
Piezoelectric sensor
Encyclopedia
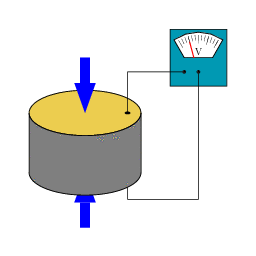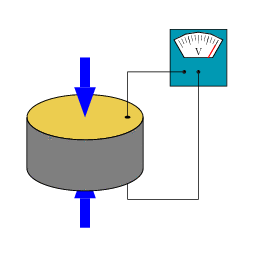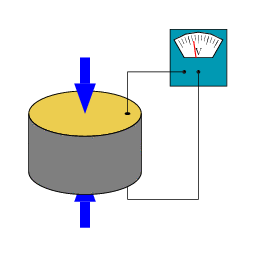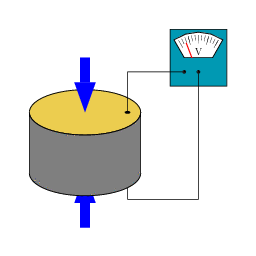
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
, acceleration
Acceleration
In physics, acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with time. In one dimension, acceleration is the rate at which something speeds up or slows down. However, since velocity is a vector, acceleration describes the rate of change of both the magnitude and the direction of velocity. ...
, strain
Strain (materials science)
In continuum mechanics, the infinitesimal strain theory, sometimes called small deformation theory, small displacement theory, or small displacement-gradient theory, deals with infinitesimal deformations of a continuum body...
or force
Force
In physics, a force is any influence that causes an object to undergo a change in speed, a change in direction, or a change in shape. In other words, a force is that which can cause an object with mass to change its velocity , i.e., to accelerate, or which can cause a flexible object to deform...
by converting them to an electrical
Electricity
Electricity is a general term encompassing a variety of phenomena resulting from the presence and flow of electric charge. These include many easily recognizable phenomena, such as lightning, static electricity, and the flow of electrical current in an electrical wire...
charge.
Applications

Quality Assurance
Quality assurance, or QA for short, is the systematic monitoring and evaluation of the various aspects of a project, service or facility to maximize the probability that minimum standards of quality are being attained by the production process...
, process control
Process control
Process control is a statistics and engineering discipline that deals with architectures, mechanisms and algorithms for maintaining the output of a specific process within a desired range...
and for research and development in many different industries. Although the piezoelectric effect was discovered by Pierre Curie
Pierre Curie
Pierre Curie was a French physicist, a pioneer in crystallography, magnetism, piezoelectricity and radioactivity, and Nobel laureate. He was the son of Dr. Eugène Curie and Sophie-Claire Depouilly Curie ...
in 1880, it was only in the 1950s that the piezoelectric effect started to be used for industrial sensing applications. Since then, this measuring principle has been increasingly used and can be regarded as a mature technology
Mature technology
A mature technology is a technology that has been in use for long enough that most of its initial faults and inherent problems have been removed or reduced by further development...
with an outstanding inherent reliability. It has been successfully used in various applications, such as in medical, aerospace
Aerospace
Aerospace comprises the atmosphere of Earth and surrounding space. Typically the term is used to refer to the industry that researches, designs, manufactures, operates, and maintains vehicles moving through air and space...
, nuclear
Nuclear engineering
Nuclear engineering is the branch of engineering concerned with the application of the breakdown as well as the fusion of atomic nuclei and/or the application of other sub-atomic physics, based on the principles of nuclear physics...
instrumentation, and as a pressure sensor in the touch pads of mobile phones. In the automotive industry
Automotive industry
The automotive industry designs, develops, manufactures, markets, and sells motor vehicles, and is one of the world's most important economic sectors by revenue....
