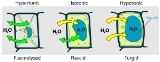
Plasmolysis
Overview
Osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, aiming to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides...
. The reverse process, cytolysis
Cytolysis
Cytolysis, or osmotic lysis, occurs when a cell bursts due to an osmotic imbalance that has caused excess water to move into the cell. It occurs in a hypotonic environment, where water diffuses into the cell and causes its volume to increase. If the volume of water exceeds the cell membrane's...
, can occur if the cell is in a hypotonic solution resulting in a higher external osmotic pressure
Osmotic pressure
Osmotic pressure is the pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of water across a semipermeable membrane....
and a net flow of water into the cell. Through observation of plasmolysis and deplasmolysis it is possible to determine the tonicity
Tonicity
Tonicity is a measure of the osmotic pressure gradient of two solutions separated by a semipermeable membrane. It is commonly used when describing the response of cells immersed in an external solution...
of the cell's environment as well as the rate solute molecules cross the cellular membrane.
A plant cell in zoe hypotonic solution will absorb water by endosmosis, so that the increased volume of water in the cell will increase pressure, making the protoplasm
Protoplasm
Protoplasm is the living contents of a cell that is surrounded by a plasma membrane. It is a general term of the Cytoplasm . Protoplasm is composed of a mixture of small molecules such as ions, amino acids, monosaccharides and water, and macromolecules such as nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and...
push against the cell wall, a condition known as turgor.

