
Placentophagy
Encyclopedia
Placentophagy is the act of mammals eating
the placenta
of their young after childbirth.
The placenta contains high levels of prostaglandin
which stimulates involution
(an inward curvature or penetration, or, a shrinking or return to a former size) of the uterus, in effect cleaning the uterus
out. The placenta also contains small amounts of oxytocin
which eases birth stress and causes the smooth muscles around the mammary cells to contract and eject milk.
There is also a school of thought that holds that placentophagy naturally occurred to hide any trace of childbirth from predators in the wild, though the fact that amniotic fluid
is not similarly ingested by the mother seems to discredit this theory. Most placental mammals participate in placentophagy, including, surprisingly, herbivorous ones. Pinnipedia and Cetacea
are exceptions to mammalian placentophagy, as is the camel
. Placentophagy has been observed in Insectivora
, Rodent
ia, Chiroptera, Lagomorpha
, Carnivora
, Perissodactyla, Artiodactyla (with the camel as a noted exception), and Primates. Marsupials, which are an order of metatherian (pouched) mammals, resorb rather than deliver the placenta, and therefore cannot engage in placentophagia; they do, however, vigorously lick birth fluids as they are excreted.
According to preliminary research performed several decades ago, ingestion of placenta can enhance opioid-mediated analgesia in pregnant rats, but only under very specific conditions. Rats only experienced increased analgesia if they received footshock or morphine and only responded if they ingested a small amounts of placenta. Ingesting large amounts of placenta did not significantly affect pain sensation. There have been no scientific studies which show that placentophagy enhances analgesia in humans.
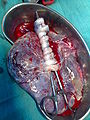 Although the placenta is revered in many cultures, very few customarily eat the placenta after the newborn's birth. Those who advocate placentophagy in humans believe that eating the placenta prevents postpartum depression
Although the placenta is revered in many cultures, very few customarily eat the placenta after the newborn's birth. Those who advocate placentophagy in humans believe that eating the placenta prevents postpartum depression
and other pregnancy complications. Obstetrician and spokesperson for the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists
Maggie Blott disputes the post-natal depression theory, stating there is no medical reason to eat the placenta; "Animals eat their placenta to get nutrition - but when people are already well-nourished, there is no benefit, there is no reason to do it."
Human placenta has also been an ingredient in some traditional Chinese medicine
s, including using dried human placenta, known as "Ziheche" , to treat wasting diseases, infertility, impotence and other conditions.
Eating
Eating is the ingestion of food to provide for all organisms their nutritional needs, particularly for energy and growth. Animals and other heterotrophs must eat in order to survive: carnivores eat other animals, herbivores eat plants, omnivores consume a mixture of both plant and animal matter,...
the placenta
Placenta
The placenta is an organ that connects the developing fetus to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake, waste elimination, and gas exchange via the mother's blood supply. "True" placentas are a defining characteristic of eutherian or "placental" mammals, but are also found in some snakes and...
of their young after childbirth.
The placenta contains high levels of prostaglandin
Prostaglandin
A prostaglandin is any member of a group of lipid compounds that are derived enzymatically from fatty acids and have important functions in the animal body. Every prostaglandin contains 20 carbon atoms, including a 5-carbon ring....
which stimulates involution
Involution (medicine)
-Thymus:The thymus continues to grow between birth and puberty and then begins to atrophy, a process directed by the high levels of circulating sex hormones. Proportional to thymic size, thymic activity is most active before puberty. Upon atrophy, the size and activity are dramatically reduced,...
(an inward curvature or penetration, or, a shrinking or return to a former size) of the uterus, in effect cleaning the uterus
Uterus
The uterus or womb is a major female hormone-responsive reproductive sex organ of most mammals including humans. One end, the cervix, opens into the vagina, while the other is connected to one or both fallopian tubes, depending on the species...
out. The placenta also contains small amounts of oxytocin
Oxytocin
Oxytocin is a mammalian hormone that acts primarily as a neuromodulator in the brain.Oxytocin is best known for its roles in sexual reproduction, in particular during and after childbirth...
which eases birth stress and causes the smooth muscles around the mammary cells to contract and eject milk.
There is also a school of thought that holds that placentophagy naturally occurred to hide any trace of childbirth from predators in the wild, though the fact that amniotic fluid
Amniotic fluid
Amniotic fluid or liquor amnii is the nourishing and protecting liquid contained by the amniotic sac of a pregnant woman.- Development of amniotic fluid :...
is not similarly ingested by the mother seems to discredit this theory. Most placental mammals participate in placentophagy, including, surprisingly, herbivorous ones. Pinnipedia and Cetacea
Cetacea
The order Cetacea includes the marine mammals commonly known as whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Cetus is Latin and is used in biological names to mean "whale"; its original meaning, "large sea animal", was more general. It comes from Ancient Greek , meaning "whale" or "any huge fish or sea...
are exceptions to mammalian placentophagy, as is the camel
Camel
A camel is an even-toed ungulate within the genus Camelus, bearing distinctive fatty deposits known as humps on its back. There are two species of camels: the dromedary or Arabian camel has a single hump, and the bactrian has two humps. Dromedaries are native to the dry desert areas of West Asia,...
. Placentophagy has been observed in Insectivora
Insectivora
The order Insectivora is a now-abandoned biological grouping within the class of mammals...
, Rodent
Rodent
Rodentia is an order of mammals also known as rodents, characterised by two continuously growing incisors in the upper and lower jaws which must be kept short by gnawing....
ia, Chiroptera, Lagomorpha
Lagomorpha
The lagomorphs are the members of the taxonomic order Lagomorpha, of which there are two living families, the Leporidae , and the Ochotonidae...
, Carnivora
Carnivora
The diverse order Carnivora |Latin]] carō "flesh", + vorāre "to devour") includes over 260 species of placental mammals. Its members are formally referred to as carnivorans, while the word "carnivore" can refer to any meat-eating animal...
, Perissodactyla, Artiodactyla (with the camel as a noted exception), and Primates. Marsupials, which are an order of metatherian (pouched) mammals, resorb rather than deliver the placenta, and therefore cannot engage in placentophagia; they do, however, vigorously lick birth fluids as they are excreted.
According to preliminary research performed several decades ago, ingestion of placenta can enhance opioid-mediated analgesia in pregnant rats, but only under very specific conditions. Rats only experienced increased analgesia if they received footshock or morphine and only responded if they ingested a small amounts of placenta. Ingesting large amounts of placenta did not significantly affect pain sensation. There have been no scientific studies which show that placentophagy enhances analgesia in humans.
Human placentophagy

Postpartum depression
Postpartum depression , also called postnatal depression, is a form of clinical depression which can affect women, and less frequently men, typically after childbirth. Studies report prevalence rates among women from 5% to 25%, but methodological differences among the studies make the actual...
and other pregnancy complications. Obstetrician and spokesperson for the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists
Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists
The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists is a professional association based in the UK. Its members, including people with and without medical degrees, work in the field of obstetrics and gynaecology, that is, pregnancy, childbirth, and female sexual and reproductive health...
Maggie Blott disputes the post-natal depression theory, stating there is no medical reason to eat the placenta; "Animals eat their placenta to get nutrition - but when people are already well-nourished, there is no benefit, there is no reason to do it."
Human placenta has also been an ingredient in some traditional Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese Medicine refers to a broad range of medicine practices sharing common theoretical concepts which have been developed in China and are based on a tradition of more than 2,000 years, including various forms of herbal medicine, acupuncture, massage , exercise , and dietary therapy...
s, including using dried human placenta, known as "Ziheche" , to treat wasting diseases, infertility, impotence and other conditions.