, piezoelectric elements are used to monitor combustion when developing internal combustion engines. The sensors are either directly mounted into additional holes into the cylinder head or the spark/glow plug is equipped with a built in miniature piezoelectric sensor.http://www.avl.com/wo/webobsession.servlet.go/encoded/YXBwPWJjbXMmcGFnZT12aWV3JiZub2RlaWQ9NDAwMDU1MjUy.html
The rise of piezoelectric technology is directly related to a set of inherent advantages. The high modulus of elasticity of many piezoelectric materials is comparable to that of many metals and goes up to . Even though piezoelectric sensors are electromechanical systems that react to compression, the sensing elements show almost zero deflection. This is the reason why piezoelectric sensors are so rugged, have an extremely high natural frequency and an excellent linearity over a wide amplitude
Amplitude
Amplitude is the magnitude of change in the oscillating variable with each oscillation within an oscillating system. For example, sound waves in air are oscillations in atmospheric pressure and their amplitudes are proportional to the change in pressure during one oscillation...
range. Additionally, piezoelectric technology is insensitive to electromagnetic field
Electromagnetic field
An electromagnetic field is a physical field produced by moving electrically charged objects. It affects the behavior of charged objects in the vicinity of the field. The electromagnetic field extends indefinitely throughout space and describes the electromagnetic interaction...
s and radiation
Radiation
In physics, radiation is a process in which energetic particles or energetic waves travel through a medium or space. There are two distinct types of radiation; ionizing and non-ionizing...
, enabling measurements under harsh conditions. Some materials used (especially gallium phosphate
Gallium phosphate
Gallium phosphate is a colorless trigonal crystal with a hardness of 5.5 on the Mohs scale. GaPO4 is isotypic with quartz, possessing very similar properties, but the silicon atoms are alternately substituted with gallium and phosphorus, thereby doubling the piezoelectric effect...
http://www.piezocryst.com or tourmaline
Tourmaline
Tourmaline is a crystal boron silicate mineral compounded with elements such as aluminium, iron, magnesium, sodium, lithium, or potassium. Tourmaline is classified as a semi-precious stone and the gem comes in a wide variety of colors...
) have an extreme stability even at high temperature, enabling sensors to have a working range of up to . Tourmaline shows pyroelectricity
Pyroelectricity
Pyroelectricity is the ability of certain materials to generate a temporary voltage when they are heated or cooled. The change in temperature modifies the positions of the atoms slightly within the crystal structure, such that the polarization of the material changes. This polarization change...
in addition to the piezoelectric effect; this is the ability to generate an electrical signal when the temperature of the crystal changes. This effect is also common to piezoceramic materials.
| Principle | Strain Sensitivity [V/µ*] | Threshold [µ*] | Span to threshold ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Piezoelectric | 5.0 | 0.00001 | 100,000,000 |
| Piezoresistive | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 2,500,000 |
| Inductive | 0.001 | 0.0005 | 2,000,000 |
| Capacitive | 0.005 | 0.0001 | 750,000 |
One disadvantage of piezoelectric sensors is that they cannot be used for truly static measurements. A static force will result in a fixed amount of charges on the piezoelectric material. While working with conventional readout electronics, imperfect insulating materials, and reduction in internal sensor resistance
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
will result in a constant loss of electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s, and yield a decreasing signal. Elevated temperatures cause an additional drop in internal resistance
Internal resistance
A practical electrical power source which is a linear electric circuit may, according to Thévenin's theorem, be represented as an ideal voltage source in series with an impedance. This resistance is termed the internal resistance of the source. When the power source delivers current, the measured...
and sensitivity. The main effect on the piezoelectric effect is that with increasing pressure loads and temperature, the sensitivity is reduced due to twin-formation. While quartz
Quartz
Quartz is the second-most-abundant mineral in the Earth's continental crust, after feldspar. It is made up of a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall formula SiO2. There are many different varieties of quartz,...
sensors need to be cooled during measurements at temperatures above , special types of crystals like GaPO4 gallium phosphate
Gallium phosphate
Gallium phosphate is a colorless trigonal crystal with a hardness of 5.5 on the Mohs scale. GaPO4 is isotypic with quartz, possessing very similar properties, but the silicon atoms are alternately substituted with gallium and phosphorus, thereby doubling the piezoelectric effect...
do not show any twin formation up to the melting point of the material itself.
However, it is not true that piezoelectric sensors can only be used for very fast processes or at ambient conditions. In fact, there are numerous applications that show quasi-static measurements, while there are other applications with temperatures higher than .
