Quadruple bond
Encyclopedia
A quadruple bond is a type of chemical bond
between two atom
s involving eight electron
s. This bond is an extension of the more familiar types double bond
s and triple bond
s. Stable quadruple bonds are most common among the middle members transition metal
elements such rhenium
, tungsten
, molybdenum
and chromium
. Typically the ligands that support quadruple bonds are π-donors, not π-acceptors.
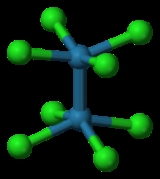
-3d-balls.png) Chromium(II) acetate
Chromium(II) acetate
, Cr2(μ-O2CMe)4(H2O)2, was the first chemical compound containing a quadruple bond to be synthesized. It was described in 1844 by E. Peligot, although its distinctive bonding was not recognized for more than a century. The quadruple bond was first characterized in potassium octachlorodirhenate(III) or K2[Re2Cl8]·2H2O by F. A. Cotton
in 1964. The rhenium-rhenium bond length
in this compound is only 224 pm. In the terminology of molecular orbital theory
, the bonding is described as σ2π4δ2 with one sigma bond
, two pi bond
s and one delta bond
.
Many other compounds with quadruple bonds have been described, often by Cotton and his coworkers. Isoelectronic with the dirhenium compound is the salt K4[Mo2Cl8] (potassium octachlorodimolybdate
). An example of a ditungsten compound with a quadruple bond is di-tungsten tetra(hpp)
.
Valence bond theory predicts a quadruple bond as the only way to satisfy the octet rule for carbon
in dicarbon
-acetate-3d-balls.png)
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electromagnetic force attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction...
between two atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s involving eight electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s. This bond is an extension of the more familiar types double bond
Double bond
A double bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two chemical elements involving four bonding electrons instead of the usual two. The most common double bond, that between two carbon atoms, can be found in alkenes. Many types of double bonds between two different elements exist, for example in...
s and triple bond
Triple bond
A triple bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two chemical elements involving six bonding electrons instead of the usual two in a covalent single bond. The most common triple bond, that between two carbon atoms, can be found in alkynes. Other functional groups containing a triple bond are...
s. Stable quadruple bonds are most common among the middle members transition metal
Transition metal
The term transition metal has two possible meanings:*The IUPAC definition states that a transition metal is "an element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell." Group 12 elements are not transition metals in this definition.*Some...
elements such rhenium
Rhenium
Rhenium is a chemical element with the symbol Re and atomic number 75. It is a silvery-white, heavy, third-row transition metal in group 7 of the periodic table. With an average concentration of 1 part per billion , rhenium is one of the rarest elements in the Earth's crust. The free element has...
, tungsten
Tungsten
Tungsten , also known as wolfram , is a chemical element with the chemical symbol W and atomic number 74.A hard, rare metal under standard conditions when uncombined, tungsten is found naturally on Earth only in chemical compounds. It was identified as a new element in 1781, and first isolated as...
, molybdenum
Molybdenum
Molybdenum , is a Group 6 chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42. The name is from Neo-Latin Molybdaenum, from Ancient Greek , meaning lead, itself proposed as a loanword from Anatolian Luvian and Lydian languages, since its ores were confused with lead ores...
and chromium
Chromium
Chromium is a chemical element which has the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6. It is a steely-gray, lustrous, hard metal that takes a high polish and has a high melting point. It is also odorless, tasteless, and malleable...
. Typically the ligands that support quadruple bonds are π-donors, not π-acceptors.
-3d-balls.png)
Chromium(II) acetate
Chromium acetate hydrate, also known as chromous acetate, is the coordination compound with the formula Cr242. This formula is commonly abbreviated Cr242. This red-coloured compound features a quadruple bond...
, Cr2(μ-O2CMe)4(H2O)2, was the first chemical compound containing a quadruple bond to be synthesized. It was described in 1844 by E. Peligot, although its distinctive bonding was not recognized for more than a century. The quadruple bond was first characterized in potassium octachlorodirhenate(III) or K2[Re2Cl8]·2H2O by F. A. Cotton
F. Albert Cotton
Frank Albert Cotton was the W.T. Doherty-Welch Foundation Chair and Distinguished Professor of Chemistry at Texas A&M University. He authored over 1700 scientific articles. Cotton was recognized for his research on the chemistry of the transition metals.-Education:Frank Albert Cotton was born on...
in 1964. The rhenium-rhenium bond length
Bond length
- Explanation :Bond length is related to bond order, when more electrons participate in bond formation the bond will get shorter. Bond length is also inversely related to bond strength and the bond dissociation energy, as a stronger bond will be shorter...
in this compound is only 224 pm. In the terminology of molecular orbital theory
Molecular orbital theory
In chemistry, molecular orbital theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule...
, the bonding is described as σ2π4δ2 with one sigma bond
Sigma bond
In chemistry, sigma bonds are the strongest type of covalent chemical bond. They are formed by head-on overlapping between atomic orbitals. Sigma bonding is most clearly defined for diatomic molecules using the language and tools of symmetry groups. In this formal approach, a σ-bond is...
, two pi bond
Pi bond
In chemistry, pi bonds are covalent chemical bonds where two lobes of one involved atomic orbital overlap two lobes of the other involved atomic orbital...
s and one delta bond
Delta bond
In chemistry, delta bonds are chemical bonds of the covalent type, where four lobes of one involved atomic orbital overlap four lobes of the other involved atomic orbital...
.
Many other compounds with quadruple bonds have been described, often by Cotton and his coworkers. Isoelectronic with the dirhenium compound is the salt K4[Mo2Cl8] (potassium octachlorodimolybdate
Potassium octachlorodimolybdate
Potassium octachlorodimolybdate is the inorganic compound with the formula K4Mo2Cl8. This red-coloured salt consists of potassium cations and the octachlorodimolybdate anion, Mo2Cl84−. The anion is of historic interest because it was one of the earliest illustrations of a quadruple bonding...
). An example of a ditungsten compound with a quadruple bond is di-tungsten tetra(hpp)
Di-tungsten tetra(hpp)
Di-tungsten tetra is the name of the coordination compound with the formula W24. This material consists of a pair of tungsten centers linked by the conjugate base of four hexahydropyrimidopyrimidine ligands...
.
Valence bond theory predicts a quadruple bond as the only way to satisfy the octet rule for carbon
in dicarbon
-acetate-3d-balls.png)

