
Piping and instrumentation diagram
Encyclopedia
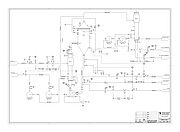
A piping and instrumentation diagram/drawing (P&ID) is a diagram in the process industry which shows the piping of the process flow together with the installed equipment and instrumentation.
 A piping and instrumentation diagram/drawing (P&ID) is defined by the Institute of Instrumentation and Control as follows:
A piping and instrumentation diagram/drawing (P&ID) is defined by the Institute of Instrumentation and Control as follows:
P&IDs play a significant role in the maintenance and modification of the process that it describes. It is critical to demonstrate the physical sequence of equipment and systems, as well as how these systems connect. During the design stage, the diagram also provides the basis for the development of system control schemes, allowing for further safety and operational investigations, such as the hazard and operability study (HAZOP).
For processing facilities, it is a pictorial representation of
For reference designation of any equipment in industrial systems the standard IEC 61346
(Industrial systems, installations and equipment and industrial products — Structuring principles and reference designations) can be applied. For the function Measurement the reference designator B is used, followed by the above listed letter for the measured variable.
For reference designation of any equipment in a power station the KKS Power Plant Classification System can be applied.
Contents and Function

- A diagram which shows the interconnection of process equipment and the instrumentation used to control the process. In the process industry, a standard set of symbols is used to prepare drawings of processes. The instrument symbols used in these drawings are generally based on International Society of Automation (ISA) Standard S5. 1.
- The primary schematic drawing used for laying out a process controlProcess controlProcess control is a statistics and engineering discipline that deals with architectures, mechanisms and algorithms for maintaining the output of a specific process within a desired range...
installation.
P&IDs play a significant role in the maintenance and modification of the process that it describes. It is critical to demonstrate the physical sequence of equipment and systems, as well as how these systems connect. During the design stage, the diagram also provides the basis for the development of system control schemes, allowing for further safety and operational investigations, such as the hazard and operability study (HAZOP).
For processing facilities, it is a pictorial representation of
- Key piping and instrument details
- Control and shutdown schemes
- Safety and regulatory requirementRegulatory requirementRegulatory requirements are part of the process of drug discovery and drug development. Regulatory requirements describe what is necessary for a new drug to be approved for marketing in any particular country. In the US, it is the function of the Food and Drug Administration to establish these...
s - Basic start up and operational information
List of P&ID items
- Instrumentation and designations
- Mechanical equipment with names and numbers
- All valves and their identifications
- Process piping, sizes and identification
- Miscellanea - vents, drains, special fittings, sampling lines, reducers, increasers and swagers
- Permanent start-up and flush lines
- Flow directions
- Interconnections references
- Control inputs and outputs, interlocks
- Interfaces for class changes
- Computer control system input
- Identification of components and subsystems delivered by others
Identification and Reference Designation
The P&ID is used for the identification of measurements within the process. Identification letters for measurements are based on Standard S5. 1 and ISO 14617-6:| First-Letter | Measurement |
| A | Analysis |
| B | Burner, Combustion |
| C | User's Choice (usually Conductivity) |
| D | User's Choice (usually Density) |
| E | Voltage |
| F | Flow |
| G | User's Choice |
| H | Hand |
| I | Current |
| J | Power |
| K | Time, Time Schedule |
| L | Level |
| M | User's Choice |
| N | User's Choice (usually Torque) |
| O | User's Choice |
| P | Pressure |
| Q | Quantity |
| R | Radiation |
| S | Speed, Frequency |
| T | Temperature |
| U | User's Choice (usually Alarm Output) |
| V | Vibration, Mechanical Analysis |
| W | Weight, Force |
| X | User's Choice (usually on-off valve as XV) |
| Y | Event, State, Presence |
| Z | Position, Dimension |
For reference designation of any equipment in industrial systems the standard IEC 61346
IEC 61346
IEC 61346 is an electrotechnical standard entitled "Industrial systems, Installations and Equipment and Industrial Products — Structuring Principles and Reference Designations"...
(Industrial systems, installations and equipment and industrial products — Structuring principles and reference designations) can be applied. For the function Measurement the reference designator B is used, followed by the above listed letter for the measured variable.
For reference designation of any equipment in a power station the KKS Power Plant Classification System can be applied.