Piezoelectric sensors are also seen in nature. The collagen in bone
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
is piezoelectric, and is thought by some to act as a biological force sensor.
Principle of operation
Depending on how a piezoelectric material is cut, three main modes of operation can be distinguished: transverse, longitudinal, and shear.Transverse effect:A force is applied along a neutral axis (y) and the charges are generated along the (x) direction, perpendicular to the line of force. The amount of charge depends on the geometrical dimensions of the respective piezoelectric element. When dimensions
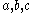 apply,
apply,
-
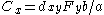 ,
,
- where
 is the dimension in line with the neutral axis,
is the dimension in line with the neutral axis, 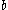 is in line with the charge generating axis and
is in line with the charge generating axis and 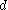 is the corresponding piezoelectric coefficient.http://www.piezo.com/tech1terms.html#d
is the corresponding piezoelectric coefficient.http://www.piezo.com/tech1terms.html#d
Longitudinal effect:The amount of charge produced is strictly proportional to the applied force and is independent of size and shape of the piezoelectric element. Using several elements that are mechanically in series and electrically in parallel
Series and parallel circuits
Components of an electrical circuit or electronic circuit can be connected in many different ways. The two simplest of these are called series and parallel and occur very frequently. Components connected in series are connected along a single path, so the same current flows through all of the...
is the only way to increase the charge output. The resulting charge is
-
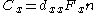 ,
,
- where
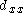 is the piezoelectric coefficient for a charge in x-direction released by forces applied along x-direction (in pC/N).
is the piezoelectric coefficient for a charge in x-direction released by forces applied along x-direction (in pC/N). 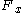 is the applied Force in x-direction [N] and
is the applied Force in x-direction [N] and  corresponds to the number of stacked elements .
corresponds to the number of stacked elements .
force applied and the element dimension.
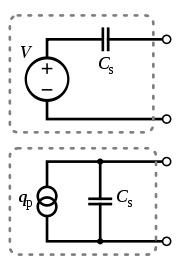
Electrical properties
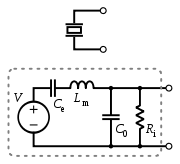
Output impedance
The output impedance, source impedance, or internal impedance of an electronic device is the opposition exhibited by its output terminals to an alternating current of a particular frequency as a result of resistance, inductance and capacitance...
and can be modeled as a proportional voltage source
Voltage source
In electric circuit theory, an ideal voltage source is a circuit element where the voltage across it is independent of the current through it. A voltage source is the dual of a current source. In analysis, a voltage source supplies a constant DC or AC potential between its terminals for any current...
and filter network
Electronic filter
Electronic filters are electronic circuits which perform signal processing functions, specifically to remove unwanted frequency components from the signal, to enhance wanted ones, or both...
. The voltage V at the source is directly proportional to the applied force, pressure, or strain. The output signal is then related to this mechanical force as if it had passed through the equivalent circuit.

Mass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
and inertia
Inertia
Inertia is the resistance of any physical object to a change in its state of motion or rest, or the tendency of an object to resist any change in its motion. It is proportional to an object's mass. The principle of inertia is one of the fundamental principles of classical physics which are used to...
of the sensor itself. Ce is inversely proportional to the mechanical elasticity
Elasticity (physics)
In physics, elasticity is the physical property of a material that returns to its original shape after the stress that made it deform or distort is removed. The relative amount of deformation is called the strain....
of the sensor. C0 represents the static capacitance of the transducer, resulting from an inertial mass of infinite size. Ri is the insulation leakage resistance of the transducer element. If the sensor is connected to a load resistance, this also acts in parallel with the insulation resistance, both increasing the high-pass cutoff frequency.
Sensor design

Artificial membrane
An artificial membrane, or synthetic membrane, is a synthetically created membrane which is usually intended for separation purposes in laboratory or in industry. Synthetic membranes have been successfully used for small and large-scale industrial processes since the middle of twentieth century. A...
and a massive base is used, ensuring that an applied pressure specifically loads the elements in one direction. For accelerometer
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a device that measures proper acceleration, also called the four-acceleration. This is not necessarily the same as the coordinate acceleration , but is rather the type of acceleration associated with the phenomenon of weight experienced by a test mass that resides in the frame...
s, a seismic mass is attached to the crystal elements. When the accelerometer experiences a motion, the invariant seismic mass loads the elements according to Newton’s second law of motion
 .
