
Pinene
Encyclopedia
Pinene is a bicyclic monoterpene
chemical compound
. There are two structural isomer
s of pinene found in nature: α-pinene
and β-pinene
. As the name suggests, both forms are important constituents of pine
resin
; they are also found in the resins of many other conifers
, as well as in non-coniferous plant
s. Both isomers are used by many insects in their chemical communication system.
, via cyclisation of linaloyl pyrophosphate followed by loss of a proton from the carbocation equivalent.
, along with pinene oxide, verbenol and verbenyl hydroperoxide.
 Pinenes are the primary constituents of turpentine
Pinenes are the primary constituents of turpentine
.
Monoterpene
Monoterpenes are a class of terpenes that consist of two isoprene units and have the molecular formula C10H16. Monoterpenes may be linear or contain rings...
chemical compound
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
. There are two structural isomer
Isomer
In chemistry, isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Isomers do not necessarily share similar properties, unless they also have the same functional groups. There are many different classes of isomers, like stereoisomers, enantiomers, geometrical...
s of pinene found in nature: α-pinene
Alpha-Pinene
α-Pinene is an organic compound of the terpene class, one of two isomers of pinene. It is an alkene and it contains a reactive four-membered ring. It is found in the oils of many species of many coniferous trees, notably the pine. It is also found in the essential oil of rosemary...
and β-pinene
Beta-Pinene
beta-Pinene is a colorless liquid, soluble in alcohol, but not water. It has a woody-green pine-like smell. It occurs naturally in rosemary, parsley, dill, basil, yarrow, and rose. It is also a major constituent of hop aroma and flavor....
. As the name suggests, both forms are important constituents of pine
Pine
Pines are trees in the genus Pinus ,in the family Pinaceae. They make up the monotypic subfamily Pinoideae. There are about 115 species of pine, although different authorities accept between 105 and 125 species.-Etymology:...
resin
Resin
Resin in the most specific use of the term is a hydrocarbon secretion of many plants, particularly coniferous trees. Resins are valued for their chemical properties and associated uses, such as the production of varnishes, adhesives, and food glazing agents; as an important source of raw materials...
; they are also found in the resins of many other conifers
Pinophyta
The conifers, division Pinophyta, also known as division Coniferophyta or Coniferae, are one of 13 or 14 division level taxa within the Kingdom Plantae. Pinophytes are gymnosperms. They are cone-bearing seed plants with vascular tissue; all extant conifers are woody plants, the great majority being...
, as well as in non-coniferous plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
s. Both isomers are used by many insects in their chemical communication system.
Isomers
Skeletal formula The skeletal formula of an organic compound is a shorthand representation of its molecular structure, developed by the organic chemist, Friedrich August Kekulé von Stradonitz. Skeletal formulae are ubiquitous in organic chemistry, because they are relatively quick and simple to draw. Carbon and... |
||||
Ball-and-stick model In chemistry, the ball-and-stick model is a molecular model of a chemical substance which is to display both the three-dimensional position of the atoms and the bonds between them... |
||||
CAS registry number CAS Registry Numbersare unique numerical identifiers assigned by the "Chemical Abstracts Service" toevery chemical described in the... |
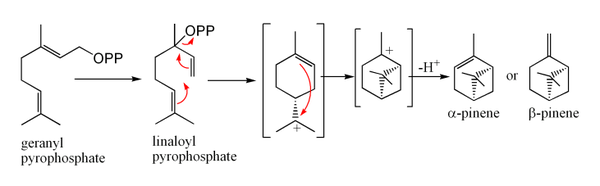
Biosynthesis
α-Pinene and β-pinene are both produced from geranyl pyrophosphateGeranyl pyrophosphate
Geranyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate in the HMG-CoA reductase pathway used by organisms in the biosynthesis of farnesyl pyrophosphate, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate, cholesterol, terpenes and terpenoids....
, via cyclisation of linaloyl pyrophosphate followed by loss of a proton from the carbocation equivalent.

Usage
In chemical industry, selective oxidation of pinene with some catalysts gives many compounds for perfumery, such as artificial odorants. An important oxidation product is verbenoneVerbenone
Verbenone is a natural organic compound classified as a terpene which is found naturally in a variety of plants. The chemical has a pleasant characteristic odor. Besides being a natural constituent of plants, it and its analogs are insect pheromones...
, along with pinene oxide, verbenol and verbenyl hydroperoxide.

Turpentine
Turpentine is a fluid obtained by the distillation of resin obtained from trees, mainly pine trees. It is composed of terpenes, mainly the monoterpenes alpha-pinene and beta-pinene...
.