Symbols of chemical apparatus and equipments
Below are listed some symbols of chemical apparatus and equipment normally used in a P&ID, according to DIN 30600 and ISO 14617.  |
Pipe Piping Within industry, piping is a system of pipes used to convey fluids from one location to another. The engineering discipline of piping design studies the efficient transport of fluid.... |
 |
Thermally insulated pipe |  |
Jacketed pipe |  |
Cooled or heated pipe |
 |
Jacketed mixing vessel (autoclave) |  |
Half pipe mixing vessel |  |
Pressurized horizontal vessel |  |
Pressurized vertical vessel |
 |
Pump Pump A pump is a device used to move fluids, such as liquids, gases or slurries.A pump displaces a volume by physical or mechanical action. Pumps fall into three major groups: direct lift, displacement, and gravity pumps... |
 |
Vacuum pump Vacuum pump A vacuum pump is a device that removes gas molecules from a sealed volume in order to leave behind a partial vacuum. The first vacuum pump was invented in 1650 by Otto von Guericke.- Types :Pumps can be broadly categorized according to three techniques:... or compressor |
 |
Bag |  |
Gas bottle |
 |
Fan |  |
Axial fan |  |
Radial fan |  |
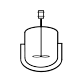
Dryer Dryer A dryer most commonly means:* Hair dryer* Hand dryer* Clothes dryer, also known as a tumble-dryer* Belt dryer* Cereal dryer, for food preservation* Desiccant, a substance that absorbs or adsorbs water... |
 |
Packing column |  |
Tray column |  |
Furnace Furnace A furnace is a device used for heating. The name derives from Latin fornax, oven.In American English and Canadian English, the term furnace on its own is generally used to describe household heating systems based on a central furnace , and sometimes as a synonym for kiln, a device used in the... |
 |
Cooling tower Cooling tower Cooling towers are heat removal devices used to transfer process waste heat to the atmosphere. Cooling towers may either use the evaporation of water to remove process heat and cool the working fluid to near the wet-bulb air temperature or in the case of closed circuit dry cooling towers rely... |
 |
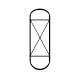
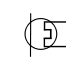
Heat exchanger Heat exchanger A heat exchanger is a piece of equipment built for efficient heat transfer from one medium to another. The media may be separated by a solid wall, so that they never mix, or they may be in direct contact... |
 |
Heat exchanger Heat exchanger A heat exchanger is a piece of equipment built for efficient heat transfer from one medium to another. The media may be separated by a solid wall, so that they never mix, or they may be in direct contact... |
 |
Cooler |  |
Plate & frame heat exchanger Plate heat exchanger A plate heat exchanger is a type of heat exchanger that uses metal plates to transfer heat between two fluids. This has a major advantage over a conventional heat exchanger in that the fluids are exposed to a much larger surface area because the fluids spread out over the plates. This facilitates... |
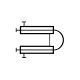 |
Double pipe heat exchanger |  |
Fixed straight tubes heat exchanger Shell and tube heat exchanger A shell and tube heat exchanger is a class of heat exchanger designs. It is the most common type of heat exchanger in oil refineries and other large chemical processes, and is suited for higher-pressure applications. As its name implies, this type of heat exchanger consists of a shell with a... |
 |
U shaped tubes heat exchanger |  |
Spiral heat exchanger |
 |
Covered gas vent | 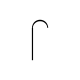 |
Curved gas vent |  |
(Air) filter Filter (chemistry) In chemistry and common usage, a filter is a device that is designed to physically block certain objects or substances while letting others through. Filters are often used to remove solid substances suspended in fluids, for example to remove air pollution, to make water drinkable, and to prepare... |
 |
Funnel |
 |
Steam trap Steam trap A steam trap is a device used to discharge condensate and non condensable gases with a negligible consumption or loss of live steam.Most steam traps are nothing more than automatic valves. They open, close or modulate automatically... |
 |
Viewing glass |  |
Pressure reducing valve |  |
Flexible pipe |
 |
Valve Valve A valve is a device that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically pipe fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category... |
 |
Control valve |  |
Manual valve |  |
Back draft damper |
 |
Needle valve Needle valve A needle valve is a type of valve having a small port and a threaded, needle-shaped plunger. It allows precise regulation of flow, although it is generally only capable of relatively low flow rates.- Construction and operation :... |
 |
Butterfly valve Butterfly valve A butterfly valve is a valve which can be used for isolating or regulating flow. The closing mechanism takes the form of a disk. Operation is similar to that of a ball valve, which allows for quick shut off. Butterfly valves are generally favored because they are lower in cost to other valve... |
 |
Diaphragm valve Diaphragm valve Diaphragm valves consists of a valve body with two or more ports, a diaphragm, and a "saddle" or seat upon which the diaphragm closes the valve. The valve is constructed from either plastic or steel.... |
 |
Ball valve Ball valve A ball valve is a valve with a spherical disc, the part of the valve which controls the flow through it. The sphere has a hole, or port, through the middle so that when the port is in line with both ends of the valve, flow will occur. When the valve is closed, the hole is perpendicular to the ends... |
See also
- Commons:Category:Chemical engineering symbols - A list of P&ID symbols in SVG format
- Process flow diagramProcess Flow diagramA process flow diagram is a diagram commonly used in engineering to indicate the general flow of plant processes and equipment.The PFD displays the relationship between major equipment of a plant facility and does not show minor details such as piping details and designations...