.The main difference in the working principle between these two cases is the way forces are applied to the sensing elements. In a pressure sensor a thin membrane is used to transfer the force to the elements, while in accelerometers the forces are applied by an attached seismic mass.
Sensors often tend to be sensitive to more than one physical quantity. Pressure sensors show false signal when they are exposed to vibrations. Sophisticated pressure sensors therefore use acceleration compensation elements in addition to the pressure sensing elements. By carefully matching those elements, the acceleration signal (released from the compensation element) is subtracted from the combined signal of pressure and acceleration to derive the true pressure information.
Vibration sensors can also be used to harvest otherwise wasted energy from mechanical vibrations. This is accomplished by using piezoelectric materials to convert mechanical strain into usable electrical energy.
Sensing materials
Two main groups of materials are used for piezoelectric sensors: piezoelectric ceramics and single crystal materials.The ceramic materials (such as PZT ceramic) have a piezoelectric constant / sensitivity that is roughly two orders of magnitude
Order of magnitude
An order of magnitude is the class of scale or magnitude of any amount, where each class contains values of a fixed ratio to the class preceding it. In its most common usage, the amount being scaled is 10 and the scale is the exponent being applied to this amount...
higher than those of the natural single crystal materials and can be produced by inexpensive sintering
Sintering
Sintering is a method used to create objects from powders. It is based on atomic diffusion. Diffusion occurs in any material above absolute zero, but it occurs much faster at higher temperatures. In most sintering processes, the powdered material is held in a mold and then heated to a temperature...
processes. The piezoeffect in piezoceramics is "trained", so unfortunately their high sensitivity degrades over time. The degradation is highly correlated with temperature.
The less sensitive 'natural' single crystal materials (gallium phosphate
Gallium phosphate
Gallium phosphate is a colorless trigonal crystal with a hardness of 5.5 on the Mohs scale. GaPO4 is isotypic with quartz, possessing very similar properties, but the silicon atoms are alternately substituted with gallium and phosphorus, thereby doubling the piezoelectric effect...
, quartz
Quartz
Quartz is the second-most-abundant mineral in the Earth's continental crust, after feldspar. It is made up of a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall formula SiO2. There are many different varieties of quartz,...
, tourmaline
Tourmaline
Tourmaline is a crystal boron silicate mineral compounded with elements such as aluminium, iron, magnesium, sodium, lithium, or potassium. Tourmaline is classified as a semi-precious stone and the gem comes in a wide variety of colors...
) have a much higher – when carefully handled, almost infinite – long term stability. There are also new single crystal materials commercially available such as Lead Magnesium Niobate-Lead Titanate (PMN-PT). These materials offer greatly improved sensitivity (compared with PZT) but suffer from a lower maximum operating temperature and are currently much more expensive to manufacture.
See also
- Charge amplifierCharge amplifierA charge amplifier is a current integrator driven by an electrical source with capacitive nature such as a piezoelectric sensor. Contrary to what its name may suggest, a charge amplifier does not amplify the electric charge present at its input...
- List of sensors
- PiezoelectricityPiezoelectricityPiezoelectricity is the charge which accumulates in certain solid materials in response to applied mechanical stress. The word piezoelectricity means electricity resulting from pressure...
- Piezoresistive effectPiezoresistive effectThe piezoresistive effect describe the changing resistivity of a semiconductor due to applied mechanical stress. The piezoresistive effect differs from the piezoelectric effect...
External links
- Material constants of gallium phosphate
- Langatate - new material for high-temperature piezoelectric sensors
- Spark-Plug with integrated miniaturized piezoelectric pressure sensor http://www.avl.com/wo/webobsession.servlet.go/encoded/YXBwPWJjbXMmcGFnZT12aWV3JiZub2RlaWQ9NDAwMDU1MjUy.html
- Overview of piezoelectric pressure sensors for automotive engine development Usingthe Piezoelectric Effect in Sensors]

