycocyanin is a pigment from the light-harvesting phycobiliprotein family, along with allophycocyanin and phycoerythrin. It is an accessory pigment to chlorophyll. All phycobiliproteins are water-soluble and therefore cannot exist within the membrane as do carotenoids, but aggregate forming...
and allophycocyanin
Allophycocyanin
Allophycocyanin is a protein from the light-harvesting phycobiliprotein family, along with phycocyanin, phycoerythrin and phycoerythrocyanin. It is an accessory pigment to chlorophyll...
.
R-Phycoerythrin, or PE, is useful in the laboratory as a fluorescence
Fluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation of a different wavelength. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore lower energy, than the absorbed radiation...
-based indicator for the presence of cyanobacteria and for labeling antibodies
Antibody
An antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin, is a large Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique part of the foreign target, termed an antigen...
in a technique called immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence is a technique used for light microscopy with a fluorescence microscope and is used primarily on biological samples. This technique uses the specificity of antibodies to their antigen to target fluorescent dyes to specific biomolecule targets within a cell, and therefore allows...
, among other applications. There are also other types of phycoerythrins, such as B-Phycoerythrin, which has slightly different spectral properties. B-Phycoerythrin absorbs strongly at about 545 nm (slightly yellowish green) and emits strongly at 572 nm (yellow) instead and could be better suited for some instruments. B-Phycoerythrin may also be less "sticky" than R-Phycoerythrin and contributes less to background signal due to non-specific binding in certain applications.
R-Phycoerythrin and B-Phycoerythrin are among the brightest fluorescent dyes ever identified.

