
Pi bond
Encyclopedia

Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, pi bonds (π bonds) are covalent
Covalent bond
A covalent bond is a form of chemical bonding that is characterized by the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they share electrons is known as covalent bonding....
chemical bond
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electromagnetic force attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction...
s where two lobes of one involved atomic orbital
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus...
overlap two lobes of the other involved atomic orbital. These orbitals share a nodal plane
Node (physics)
A node is a point along a standing wave where the wave has minimal amplitude. For instance, in a vibrating guitar string, the ends of the string are nodes. By changing the position of the end node through frets, the guitarist changes the effective length of the vibrating string and thereby the...
which passes through both of the involved nuclei
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the very dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. It was discovered in 1911, as a result of Ernest Rutherford's interpretation of the famous 1909 Rutherford experiment performed by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, under the direction of Rutherford. The...
.

Quintuple bond
A quintuple bond in chemistry is an unusual type of chemical bond first reported in 2005 for a dichromium compound. Single bonds, double bonds, and triple bonds are commonplace in chemistry. Quadruple bonds are rarer but occur especially for Cr, Mo, W, and Re, e.g. [Mo2Cl8]4− and [Re2Cl8]2−...
.
Pi bonds are usually weaker than sigma bond
Sigma bond
In chemistry, sigma bonds are the strongest type of covalent chemical bond. They are formed by head-on overlapping between atomic orbitals. Sigma bonding is most clearly defined for diatomic molecules using the language and tools of symmetry groups. In this formal approach, a σ-bond is...
s. From the perspective of quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
, this bond's weakness is explained by significantly less overlap between the component p-orbitals due to their parallel orientation.
Pi bonds result from overlap of atomic orbitals that are in contact through two areas of overlap. Pi-bonds are more diffuse bonds than the sigma bonds. Electrons in pi bonds are sometimes referred to as pi electrons. Molecular fragments joined by a pi bond cannot rotate about that bond without breaking the pi bond, because rotation involves destroying the parallel orientation of the constituent p orbitals.
For homonuclear
Homonuclear molecule
Homonuclear molecules, or homonuclear species, are molecules composed of only one type of element. Homonuclear molecules may consist of various numbers of atoms, depending on the element's properties. Some elements form molecules of more than one size. Noble gases rarely form bonds, so they only...
diatomic molecules, bonding π molecular orbital
Molecular orbital
In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The term "orbital" was first...
s have no nodal planes that pass between the bonded atoms. The corresponding antibonding, or π* ("pi-star") molecular orbital, is defined by the presence of an additional nodal plane between these two bonded atoms.
Multiple bonds
A typical double bondDouble bond
A double bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two chemical elements involving four bonding electrons instead of the usual two. The most common double bond, that between two carbon atoms, can be found in alkenes. Many types of double bonds between two different elements exist, for example in...
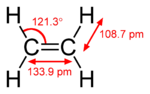
consists of one sigma bond and one pi bond, for example the C=C double bond in ethylene
Ethylene
Ethylene is a gaseous organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest alkene . Because it contains a carbon-carbon double bond, ethylene is classified as an unsaturated hydrocarbon. Ethylene is widely used in industry and is also a plant hormone...
. A typical triple bond
Triple bond
A triple bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two chemical elements involving six bonding electrons instead of the usual two in a covalent single bond. The most common triple bond, that between two carbon atoms, can be found in alkynes. Other functional groups containing a triple bond are...
, for example in acetylene
Acetylene
Acetylene is the chemical compound with the formula C2H2. It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution.As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because...
, consists of one sigma bond and two pi bonds in two mutually perpendicular planes containing the bond axis. Two pi bonds are the maximum that can exist between a given pair of atoms. Quadruple bond
Quadruple bond
A quadruple bond is a type of chemical bond between two atoms involving eight electrons. This bond is an extension of the more familiar types double bonds and triple bonds. Stable quadruple bonds are most common among the middle members transition metal elements such rhenium, tungsten, molybdenum...
s are extremely rare and can be formed only between transition metal
Transition metal
The term transition metal has two possible meanings:*The IUPAC definition states that a transition metal is "an element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell." Group 12 elements are not transition metals in this definition.*Some...
atoms, and consist of one sigma bond, two pi bonds and one delta bond
Delta bond
In chemistry, delta bonds are chemical bonds of the covalent type, where four lobes of one involved atomic orbital overlap four lobes of the other involved atomic orbital...
.
A pi bond is weaker than a sigma bond, but the combination of pi and sigma bond is stronger than either bond by itself. The enhanced strength of a multiple bond versus a single (sigma bond) is indicated in many ways, but most obviously by a contraction in bond lengths. For example in organic chemistry, carbon–carbon bond length
Bond length
- Explanation :Bond length is related to bond order, when more electrons participate in bond formation the bond will get shorter. Bond length is also inversely related to bond strength and the bond dissociation energy, as a stronger bond will be shorter...
s are 154 pm) in ethane
Ethane
Ethane is a chemical compound with chemical formula C2H6. It is the only two-carbon alkane that is an aliphatic hydrocarbon. At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas....
, 134 pm in ethylene and 120 pm in acetylene. More bonds make the total bond shorter and stronger.
 |
 |
|
| ethane Ethane Ethane is a chemical compound with chemical formula C2H6. It is the only two-carbon alkane that is an aliphatic hydrocarbon. At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas.... |
ethylene Ethylene Ethylene is a gaseous organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest alkene . Because it contains a carbon-carbon double bond, ethylene is classified as an unsaturated hydrocarbon. Ethylene is widely used in industry and is also a plant hormone... |
acetylene Acetylene Acetylene is the chemical compound with the formula C2H2. It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution.As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because... |
Special cases
Pi bonds do not necessarily connect a pair of atoms that are also sigma-bonded.In certain metal complexes, pi interactions between a metal atom and alkyne
Alkyne
Alkynes are hydrocarbons that have a triple bond between two carbon atoms, with the formula CnH2n-2. Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name acetylene also refers specifically to C2H2, known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature...
and alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
pi antibonding orbitals form pi-bonds.
In some cases of multiple bonds between two atoms, there is no sigma bond at all, only pi bonds. Examples include diiron hexacarbonyl (Fe2(CO)6), dicarbon (C2) and the borane B2H2. In these compounds the central bond consists only of pi bonding, and in order to achieve maximum orbital overlap
Orbital overlap
Orbital overlap was an idea first introduced by Linus Pauling to explain the molecular bond angles observed through experimentation and is the basis for the concept of orbital hybridisation. s orbitals are spherical and have no directionality while p orbitals are oriented 90° to one another...
the bond distances are much shorter than expected.
See also
- Aromatic interaction
- Delta bondDelta bondIn chemistry, delta bonds are chemical bonds of the covalent type, where four lobes of one involved atomic orbital overlap four lobes of the other involved atomic orbital...
- Molecular geometryMolecular geometryMolecular geometry or molecular structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It determines several properties of a substance including its reactivity, polarity, phase of matter, color, magnetism, and biological activity.- Molecular geometry determination...
- Pi interaction

